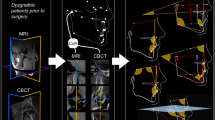
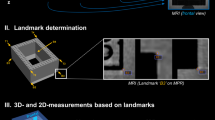
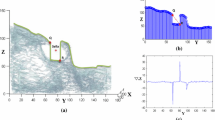
Abstract
Objective
3D cephalometric analysis performed on cone-beam or multi-slice computed tomography (CBCT, MSCT) has superior diagnostic value compared to 2D cephalometry based on radiographs. However, this comes at the expense of increased radiation risks for the predominantly young patients. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has the potential to overcome this diagnostic dilemma but has not been established for 3D cephalometry so far. Since landmark reliability forms the basis for 3D cephalometry, we evaluated the in vivo reliability of established 3D landmarks using MRI.
Materials and methods
Sixteen orthodontic patients underwent MRI at 3 Tesla using a 0.5 mm 3D sequence. On each MRI scan, 44 cephalometric landmarks were determined. Image analysis was performed twice by two independent observers. Intra- and inter-rater agreement was assessed by mean measurement errors and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs). Measurement errors were calculated as Euclidean distances and distances for x-, y-, and z-coordinates.
Results
Overall, MRI-based 3D cephalometric landmarks revealed a high reliability comparable to prior in vivo studies using CBCT/MSCT. Intra- and inter-rater ICCs were consistently higher than 0.9. Intra-rater comparisons showed mean measurement differences (ranges) of 0.87 mm (0.41–1.63) for rater I and 0.94 mm (0.49–1.28) for rater II. Average inter-rater difference was 1.10 mm (0.52–2.29). Distinct differences in reliability between the various landmarks were observed, corresponding well with the landmarks’ specific shapes.
Conclusions
The present study demonstrates that MRI enables reliable determination of 3D cephalometric landmarks in vivo.
Clinical relevance
This study emphasizes the potential of MRI to perform treatment planning and monitoring in orthodontics as well as oral and maxillofacial surgery without radiation exposure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumrind S, Frantz RC (1971) The reliability of head film measurements. 1. Landmark identification. Am J Orthod 60(2):111–127
Baumrind S, Frantz RC (1971) The reliability of head film measurements. 2. Conventional angular and linear measures. Am J Orthod 60(5):505–517
Moyers RE, Bookstein FL (1979) The inappropriateness of conventional cephalometrics. Am J Orthod 75(6):599–617
Ahlqvist J, Eliasson S, Welander U (1986) The effect of projection errors on cephalometric length measurements. Eur J Orthod 8(3):141–148
Park SH, Yu HS, Kim KD, Lee KJ, Baik HS (2006) A proposal for a new analysis of craniofacial morphology by 3-dimensional computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 129(5):600 e623–600 e634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2005.11.032
Stratemann SA, Huang JC, Maki K, Miller AJ, Hatcher DC (2008) Comparison of cone beam computed tomography imaging with physical measures. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 37(2):80–93. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr/31349994
Periago DR, Scarfe WC, Moshiri M, Scheetz JP, Silveira AM, Farman AG (2008) Linear accuracy and reliability of cone beam CT derived 3-dimensional images constructed using an orthodontic volumetric rendering program. Angle Orthod 78(3):387–395. https://doi.org/10.2319/122106-52.1
Hassan B, van der Stelt P, Sanderink G (2009) Accuracy of three-dimensional measurements obtained from cone beam computed tomography surface-rendered images for cephalometric analysis: influence of patient scanning position. Eur J Orthod 31(2):129–134. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjn088
Olmez H, Gorgulu S, Akin E, Bengi AO, Tekdemir I, Ors F (2011) Measurement accuracy of a computer-assisted three-dimensional analysis and a conventional two-dimensional method. Angle Orthod 81(3):375–382. https://doi.org/10.2319/070810-387.1
Gribel BF, Gribel MN, Frazao DC, McNamara JA Jr, Manzi FR (2011) Accuracy and reliability of craniometric measurements on lateral cephalometry and 3D measurements on CBCT scans. Angle Orthod 81(1):26–35. https://doi.org/10.2319/032210-166.1
Gribel BF, Gribel MN, Manzi FR, Brooks SL, McNamara JA Jr (2011) From 2D to 3D: an algorithm to derive normal values for 3-dimensional computerized assessment. Angle Orthod 81(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.2319/032910-173.1
Damstra J, Fourie Z, De Wit M, Ren Y (2012) A three-dimensional comparison of a morphometric and conventional cephalometric midsagittal planes for craniofacial asymmetry. Clin Oral Investig 16(1):285–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-011-0512-4
