Abstract
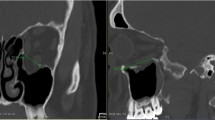
This retrospective study aimed at investigating indications, surgical approaches, and the materials used for orbital floor reconstructions, as well as the clinical follow-up, particularly with regard to postoperative complications. This study comprised 189 patients who underwent surgery for fractures of the orbital floor between 2003 and 2007. Diagnosis and treatment were based on both physical examination and computed tomography scan of the orbit. Patients were retrospectively analyzed for data, such as mechanism of injury, classification of fracture, and complications. The most common cause of injury was physical assault followed by traffic accidents. Surgery was conducted with a mean delay of 2.9 days after the incident. Mid lower eyelid incision was the most common surgical approach to the orbital floor. For orbital floor reconstruction, polydioxanone sheets (70.5%) were mainly used, followed by Ethisorb Dura (23.3%) and titanium mesh (6.2%). There were 19.0% of patients who showed postoperative complications: 5.8% suffered from persisting motility impairment, 3.7% from enophthalmos, 3.2% from consistent diplopia, 2.6% from ectropion, and 0.5% from orbital infection. Intraorbital hematoma (3.2%) represented the most severe complications, one patient suffered lasting impairment of sight and another one, complete blindness of the affected eye. If postoperative impairment of vision becomes evident, immediate surgical intervention is mandatory. Retrobulbar hematoma is more likely to occur in heavily traumatized patients with comminuted fractures and also in patients taking anticoagulative medication. The subciliary approach to the orbit and repeated operations by the same approach are associated with a higher risk of developing ectropion.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carr RM, Methog RH (1997) Early and delayed repair of orbit-zygomatic complex fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:253–258
Howard G, Osguthorpe JD (1997) Concepts in orbital reconstruction. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 30:541–562
Wang S, Xiao J, Liu L, Lin Y, Li X, Tang W, Wang H, Long J, Zheng X, Tian W (2008) Orbital floor reconstruction: a retrospective study of 21 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 106:324–330
Folkestad L, Westin T (1999) Long-term sequelae after surgery for orbital floor fractures. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120:914–921
Dutton JJ, Manson PN, Putterman AM, Iliff N (1991) Management of blow-out fractures of the orbital floor. Surv Ophthalmol 35:279–298
Nam SB, Bae YC, Moon JS, Kang YS (2006) Analysis of the postoperative outcome in 405 cases of orbital fracture using 2 synthetic orbital implants. Ann Plast Surg 56:263–267
Lee S, Maronian N, Most SP, Whipple ME, McCulloch TM, Stanley RB, Farwell DG (2005) Porous high-density polyethylene for orbital reconstruction. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:446–450
Girotto JA, Gamble WB, Robertson B, Muehlberger T, Mayer M, Zinreich J, Ilif N, Miller N, Manson PN (1998) Blindness after reduction of facial fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:1821–1834
Gerbino G, Ramieri GA, Nasi A (2005) Diagnosis and treatment of retrobulbar haematomas following blunt orbital trauma: a description of eight cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34:127–131
Cole P, Boyd V, Banerji S, Hollier LH (2007) Comprehensive management of orbital fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:57–63
Burnstine MA (2003) Clinical recommendations for repair of orbital facial fractures. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 14:236–240
Yoon KC, Seo MS, Park YG (2003) Orbital trapdoor fracture in children. J Korean Med Sci 18:881–885
Bansagi ZC, Meyer DR (2000) Internal orbital fractures in the pediatric age group: characterization and management. Ophthalmology 107:829–836
Egbert JE, May K, Kersten RC, Kulwin DR (2000) Pediatric orbital floor fracture: direct extraocular muscle involvement. Ophthalmology 107:1875–1879
Burnstine MA (2002) Clinical recommendations for repair of isolated orbital floor fractures: an evidence-based analysis. Ophthalmology 109:1207–1210
Harris GJ (2006) Orbital blow-out fractures: surgical timing and technique. Eye 20:1207–1212
Boush GA, Lemke BN (1994) Progressive infraorbital nerve hypesthesia as a primary indication for blow-out fracture repair. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 10:271–275
Liu D (1994) Blindness after blow-out fracture repair. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 10:206–210
Rinna C, Ungari C, Saltarel A, Cassoni A, Reale G (2005) Orbital floor restoration. J Craniofac Surg 16:968–972
Ng SG, Madill SA, Inkster CF, Maloof AJ, Leatherbarrow B (2001) Medpor porous polyethylene implants in orbital blowout fracture repair. Eye 15:578–582
