Abstract
Objective
To assess the effects of epidermal growth factor (EGF)–coated titanium (Ti) discs on the adhesion and metabolism of keratinocytes and gingival fibroblasts exposed to nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates.
Materials and methods
Keratinocytes and fibroblasts were seeded (1 × 105 cells/disc) on Ti discs coated with EGF (100 nM). After 24 h, cells were exposed or not to sodium alendronate (SA) or zoledronic acid (ZA) at different concentrations (0 = control, 0.5, 1, or 5 μM) for 48 h. Cell adhesion to the substrates was evaluated by fluorescence microscopy. Cell viability (alamarBlue, n = 6) and synthesis of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), and keratinocytes growth factor (KGF) (ELISA, n = 6) were assessed. Data were statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey tests (α = 0.05).
Results
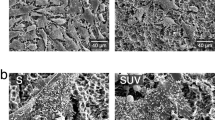
Higher cell adhesion rate was observed when keratinocytes and fibroblasts were seeded onto EGF-coated discs in comparison to uncoated discs. ZA treatment hindered the adhesion of both cell lines on the Ti discs as well as reduced the viability and synthesis of VEGF, KGF and MMP-2 by cells (p < 0.05). SA treatment did not affect cell viability, but interfered negatively on the adhesion and synthesis of EGF and KGF by the cells (p < 0.05). EGF-coated surface increased cell viability and synthesis of growth factors as well as downregulated the synthesis of MMP-2 in comparison to control (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
EGF applied on Ti surface improves the biological responses of oral mucosa cells exposed to SA and ZA.
Clinical relevance
EGF-coating on titanium may be a suitable strategy to improve oral mucosa cellular events related to biological sealing, especially for patients under bisphosphonate therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russell RG (2011) Bisphosphonates: the first 40 years. Bone 49:2–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2011.04.022
Basso FG, Pansani TN, Cardoso LM, Hebling J, Real RPV, de Souza Costa CA (2020) Influence of bisphosphonates on the behavior of osteoblasts seeded onto titanium discs. Braz Dent J 31:304–309. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-6440202003128
Basso FG, Pansani TN, de Oliveira CF, Turrioni AP, Soares DG, Hebling J, Costa CA (2013) Cytotoxic effects of zoledronic acid on human epithelial cells and gingival fibroblasts. Braz Dent J 24:551–558. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-6440201302229
Marx RE (2003) Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: a growing epidemic. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:1115–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0278-2391(03)00720-1
Khan AA, Morrison A, Hanley DA, Felsenberg D, McCauley LK, O’Ryan F, Reid IR, Ruggiero SL, Taguchi A, Tetradis S, Watts NB, Brandi ML, Peters E, Guise T, Eastell R, Cheung AM, Morin SN, Masri B, Cooper C, Morgan SL, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Langdahl BL, Al Dabagh R, Davison KS, Kendler DL, Sándor GK, Josse RG, Bhandari M, El Rabbany M, Pierroz DD, Sulimani R, Saunders DP, Brown JP, Compston J (2015) Diagnosis and management of osteonecrosis of the jaw: a systematic review and international consensus. International Task Force on Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. J Bone Miner Res 30(1):3–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2405
Fliefel R, Tröltzsch M, Kühnisch J, Ehrenfeld M, Otto S (2015) Treatment strategies and outcomes of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ) with characterization of patients: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44(5):568–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2015.01.026
Reid IR, Bolland MJ, Grey AB (2007) Is bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw caused by soft tissue toxicity? Bone 41(3):318–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2007.04.196
Allen MR, Burr DB (2009) The pathogenesis of bisphosphonate-related osteonecroses of the jaw: so many hypotheses, so few data. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2009.01.007
Bedogni A, Bettini G, Totola A, Saia G, Nocini PF (2010) Oral bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw after implant surgery: a case report and literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1662–1666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2010.02.037
Basso FG, Pansani TN, Soares DG, Cardoso LM, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA (2018) Influence of bisphosphonates on the adherence and metabolism of epithelial cells and gingival fibroblasts to titanium surfaces. Clin Oral Investig 22:893–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2167-2
Basso FG, Pansani TN, Cardoso LM, Citta M, Soares DG, Scheffel DS, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA (2017) Epithelial cell-enhanced metabolism by low-level laser therapy and epidermal growth factor. Lasers Med Sci 33:445–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-017-2176-z
Atsuta I, Ayukawa Y, Kondo R, Oshiro W, Matsuura Y, Furuhashi A, Tsukiyama Y, Koyano K (2016) Soft tissue sealing around dental implants based on histological interpretation. J Prosthodont Res 60:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpor.2015.07.001
Blázquez-Hinarejos M, Ayuso-Montero R, Jané-Salas E, López-López J (2017) Influence of surface modified dental implant abutments on connective tissue attachment: a systematic review. Arch Oral Biol 80:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.04.020
Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O, Golinko MS, Brem H, Tomic-Canic M (2008) Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen 16:585–601. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2008.00410.x
Carreira A, Lojudice F, Halcsik E, Navarro R, Sogayar M, Granjeiro J (2014) Bone morphogenetic proteins facts, challenges, and future perspectives. J Dent Res 93:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034513518561
Carpenter G, Cohen S (1990) Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 265:7709–7712
Pansani TN, Basso FG, Turrioni AP, Soares DG, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA (2017) Effects of low-level laser therapy and epidermal growth factor on the activities of gingival fibroblasts obtained from young or elderly individuals. Lasers Med Sci 32:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-2081-x