Shin SM, Kim YM, Kim NR, Choi YS, Park SB, Kim YI (2016) Statistical shape analysis-based determination of optimal midsagittal reference plane for evaluation of facial asymmetry. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 150(2):252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.01.017
Pauwels R, Beinsberger J, Collaert B, Theodorakou C, Rogers J, Walker A, Cockmartin L, Bosmans H, Jacobs R, Bogaerts R, Horner K, Consortium SP (2012) Effective dose range for dental cone beam computed tomography scanners. Eur J Radiol 81(2):267–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2010.11.028
Pauwels R, Cockmartin L, Ivanauskaité D, Urbonienė A, Gavala S, Donta C, Tsiklakis K, Jacobs R, Bosmans H, Bogaerts R, Horner K, Consortium S (2014) Estimating cancer risk from dental cone-beam CT exposures based on skin dosimetry. Phys Med Biol 59(14):3877–3891. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/59/14/3877
American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology (2013) Clinical recommendations regarding use of cone beam computed tomography in orthodontics. [corrected]. Position statement by the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 116(2):238–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2013.06.002
Pittayapat P, Limchaichana-Bolstad N, Willems G, Jacobs R (2014) Three-dimensional cephalometric analysis in orthodontics: a systematic review. Orthod Craniofacial Res 17(2):69–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr.12034
Goto TK, Nishida S, Nakamura Y, Tokumori K, Nakamura Y, Kobayashi K, Yoshida Y, Yoshiura K (2007) The accuracy of 3-dimensional magnetic resonance 3D vibe images of the mandible: an in vitro comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103(4):550–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2006.03.011
Juerchott A, Saleem MA, Hilgenfeld T, Freudlsperger C, Zingler S, Lux CJ, Bendszus M, Heiland S (2018) 3D cephalometric analysis using magnetic resonance imaging: validation of accuracy and reproducibility. Sci Rep 8(1):13029. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31384-8
Lisboa Cde O, Masterson D, da Motta AF, Motta AT (2015) Reliability and reproducibility of three-dimensional cephalometric landmarks using CBCT: a systematic review. J Appl Oral Sci 23(2):112–119. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-775720140336
Hilgenfeld T, Prager M, Heil A, Schwindling FS, Nittka M, Grodzki D, Rammelsberg P, Bendszus M, Heiland S (2017) PETRA, MSVAT-SPACE and SEMAC sequences for metal artefact reduction in dental MR imaging. Eur Radiol 27(12):5104–5112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-4901-1
Titiz I, Laubinger M, Keller T, Hertrich K, Hirschfelder U (2012) Repeatability and reproducibility of landmarks—a three-dimensional computed tomography study. Eur J Orthod 34(3):276–286. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjq190
Hassan B, Nijkamp P, Verheij H, Tairie J, Vink C, van der Stelt P, van Beek H (2013) Precision of identifying cephalometric landmarks with cone beam computed tomography in vivo. Eur J Orthod 35(1):38–44. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjr050
Schlicher W, Nielsen I, Huang JC, Maki K, Hatcher DC, Miller AJ (2012) Consistency and precision of landmark identification in three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography scans. Eur J Orthod 34(3):263–275. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjq144
Naji P, Alsufyani NA, Lagravere MO (2014) Reliability of anatomic structures as landmarks in three-dimensional cephalometric analysis using CBCT. Angle Orthod 84(5):762–772. https://doi.org/10.2319/090413-652.1
Pittayapat P, Jacobs R, Bornstein MM, Odri GA, Kwon MS, Lambrichts I, Willems G, Politis C, Olszewski R (2016) A new mandible-specific landmark reference system for three-dimensional cephalometry using cone-beam computed tomography. Eur J Orthod 38(6):563–568. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjv088
Olszewski R, Reychler H, Cosnard G, Denis JM, Vynckier S, Zech F (2008) Accuracy of three-dimensional (3D) craniofacial cephalometric landmarks on a low-dose 3D computed tomograph. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 37(5):261–267. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr/33343444
Olszewski R, Tanesy O, Cosnard G, Zech F, Reychler H (2010) Reproducibility of osseous landmarks used for computed tomography based three-dimensional cephalometric analyses. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 38(3):214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2009.05.005
Olszewski R, Frison L, Wisniewski M, Denis JM, Vynckier S, Cosnard G, Zech F, Reychler H (2013) Reproducibility of three-dimensional cephalometric landmarks in cone-beam and low-dose computed tomography. Clin Oral Investig 17(1):285–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-012-0688-2
