Abstract
Objectives
This study assessed the effect of three commercial dentifrices with different fluoride-containing compounds in controlling the progression of dentin loss using an in vitro erosion-abrasion model.
Materials and methods
Dentin specimens were randomized into four groups (n = 10): control (no F), Elmex (1,400 ppm AmF), Meridol (1,400 ppm AmF/SnF2), and Crest Pro-Health (1,100 ppm SnF2). The dentin specimens were submitted to cycles of demineralization (HCl 0.01 M for 60 s), remineralization (artificial saliva for 60 min), and immersion in 1:3 w/w of dentifrice/artificial saliva, followed by toothbrushing (150 brushing strokes). The cycle was repeated three times daily for 5 days. Surface loss was quantified by stylus profilometry. Data were submitted to one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s tests (p < 0.05).
Results
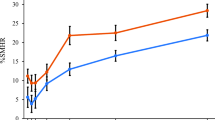
Wear (μm ± SD) was control 4.1 ± 1.2, Elmex 3.7 ± 1.5, Meridol 1.3 ± 0.4, and Crest Pro-Health 2.1 ± 0.7. Therefore, all products (except Elmex) produced statistically significantly less mineral loss (p < 0.05) when compared with the control.
Conclusion
None of the dentifrices avoided the erosive-abrasive process; however, SnF2-containing dentifrices were effective in statistically significantly reducing dentin loss.
Clinical relevance
Scientific literature shows evidence that fluoride can strengthen dental tissue against erosive acid damage. However, the beneficial effect of different fluorides present in commercial dentifrices is questionable. Thus, a determination of an effective fluoride dentifrice may be beneficial in the reduction of the erosive process in patients with gastric disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Imfeld T (1996) Dental erosion. Definition, classification and links. Eur J Oral Sci 104:151–155
Lussi A, Schlueter N, Rakhmatullina E, Ganss C (2011) Dental erosion—an overview with emphasis on chemical and histopathological aspects. Caries Res 45(Suppl 1):2–12. doi:10.1159/000325915
Ranjitkar S, Kaidonis JA, Smales RJ (2012) Gastroesophageal reflux disease and tooth erosion. Int J Dent 2012:479850. doi:10.1155/2012/479850
Lussi A, Hellwig E (2006) Risk assessment and preventive measures. Monogr Oral Sci 20:190–199
Saxegaard E, Rolla G (1988) Fluoride acquisition on and in human enamel during topical application in vitro. Scand J Dent Res 96:523–535
Magalhães AC, Wiegand A, Rios D, Buzalaf MA, Lussi A (2011) Fluoride in dental erosion. Monogr Oral Sci 22:158–170. doi:10.1159/000325167
Willumsen T, Ogaard B, Hansen BF, Rølla G (2004) Effects from pretreatment of stannous fluoride versus sodium fluoride on enamel exposed to 0.1 M or 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. Acta Odontol Scand 62:278–281
Hove L, Holme B, Øgaard B, Willumsen T, Tveit AB (2006) The protective effect of TiF4, SnF2, and NaF on erosion of enamel by hydrochloric acid in vitro measured by white light interferometry. Caries Res 40:440–443
Ganss C, Schlueter N, Hardt M, Schattenberg P, Klimek J (2008) Effect of fluoride compounds on enamel erosion in vitro: a comparison of amine, sodium and stannous fluoride. Caries Res 42:2–7
Schlueter N, Klimek J, Ganss C (2011) Efficacy of tin-containing solutions on erosive mineral loss in enamel and dentine in situ. Clin Oral Investig 15:361–367. doi:10.1007/s00784-010-0386-x
Wiegand A, Magalhães AC, Navarro RS, Schmidin PR, Rios D, Buzalaf MAR et al (2010) Effect of titanium tetrafluoride and amine fluoride treatment combined with carbon dioxide laser irradiation on enamel and dentin erosion. Photomed Laser Surg 28:219–226. doi:10.1089/pho.2009.2551
Wegehaupt FJ, Sener B, Attin T, Schmidlin PR (2011) Anti-erosive potential of amine fluoride, cerium chloride and laser irradiation application on dentine. Arch Oral Biol 56:1541–1547. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.06.010
Wiegand A, Bichsel D, Magalhães AC, Becker K, Attin T (2009) Effect of sodium, amine and stannous fluoride at the same concentration and different pH on in vitro erosion. J Dent 37:591–595. doi:10.1016/j.jdent.2009.03.020
Ganss C, Lussi A, Sommer N, Klimek J, Schlueter N (2010) Efficacy of fluoride compounds and stannous chloride as erosion inhibitors in dentine. Caries Res 44:248–252. doi:10.1159/000314671
Ganss C, Neutard L, von Hinckeldey J, Klimek J, Schlueter N (2010) Efficacy of a tin/fluoride rinse: a randomized in situ trial on erosion. J Dent Res 89:1214–1218. doi:10.1177/0022034510375291
Ganss C, Hardt M, Lussi A, Cocks A, Klimek J, Schlueter N (2010) Mechanism of action of tin-containing fluoride solutions as anti-erosive agents in dentine—an in vitro tin-uptake, tissue loss, and scanning electron microscopy study. Eur J Oral Sci 118:376–384. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0722.2010.00742.x
