Abstract
Objectives
Recent developments in digital computer technology have enabled radiological diagnosis to be performed using a monitor screen. In medical radiography, the importance of monitors has been shown in many diseases. Digital imaging and communication in medicine (DICOM)-compatible monitors are widely used. However, the effect of monitors on the diagnosis of oral disease has not yet been clarified and remains controversial. The aims of this study are to compare the caries diagnostic ability between DICOM monitors and other monitors and to examine if monitor capability affects the diagnosis.
Materials and methods
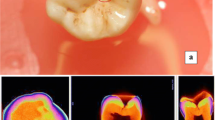
One hundred proximal surfaces of 50 extracted human upper premolar teeth were used as specimens. Intra-oral radiographs of all specimens were taken digitally. Three types of monitors were compared in terms of caries diagnostic ability: a DICOM standard-compatible monitor, a standardized personal computer (PC) monitor, and a tablet PC. Six oral radiologists diagnosed each radiograph independently. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were generated and compared.
Results
Area under the ROC curve (AUC) of the DICOM monitor, PC monitor, and tablet PC was 0.68147, 0.67002, and 0.60189, respectively. There was no significant difference between the DICOM monitor and the PC monitor, but the tablet PC showed significantly lower accuracy. There were no significant differences among the monitors for dentin caries (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
DICOM-compatible monitors and PC monitors have similar capabilities, but tablet PCs showed lower diagnostic accuracy, especially for superficial caries.
Clinical relevance
Appropriate monitors are needed for radiographic diagnosis on monitor screens.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samei E (2005) Assessment of display performance for medical imaging systems: executive summary of AAPM TG18 report. Med Phys 32:1205–1225
Kamitani T, Yabuuchi H, Matsuo Y, Setoguchi T, Sakai S, Okafuji T et al (2011) Diagnostic performance in differentiation of breast lesion on digital mammograms: comparison among hard-copy film, 3-megapixel LCD monitor, and 5-megapixel LCD monitor. Clin Imaging 35:341–345
Buls N, Shabana W, Verbeek P, Pevenage P, De Mey J (2007) Influence of display quality on radiologists’ performance in the detection of lung nodules on radiographs. Br J Radiol 80:738–743
Liang Z, Li K, Yang X, Du X, Liu J, Zhao X et al (2006) ROC analysis for diagnostic accuracy of fracture by using different monitors. J Digit Imaging 19:276–278
Krupinski EA (2004) Use of a human visual system model to predict observer performance with CRT vs LCD display of images. J Digit Imaging 17:258–263
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (2008) Rosslyn, VA: NEMA Publishing PS3.14-2008:
Hellen-Halme K, Nilsson M, Petersson A (2009) Effect of monitors on approximal caries detection in digital radiographs—standard versus precalibrated DICOM part 14 displays: an in vitro study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107:716–720
Isidor S, Faaborg-Andersen M, Hintze H, Kirkevang LL, Frydenberg M, Haiter-Neto F et al (2009) Effect of monitor display on detection of approximal caries lesions in digital radiographs. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 38:537–541
Abboud S, Weiss F, Siegel E, Jeudy J (2013) TB or not TB: interreader and intrareader variability in screening diagnosis on an iPad versus a traditional display. J Am Coll Radiol 10:42–44
Pretty IA (2006) Caries detection and diagnosis: novel technologies. J Dent 34:727–739
Wenzel A (1998) Digital radiography and caries diagnosis. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 27:3–11
Hillis SL, Berbaum KS, Metz CE (2008) Recent developments in the Dorfman–Berbaum–Metz procedure for multireader ROC study analysis. Acad Radiol 15:647–661
Espelid I (2003) EAPD guidelines for use of radiographs in children. Eur J Paediatr Dent 4:40–48
Tofangchiha M, Adel M, Bakhshi M, Esfehani M, Nazeman P, Ghorbani Elizeyi M et al (2013) Digital radiography with computerized conventional monitors compared to medical monitors in vertical root fracture diagnosis. Iran Endod J 8:14–17
Ilguy M, Dincer S, Ilguy D, Bayirli G (2009) Detection of artificial occlusal caries in a phosphor imaging plate system with two types of LCD monitors versus three different films. J Digit Imaging 22:242–249
Shintaku WH, Scarbecz M, Venturin JS (2012) Evaluation of interproximal caries using the IPad 2 and a liquid crystal display monitor. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 113:e40–e44
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Araki, K., Fujikura, M. & Sano, T. Effect of display monitor devices on intra-oral radiographic caries diagnosis. Clin Oral Invest 19, 1875–1879 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-015-1401-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-015-1401-z