Abstract
Objective
To compare the clinical, radiographic, and histological healing patterns between the immediate and delayed applications of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) in damaged extraction sockets in dogs.
Materials and methods
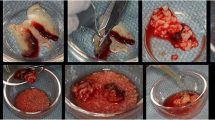
The distal roots of the fourth premolars of the mandible were extracted bilaterally in five beagle dogs, and buccal bone defects (4 mm wide and 9 mm high) were surgically created. Collagenated biphasic calcium phosphate (CBCP) soaked for 10 min in 100 μL of BMP-2 solution was applied immediately to the defect site in the control group. In the test group, the BMP-2 solution of same dose was injected into the grafted site 2 weeks after grafting with a saline-soaked CBCP. The dogs were sacrificed 2 weeks later. Clinical, histological, and radiographic analyses were followed.
Results
Swelling and inflammatory reactions were predominantly observed in the control group at 2 weeks. The area of new bone formation was significantly larger in the control group compared with the test group (10.8 ± 7.0 mm2 [mean ± SD] and 6.3 ± 3.1 mm2, respectively; p = 0.043). No significant difference was found in ridge width at 2 mm, 4 mm and 6 mm below the lingual bone crest between the control (2.6 ± 1.0 mm, 3.2 ± 0.9 mm and 4.5 ± 0.5 mm, respectively) and test group (3.3 ± 1.0 mm, 3.7 ± 1.3 mm and 4.2 ± 1.0 mm; all p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Delayed application of BMP-2 2 weeks after surgery did not show any advantage over immediate application of BMP-2 in terms of new bone formation.
Clinical relevance
This study suggests that it might be better to apply BMP-2 immediately in alveolar ridge preservation, instead of delayed application, in order to enhance new bone formation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo MG, Sukekava F, Wennstrom JL, Lindhe J (2005) Ridge alterations following implant placement in fresh extraction sockets: an experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol 32:645–652
Cardaropoli G, Araujo M, Lindhe J (2003) Dynamics of bone tissue formation in tooth extraction sites. An experimental study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol 30:809–818
Araujo MG, Liljenberg B, Lindhe J (2010) Dynamics of Bio-Oss Collagen incorporation in fresh extraction wounds: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 21:55–64
Avila-Ortiz G, Elangovan S, Kramer KW, Blanchette D, Dawson DV (2014) Effect of alveolar ridge preservation after tooth extraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent Res 93:950–958
Barone A, Ricci M, Tonelli P, Santini S, Covani U (2013) Tissue changes of extraction sockets in humans: a comparison of spontaneous healing vs. ridge preservation with secondary soft tissue healing. Clin Oral Implants Res 24:1231–1237
Vittorini Orgeas G, Clementini M, De Risi V, de Sanctis M (2013) Surgical techniques for alveolar socket preservation: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 28:1049–1061
MacBeth N, Trullenque-Eriksson A, Donos N, Mardas N (2017) Hard and soft tissue changes following alveolar ridge preservation: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 28:982–1004
Araujo MG, Lindhe J (2009) Ridge preservation with the use of Bio-Oss collagen: a 6-month study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 20:433–440
Carmagnola D, Adriaens P, Berglundh T (2003) Healing of human extraction sockets filled with Bio-Oss. Clin Oral Implants Res 14:137–143
Hong JY, Lee JS, Pang EK, Jung UW, Choi SH, Kim CK (2014) Impact of different synthetic bone fillers on healing of extraction sockets: an experimental study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res 25:e30–e37
Choi Y, Yun JH, Kim CS, Choi SH, Chai JK, Jung UW (2012) Sinus augmentation using absorbable collagen sponge loaded with Escherichia coli-expressed recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 in a standardized rabbit sinus model: a radiographic and histologic analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 23:682–689