Ganss C, Klimek J, Starck C (2004) Quantitative analysis of the impact of the organic matrix on the fluoride effect on erosion progression in human dentine using longitudinal microradiography. Arch Oral Biol 49:931–935
Mühlemann HR, Saxer UP (1981) Reduction of plaque and gingivitis by stannous fluoride stabilized with amine fluoride (abstract). Caries Res 15:18619. Yu H, Attin T, Wiegand A, Buchalla W (2010) Effects of various fluoride solutions on enamel erosion in vitro. Caries Res 44:390–401. doi:10.1159/000316539
Yu H, Attin T, Wiegand A, Buchalla W (2010) Effects of various fluoride solutions on enamel erosion in vitro. Caries Res 44:390–401. doi:10.1159/000316539
Wiegand A, Attin T (2011) Design of erosion/abrasion studies—insights and rational concepts. Caries Res 45(Suppl 1):53–59. doi:10.1159/000325946
Morita I, Nakagaki H, Toyama A, Hayashi M, Shimozato M, Watanabe T, Tohmatsu S, Igo J, Sheiham A (2006) Behavioral factors to include in guidelines for lifelong oral healthiness: an observational study in Japanese adults. BMC Oral Health 20:6–15
Vettore MV, Moysés SJ, Sardinha LM, Iser BP (2012) Socioeconomic status, toothbrushing frequency, and health-related behaviors in adolescents: an analysis using the PeNSE database. Cad Saude Publica 28(Suppl:s):101–113, Article in Portuguese
Wiegand A, Bliggenstorfer S, Magalhaes AC, Sener B, Attin T (2008) Impact of the in situ formed salivary pellicle on enamel and dentine erosion induced by different acids. Acta Odontol Scand 66:225–230. doi:10.1080/00016350802183401
Attin T (2006) Methods for assessment of dental erosion. Monogr Oral Sci 20:152–172
Magalhães AC, Rios D, Moino AL, Wiegand A, Attin T, Buzalaf MA (2008) Effect of different concentrations of fluoride in dentifrices on dentin erosion subjected or not to abrasion in situ/ex vivo. Caries Res 42(2):112–116. doi:10.1159/000117807
Hara AT, González-Cabezas C, Creeth J, Parmar M, Eckert GJ, Zero DT (2009) Interplay between fluoride and abrasivity of dentifrices on dental erosion–abrasion. J Dent 37:781–785. doi:10.1016/j.jdent.2009.06.006
Wiegand A, Kuhn M, Sener B, Roos M, Attin T (2009) Abrasion of eroded dentin caused by toothpaste slurries of different abrasivity and toothbrushes of different filament diameter. J Dent 37:480–484. doi:10.1016/j.jdent.2009.03.005
Hooper S, West NX, Pickles M, Joiner A, Newcombe RG, Addy M (2003) Investigation of erosion and abrasion of enamel and dentine: a model in situ using toothpastes of different abrasivity. J Clin Perio 30:802–807
Passos VF, Santiago SL, Tenuta LM, Cury JA (2010) Protective effect of NaF/triclosan/copolymer and MFP dentifrice on enamel erosion. Am J Dent 23:193–195
Zero DT, Hara AT, Kelly SA, González-Cabezas C (2006) Evaluation of a desensitizing test dentifrice using an in situ erosion remineralization model. J Clin Dent 17:112–116
Ponduri S, Macdonald E, Addy M (2005) A study in vitro of the combined effects of soft drinks and tooth brushing with fluoride toothpaste on the wear of dentine. Int J Dent Hyg 3(1):7–12
Comar LP, Gomes MF, Ito N, Salomão PA, Grizzo LT, Magalhães AC (2012) Effect of NaF, SnF2, and TiF4 toothpastes on bovine enamel and dentin erosion-abrasion in vitro. Int J Dent 6 pages. doi: 10.1155/2012/134350
Rosin-Grget K, Sutej I, Lincir I (2007) The effect of saliva on the formation of KOH-soluble fluoride after topical application of amine fluoride solutions of varying fluoride concentration and pH. Caries Res 41:235–238
Ganss C, Schlueter N, Klimek J (2007) Retention of KOH-soluble fluoride on enamel and dentine under erosive conditions—a comparison of in vitro and in situ results. Arch Oral Biol 52:9–14
Wiegand A, Schneider S, Sener B, Roos M, Attin T (2014) Stability against brushing abrasion and the erosion-protective effect of different fluoride compounds. Caries Res 48:154–162
Babcock FD, King JC, Jordan TH (1978) The reaction of stannous fluoride and hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res 57:933–938
Ganss C, Hardt M, Blazek D, Klimek J, Schlueter N (2009) Effects of toothbrushing force on the mineral content and demineralized organic matrix of eroded dentine. Eur J Oral Sci 117:255–260. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0722.2009.00617.x
Hara AT, Lippert F, Zero DT (2013) Interplay between experimental dental pellicles and stannous-containing toothpaste on dental erosion-abrasion. Caries Res 47:325–329. doi:10.1159/000347051
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Passos, V.F., de Vasconcellos, A.A., Pequeno, J.H.P. et al. Effect of commercial fluoride dentifrices against hydrochloric acid in an erosion-abrasion model. Clin Oral Invest 19, 71–76 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-014-1213-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-014-1213-6