Park JH, Olivares-Navarrete R, Baier RE, Meyer AE, Tannenbaum R, Boyan BD, Schwartz Z (2012) Effect of cleaning and sterilization on titanium implant surface properties and cellular response. Acta Biomater 8:1966–1975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2011.11.026
Pansani TN, Basso FG, Souza IDR, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA (2019) Characterization of titanium surface coated with epidermal growth factor and its effect on human gingival fibroblasts. Arch Oral Biol 102:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.03.025
Touyz LZG, Afrashtehfar KI (2017) Implications of bisphosphonate calcium ion depletion interfering with desmosome epithelial seal in osseointegrated implants and pressure ulcers. Med Hypotheses 107:22–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2017.07.013
Lotz EM, Lohmann CH, Boyan BD, Schwartz Z (2020) Bisphosphonates inhibit surface-mediated osteogenesis. J Biomed Mater Res A 108:1774–1786. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36944
Walter C, Al-Nawas B, Wolff T, Schiegnitz E, Grötz KA (2016) Dental implants in patients treated with antiresorptive medication - a systematic literature review. Int J Implant Dent 2:9–23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-016-0041-7
Hasmim M, Bieler G, Rüegg C (2007) Zoledronate inhibits endothelial cell adhesion, migration and survival through the suppression of multiple, prenylation-dependent signaling pathways. J Thromb Haemost 5:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.02259.x
Rogers MJ (2003) New insights into the molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Curr Pharm Des 9:2643–2658. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612033453640
Gosain A, DiPietro LA (2004) Aging and wound healing. World J Surg 28:321–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-003-7397-6
Fournier P, Boissier S, Filleur S, Guglielmi J, Cabon F, Colombel M, Clézardin P (2002) Bisphosphonates inhibit angiogenesis in vitro and testosterone-stimulated vascular regrowth in the ventral prostate in castrated rats. Cancer Res 62:6538–6544
Ferretti G, Fabi A, Carlini P, Papaldo P, Fei PC, Di Cosimo S, Salesi N, Giannarelli D, Alimonti A, Di Cocco B, D’Agosto G, Bordignon V, Trento E, Cognetti F (2005) Zoledronic-acid-induced circulating level modifications of angiogenic factors, metalloproteinases and proinflammatory cytokines in metastatic breast cancer patients. Oncology 69:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1159/000087286
Stresing V, Fournier PG, Bellahcène A, Benzaïd I, Mönkkönen H, Colombel M, Ebetino FH, Castronovo V, Clézardin P (2011) Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates can inhibit angiogenesis in vivo without the involvement of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase. Bone 48:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2010.09.035
Birkedal-Hansen H (1993) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in human periodontal diseases. J Periodontol 64:474–484. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.1993.64.5s.474
Birkedal-Hansen H, Moore WG, Bodden MK, Windsor LJ, Birkedal-Hansen B, DeCarlo A, Engler JA (1993) Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 4:197–250. https://doi.org/10.1177/10454411930040020401
Teronen O, Heikkila P, Konttinen YT, Laitinen M, Salo T, Hanemaaijer R, Teronen A, Maisi P, Sorsa T (1999) MMP inhibition and downregulation by bisphosphonates. Ann N Y Acad Sci 878:453–465. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07702.x
Boissier S, Ferreras M, Peyruchaud O, Magnetto S, Ebetino FH, Colombel M, Delmas P, Delaisse JM, Clezardin P (2000) Bisphosphonates inhibit breast and prostate carcinoma cell invasion, an early event in the formation of bone metastases. Cancer Res 60:2949–2954
Lee PP, Hwang JJ, Mead L, Ip MM (2001) Functional role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in mammary epithelial cell development. J Cell Physiol 188:75–88. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.1090
Lee PP, Hwang JJ, Murphy G, Ip MM (2000) Functional significance of MMP-9 in tumor necrosis factor induced proliferation and branching morphogenesis of mammary epithelial cells. Endocrinology 141:3764–3773. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.141.10.7697
Finch PW, Rubin JS, Miki T, Ron D, Aaronson SA (1989) Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth. Science 245(4919):752–755. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2475908
Finch PW, Rubin JS (2004) Keratinocyte growth factor/fibroblast growth factor 7, a homeostatic factor with therapeutic potential for epithelial protection and repair. Adv Cancer Res 9:69–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-230X(04)91003-2
Kerpedjieva SS, Kim DS, Barbeau DJ, Tamama K (2012) EGFR ligands drive multipotential stromal cells to produce multiple growth factors and cytokines via early growth response-1. Stem Cells Dev 21(13):2541–2551. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2011.0711
Oda K, Matsuaka U, Finahashi A, Kitano H (2005) A comprehensive pathway map of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Mol Syst Biol 1:2005.0010. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb4100014
Dhillon S, Lyseng-Williamson KA (2008) Zoledronic acid: a review of its use in the management of bone metastases of malignancy. Drugs 68:507–534. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200868040-00010
Acknowledgements
The authors received financial support from the São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP (grants no. 2015/19364-8/2018/11211-6) and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development - CNPq (grant no. 442637/2014-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was performed in accordance with the local Ethics Committee (CAAE: 55629215.7.0000.5416).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pansani, T.N., Cardoso, L.M., Augusto, L.A. et al. Effects of EGF-coated titanium surfaces on adhesion and metabolism of bisphosphonate-treated human keratinocytes and gingival fibroblasts. Clin Oral Invest 25, 5775–5784 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-03880-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-03880-1