Lagravere MO, Gordon JM, Guedes IH, Flores-Mir C, Carey JP, Heo G, Major PW (2009) Reliability of traditional cephalometric landmarks as seen in three-dimensional analysis in maxillary expansion treatments. Angle Orthod 79(6):1047–1056. https://doi.org/10.2319/010509-10R.1
Lagravere MO, Low C, Flores-Mir C, Chung R, Carey JP, Heo G, Major PW (2010) Intraexaminer and interexaminer reliabilities of landmark identification on digitized lateral cephalograms and formatted 3-dimensional cone-beam computerized tomography images. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 137(5):598–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2008.07.018
Katkar RA, Kummet C, Dawson D, Moreno Uribe L, Allareddy V, Finkelstein M, Ruprecht A (2013) Comparison of observer reliability of three-dimensional cephalometric landmark identification on subject images from Galileos and i-CAT cone beam CT. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 42(9):20130059. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20130059
Neiva MB, Soares AC, Lisboa Cde O, Vilella Ode V, Motta AT (2015) Evaluation of cephalometric landmark identification on CBCT multiplanar and 3D reconstructions. Angle Orthod 85(1):11–17. https://doi.org/10.2319/120413-891.1
Muramatsu A, Nawa H, Kimura M, Yoshida K, Maeda M, Katsumata A, Ariji E, Goto S (2008) Reproducibility of maxillofacial anatomic landmarks on 3-dimensional computed tomographic images determined with the 95% confidence ellipse method. Angle Orthod 78(3):396–402. https://doi.org/10.2319/040207-166.1
Fuyamada M, Nawa H, Shibata M, Yoshida K, Kise Y, Katsumata A, Ariji E, Goto S (2011) Reproducibility of landmark identification in the jaw and teeth on 3-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography images. Angle Orthod 81(5):843–849. https://doi.org/10.2319/010711-5.1
Fuyamada M, Shibata M, Nawa H, Yoshida K, Kise Y, Katsumata A, Ariji E, Goto S (2014) Reproducibility of maxillofacial landmark identification on three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography images of patients with mandibular prognathism: comparative study of a tentative method and traditional cephalometric analysis. Angle Orthod 84(6):966–973. https://doi.org/10.2319/111313-836.1
Ludlow JB, Gubler M, Cevidanes L, Mol A (2009) Precision of cephalometric landmark identification: cone-beam computed tomography vs conventional cephalometric views. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 136(3):312 e311–312 e310; discussion 312–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2008.12.018
de Oliveira AE, Cevidanes LH, Phillips C, Motta A, Burke B, Tyndall D (2009) Observer reliability of three-dimensional cephalometric landmark identification on cone-beam computerized tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107(2):256–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.05.039
Theodorakou C, Walker A, Horner K, Pauwels R, Bogaerts R, Jacobs R, Consortium SP (2012) Estimation of paediatric organ and effective doses from dental cone beam CT using anthropomorphic phantoms. Br J Radiol 85(1010):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/19389412
Sedlacik J, Kutzner D, Khokale A, Schulze D, Fiehler J, Celik T, Gareis D, Smeets R, Friedrich RE, Heiland M, Assaf AT (2016) Optimized 14 + 1 receive coil array and position system for 3D high-resolution MRI of dental and maxillomandibular structures. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 45(1):20150177. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20150177
Li GN, M.; Paul, D.; Lauer, L.. (2011) MSVAT-SPACE for fast metal implants imaging. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 19:3171
Eggers G, Rieker M, Kress B, Fiebach J, Dickhaus H, Hassfeld S (2005) Artefacts in magnetic resonance imaging caused by dental material. MAGMA 18(2):103–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-005-0101-0
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Dietmar Hopp Foundation for their friendly support of this research project. Many thanks to Mathias Nittka, PhD, from Siemens Healthcare for his cooperation and assistance in the setup of the MSVAT-SPACE sequence. A.J. receives funding from a postdoctoral fellowship of the Medical Faculty of the University of Heidelberg.
Funding
This study was supported by the Dietmar Hopp Foundation (grant no. 23011228; grant holders—A.J., S.H., C.J.L., and S.Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All methods were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the local research ethics committee of the University of Heidelberg (approval no. S-294/2014).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juerchott, A., Freudlsperger, C., Zingler, S. et al. In vivo reliability of 3D cephalometric landmark determination on magnetic resonance imaging: a feasibility study. Clin Oral Invest 24, 1339–1349 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03015-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03015-7