Jung RE, Weber FE, Thoma DS, Ehrbar M, Cochran DL, Hammerle CH (2008) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 enhances bone formation when delivered by a synthetic matrix containing hydroxyapatite/tricalciumphosphate. Clin Oral Implants Res 19:188–195
Yon J, Lee JS, Lim HC, Kim MS, Hong JY, Choi SH, Jung UW (2015) Pre-clinical evaluation of the osteogenic potential of bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded onto a particulate porcine bone biomaterial. J Clin Periodontol 42:81–88
Lee JS, Jung JS, Im GI, Kim BS, Cho KS, Kim CS (2015) Ridge regeneration of damaged extraction sockets using rhBMP-2: an experimental study in canine. J Clin Periodontol 42:678–687
Schwarz F, Rothamel D, Herten M, Ferrari D, Sager M, Becker J (2008) Lateral ridge augmentation using particulated or block bone substitutes biocoated with rhGDF-5 and rhBMP-2: an immunohistochemical study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res 19:642–652
Jung UW, Lee IK, Park JY, Thoma DS, Hammerle CH, Jung RE (2015) The efficacy of BMP-2 preloaded on bone substitute or hydrogel for bone regeneration at peri-implant defects in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res 26:1456–1465
James AW, LaChaud G, Shen J, Asatrian G, Nguyen V, Zhang X, Ting K, Soo C (2016) A review of the clinical side effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 22:284–297
Kim JS, Cha JK, Cho AR, Kim MS, Lee JS, Hong JY, Choi SH, Jung UW (2015) Acceleration of bone regeneration by BMP-2-loaded collagenated biphasic calcium phosphate in rabbit sinus. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 17:1103–1113
Lee JS, Choe SH, Cha JK, Seo GY, Kim CS (2018) Radiographic and histologic observations of sequential healing processes following ridge augmentation after tooth extraction in buccal-bone-deficient extraction sockets in beagle dogs. J Clin Periodontol 45:1388–1397
Lee KB, Taghavi CE, Song KJ, Sintuu C, Yoo JH, Keorochana G, Tzeng ST, Fei Z, Liao JC, Wang JC (2011) Inflammatory characteristics of rhBMP-2 in vitro and in an in vivo rodent model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36:E149–E154
Wong DA, Kumar A, Jatana S, Ghiselli G, Wong K (2008) Neurologic impairment from ectopic bone in the lumbar canal: a potential complication of off-label PLIF/TLIF use of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2). Spine J 8:1011–1018
Tazaki J, Murata M, Akazawa T, Yamamoto M, Ito K, Arisue M, Shibata T, Tabata Y (2009) BMP-2 release and dose-response studies in hydroxyapatite and beta-tricalcium phosphate. Biomed Mater Eng 19:141–146
Cha JK, Lee JS, Kim MS, Choi SH, Cho KS, Jung UW (2014) Sinus augmentation using BMP-2 in a bovine hydroxyapatite/collagen carrier in dogs. J Clin Periodontol 41:86–93
Terbish M, Yoo SH, Kim HJ, Yu HS, Hwang CJ, Baik HS, Cha JY (2015) Accelerated bone formation in distracted alveolar bone after injection of recombinant human bone morphogenetic Protein-2. J Periodontol 86:1078–1086
Arau’jo MG, Lindhe J (2005) Dimensional ridge alterations following tooth extraction. An experimental study in the dog. J Periodontol 32:212–218
Funding
The work was suuported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning) (No. NRF-2017R1A2B2002537).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Jae-Kook Cha and Ui-Won Jung
Formal analysis: Myong Ji Kim and Kyeong-Won Paeng
Investigation: Myong Ji Kim, Young Woo Song and Jae-Kook Cha
Methodology: Daniel S. Thoma and Ronald E. Jung
Project administration: Jae-Kook Cha and Ui-Won Jung
Writing—original draft: Ui-Won Jung, Daniel S. Thoma and Ronald E. Jung
Writing—review and editing: Myong Ji Kim and Jae-Kook Cha
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed under the approval of the Animal Care and Use Committee, Yonsei Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea (Permission no. 2013-0317-3).
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.J., Cha, JK., Paeng, KW. et al. Immediate versus delayed application of bone morphogenetic protein-2 solution in damaged extraction sockets: a preclinical in vivo investigation. Clin Oral Invest 25, 275–282 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-020-03362-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-020-03362-w