Hosal BM, Beatty RL (2002) Diplopia and enophthalmos after surgical repair of orbital fracture. Orbit 21:27–33
Dal Canto AJ, Linberg JV (2008) Comparison of orbital fracture repair performed within 14 days versus 15 to 29 days after trauma. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 24:437–443
Ben Simon GJ, Molina M, Schwarcz RM, McCann JD, Goldberg RA (2005) External (subciliary) vs internal (transconjunctival) involutional entropion repair. Am J Ophthalmol 139:482–487
De Riu G, Meloni SM, Gobbi R, Soma D, Baj A, Tullio A (2008) Subciliary versus swinging eyelid approach to the orbital floor. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 36:439–442
Bähr W, Bagambis FB, Schlegel G, Schilli W (1992) Comparision of transcutaneous incisions used for exposure of the infraorbital rim. Plast Reconstru Surg 90:585–591
Zide MF (1997) The long-term unfavourable result in midface trauma. In: Kaban LB, Pogrel MA, Perrott DH (eds) Complications in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 315–317
Kontio R, Suuronen R, Salonen O, Paukku P, Konttinen YT, Lindqvist C (2001) Effectiveness of operative treatment of internal orbital wall fracture with polydioxanone implant. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 30:278–285
Villarreal PM, Monje F, Morillo AJ, Junquera LM, González C, Barbón JJ (2002) Porous polyethylene implants in orbital floor reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:877–885
Ozturk S, Sengezer M, Isik S, Turegun M, Deveci M, Cil Y (2005) Long-term outcomes of ultra-thin porous polyethylene implants used for reconstruction of orbital floor defects. J Craniofac Surg 16:973–977
Hollier LH, Rogers N, Berzin E, Stal S (2001) Resorbable mesh in the treatment of orbital floor fractures. J Craniofac Surg 12:242–246
Baumann A, Burggasser G, Gauss N, Ewers R (2002) Orbital floor reconstruction with an alloplastic resorbable polydioxanone sheet. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 31:367–373
Kontio R, Lindqvist C (2009) Management of orbital fractures. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 21:209–220
De Roche R, Adolphs N, Kuhn A, Gogolewski S, Hammer B, Rahn B (2001) Reconstruction of the orbits with polylactate implants: animal experimental results after 12 months and clinical prospects. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir 5:49–56
Gosau M, Schiel S, Draenert GF, Ihrler S, Mast G, Ehrenfeld M (2006) Craniofacial augmentation with porous polyethylene implants—Medpor: first clinical results. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir 10:178–184
Gosau M, Draenert FG, Ihrler S (2008) Facial augmentation with porous polyethylene (Medpor)—histological evidence of intense foreign body reaction. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 87:83–87
Draenert GF, Doeblinger M, Draenert M, Gosau M (2009) High-density polyethylene facial implants show surface oxidation in SEM and EDX examination: a pilot study. Acta Biomater 5:1158–1162
Mackenzie DJ, Arora B, Hansen J (1999) Orbital floor repair with titanium mesh screen. J Craniomaxillofac Trauma 5:9–16
Lee HB, Nunery WR (2009) Orbital adherence syndrome secondary to titanium implant material. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 25:33–36
Hislop WS, Dutton GN, Douglas PS (1996) Treatment of retrobulbar haemorrhage in accident and emergency departments. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34:289–292
Kontio RK, Laine P, Salo A, Paukku P, Lindqvist C, Suuronen R (2006) Reconstruction of internal orbital wall fracture with iliac crest free bone graft: clinical, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging follow-up study. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:1365–1374
Sakakibara S, Hashikawa K, Terashi H, Tahara S (2009) Reconstruction of the orbital floor with sheets of autogenous iliac cancellous bone. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:957–961
Guo L, Tian W, Feng F, Long J, Li P, Tang W (2009) Reconstruction of orbital floor fractures: comparison of individual prefabricated titanium implants and calvarial bone grafts. Ann Plast Surg 63:624–631
Ord RA (1981) Post-operative retrobulbar haemorrhage and blindness complicating trauma surgery. Br J Oral Surg 19:202–207
Li KK, Meara JG, Joseph MP (1997) Reversal of blindness after facial fracture repair by prompt optic nerve decompression. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:648–650
Eo S, Kim J, Azari K (2005) Temporary orbital apex syndrom after repair of orbital wall fracture. Plast Reconstr Surg 116:85–89
Ellis E, Tan Y (2003) Assessment of internal orbital reconstructions for pure blowout fractures: cranial bone grafts versus titanium mesh. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:442–453
Popat H, Doyle PT, Davies SJ (2007) Blindness following retrobulbar haemorrhage—it can be prevented. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45:163–164
