Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the cyclic fatigue using severely curved canals and torsional resistance of ProDesign R (Easy Equipamentos Odontológicos, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil), Reciproc Blue (VDW, Munich, Germany), and WaveOne Gold (Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) reciprocating instruments
Materials and methods
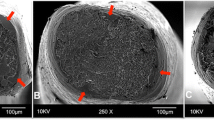
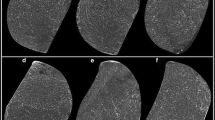
Twenty instruments of the ProDesign R (25/0.06) system, 20 instruments of the Reciproc Blue (25/0.08v) system, and 20 instrument of the WaveOne Gold (25/0.07v) system were used. Cyclic fatigue resistance was tested measuring the time to fracture and the number of cycles to fracture in an artificial stainless steel severely curved canal with 80° angle and a 3-mm radius of curvature (n = 10). Torque and angle of rotation at failure of new instruments (n = 10) were measured according to ISO 3630-1. The fracture surfaces of all fragments were examined with a scanning electron microscope. Results were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test at a significance level of p < 0.05.
Results
ProDesign R instruments showed a significantly longer cyclic fatigue life than the other tested instruments (p < 0.05). Reciproc Blue showed longer cyclic life than WaveOne Gold (p < 0.05). Reciproc Blue showed the higher torsional strength, followed by WaveOne Gold and ProDesign R instruments (p < 0.05). Moreover, Reciproc Blue showed significantly higher angular rotation to fracture than ProDesign R (p < 0.05). WaveOne Gold showed intermediary results regarding angular rotation to fracture with no differences when compared to Reciproc Blue or ProDesign R instruments (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
ProDesign R presented the highest cyclic fatigue resistance in severely curved canals when compared with Reciproc Blue and WaveOne Gold. However, Reciproc Blue showed the higher torsional strength overall and higher angular rotation to fracture when compared to ProDesign R.
Clinical relevance
Despite the numerous advantages of reciprocating instruments, these instruments still have some risk of fracture during its use, especially in severely curved canals. The present study evaluated the cyclic fatigue and torsional resistance of thermally treated reciprocating instruments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peters OA, de Azevedo Bahia MG, Pereira ES (2017) Contemporary root canal preparation: innovations in biomechanics. Dent Clin North Am 61(1):37–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2016.08.002
Ferreira F, Adeobato C, Barbosa I, Aboud L, Scelza P, Zaccaro Scelza M (2017) Movement kinematics and cyclic fatigue of NiTi rotary instruments: a systematic review. Int Endod J 50(2):143–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12613
Pérez-Higueras JJ, Arias A, de la Macorra JC (2013) Cyclic fatigue resistance of K3, K3XF, and twisted file nickel-titanium files under continuous rotation or reciprocating motion. J Endod 39:1585–1588
Lopes HP, Gambarra-Soares T, Elias CN, Siqueira JF Jr, Inojosa IF, Lopes WS et al (2013) Comparison of the mechanical properties of rotary instruments made of conventional nickel-titanium, M-wire, or nickel-titanium alloy in R-phase. J Endod 39:516–520
De-Deus G, Silva EJ, Vieira VT, Belladonna FG, Elias CN, Plotino G et al (2017) Blue thermomechanical treatment optimizes fatigue resistance and flexibility of the Reciproc files. J Endod 43(3):462–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2016.10.039
Adıgüzel M, Capar ID (2017) Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne and WaveOne Gold small, primary, and large instruments. J Endod 43(4):623–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2016.11.021
Shen Y, Zhou HM, Zheng YF, Peng B, Haapasalo M (2013) Current challenges and concepts of the thermomechanical treatment of nickel-titanium instruments. J Endod 39(2):163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2012.11.005
Silva EJ, Rodrigues C, Vieira VT, Belladona FD, De-Deus G, Lopes HP (2016) Bending resistance and cyclic fatigue of a new heat-treated reciprocating instrument. Scanning 38(6):837–841. https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.21333
International Organization for Standardization ISO 3630-1 (1992) Dental root canal instruments: part 1—files, reamers, barbed broaches, rasps, paste carriers, explorers and cotton broaches. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
Sattapan B, Nervo GJ, Palamara JE, Messer HH (2000) Defects in rotary nickel-titanium files after clinical use. J Endod 26(3):161–165. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004770-200003000-00008
Plotino G, Grande NM, Cordaro M, Testarelli L, Gambarini G (2009) A review of cyclic fatigue testing of nickel titanium rotary instruments. J Endod 35(11):1469–1476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2009.06.015
Silva EJ, Villarino LS, Vieira VT, Accorsi-Mendonça T, Antunes HD, De-Deus G et al (2016) Bending resistance and cyclic fatigue life of Reciproc, Unicone, and WaveOne reciprocating instruments. J Endod 42(12):1789–1793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2016.08.026
Gabliardi J, Versiani MA, de Sousa-Neto MD, Plazas-Garzon A, Basrani B (2015) Evaluation of the shaping characteristics of ProTaper Gold, ProTaper NEXT, and ProTaper Universal in curved canals. J Endod 41(10):1718–1724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2015.07.009
Duque JA, Vivan RR, Cavenago BC, Amoroso-Silva PA, Bernardes RA, Vasconcelos BC et al (2017) Influence of NiTi alloy on the root canal shaping capabilities of the ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold rotary instrument systems. J Appl Oral Sci 25(1):27–33. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-77572016-0230
Özyürek T, Yilmaz K, Uslu G (2017) Shaping ability of Reciproc, WaveOne GOLD, and Hyflex EDM single-file systems in simulated S-shaped canals. J Endod 43:805–809
de Vasconcelos RA, Murphy S, Carvalho CA, Govindjee RG, Govindjee S, Peters A (2016) Evidence for reduced fatigue resistance of contemporary rotary instruments exposed to body temperature. J Endod 42(5):782–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2016.01.025
Alcalde MP, Tanomaru-Filho M, Bramante CM, Duarte MAH, Guerreiro-Tanomaru J, Camilo-Pinto J et al (2017) Cyclic and torsional fatigue resistance of reciprocating single files manufactured by different nickel-titanium alloys. J Endod 43(7):1186–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2017.03.008
Keskin C, Inan U, Demiral M, Keles A (2017) Cyclic fatigue resistance of Reciproc Blue, Reciproc, and WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments. J Endod 43(8):1360–1363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2017.03.036
De-Deus G, Vieira VT, Silva EJ, Lopes H, Elias CN, Moreira EJ (2014) Bending resistance and dynamic and static cyclic fatigue life of Reciproc and WaveOne large instruments. J Endod 40(4):575–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2013.10.013
Pedullà E, Lo Savio F, Boninelli S, Plotino G, Grande NM, La Rosa G, Rapisarda E (2016) Torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of a new nickel-titanium instrument manufactured by electrical discharge machining. J Endod 42(1):156–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2015.10.004
Funding
This study was partially funded by FAPERJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, E.J.N.L., Vieira, V.T.L., Hecksher, F. et al. Cyclic fatigue using severely curved canals and torsional resistance of thermally treated reciprocating instruments. Clin Oral Invest 22, 2633–2638 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-018-2362-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-018-2362-9