Bailey WK, Paul C, Evans LS (1993) Diagnosis and treatment of retrobulbar haemorrhage. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 51:780–781
Korinth MC, Ince A, Banghard W, Huffmann BC, Gilsbach JM (2002) Pterional orbital decompression in orbital haemorrhage and trauma. J Trauma 53:73–78
Saussez S, Choufani G, Brutus JP, Cordonnier M, Hassid S (1998) Lateral canthotomy: a simple and safe procedure for orbital haemorrhage secondary to endoscopic sinus surgery. Rhinology 36:37–39
Babajews A, Williams JL (1986) Blindness after trauma insufficient to cause bony injury: case report and review. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 24:7–11
Ghufoor K, Sandhu G, Sutcliffe J (1998) Delayed onset of retrobulbar haemorrhage following severe head injury: a case report and review. Injury 29:139–141
Rosdeutscher JD, Stadelmann WK (1998) Diagnosis and treatment of retrobulbar hematoma resulting from blunt periorbital trauma. Ann Plast Surg 41:618–622
Goodall KL, Brahma A, Bates A, Leatherbarrow B (1999) Lateral canthotomy and inferior cantholysis: an effective method of urgent orbital decompression for sight threatening acute retrobulbar haemorrhage. Injury 30:485–490
Yung CW, Moorthy RS, Lindley D, Ringle M, Nunery WR (1994) Efficacy of lateral canthotomy and cantholysis in orbital hemorrhage. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 10:137–141
Han JK, Caughey RJ, Gross CW, Newman S (2008) Management of retrobulbar hematoma. Am J Rhinol 22:522–524
Stoll W, Busse H, Kroll P (1988) Decompression of the orbit and optic nerve in different diseases. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 16:308–311
Sullivan WG, Kawamoto HK (1989) Periorbital margionotomies: anatomy and application. J Cranio-Max-Fac Surg 17:206–209
Sargent LA, Fulks KD (1991) Reconstruction of internal orbital fractures with Vitallium mesh. Plast Reconstr Surg 88:31–38
Hidding J, Deitmer T, Hemprich A, Ahrberg W (1991) Primary correction of orbital fractures using PDS-foil. Fortschr Kiefer Gesichtschir 36:195–196
Iizuka T, Mikkonen P, Paukku P, Lindqvist C (1991) Reconstruction of orbital floor with polydioxanone plate. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 20:83–87
Samek M, Pape HD, Rüßmann W, Berg S (1991) Lokalisation und Ausmaß von Orbitabodenfrakturen und Indikation zur Defektdeckung. In: Schwenzer G, Pfeifer G (eds) Fortschritte der Kiefer- und Gesichtschirurgie, XXXVI. Stuttgart, Thieme, pp 193–194
Hessling KH, Eckhardt A, Schmelzeisen R, Mayer H (1991) Indikation, Technik und Ergebnisse der Rekonstruktion von traumatischen Defekten des knöchernen Orbitabodens. In: Schwenzer G, Pfeifer G (eds) Fortschritte der Kiefer- und Gesichtschirurgie, XXXVI. Stuttgart, Thieme, pp 207–209
Hammer B (1995) Orbital fractures diagnosis, treatment, secondary corrections. Hoegrefe & Huber, Seattle, pp 1–100
Friesenecker J, Dammer R, Moritz M, Niederdellmann H (1995) Long-term results after primary restoration of the orbital floor. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 23:31–33
Kinnunen I, Aitasalo K, Pöllönen M, Varpula M (2000) Reconstruction of orbital floor fractures using bioactive glass. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 28:229–234
Guerra MF, Pérez JS, Rodriguez-Campo FJ, Gías LN (2000) Reconstruction of orbital fractures with dehydrated human dura mater. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:1361–1366
Dietz A, Ziegler CM, Dacho A, Althof F, Conradt C, Kolling G, von Boehmer H, Steffen H (2001) Effectiveness of a new perforated 0.15 mm poly-p-dioxanon-foil versus titanium-dynamic mesh in reconstruction of the orbital floor. J Maxillofac Surg 29:82–88
Aitasalo K, Kinnunen I, Palmgren J, Varpula M (2001) Repair of orbital floor fractures with bioactive glass implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59:1390–1395
Brady SM, McMann MA, Mazzoli RA, Bushley DM, Ainbinder DJ, Carroll RB (2001) The diagnosis and management of orbital blowout fractures: update 2001. Am J Emerg Med 19:147–154
Jank S, Emshoff R, Schuchter B, Strobl H, Brandlmaier I, Norer B (2003) Orbital floor reconstruction with flexible Ethisorb patches: a retrospective long-term follow-up study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 95:16–22
Büchel P, Rahal A, Seto I, Iizuka T (2005) Reconstruction of orbital floor fracture with polyglactin 910/polydioxanon patch (ethisorb): a retrospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:646–650
Tuncer S, Yavuzer R, Kandal S, Demir YH, Ozmen S, Latifoglu O, Atabay K (2007) Reconstruction of traumatic orbital floor fractures with resorbable mesh plate. J Craniofac Surg 18:598–605
Lin IC, Liao SL, Lin LL (2007) Porous polyethylene implants in orbital floor reconstruction. J Formos Med Assoc 106:51–57
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gosau, M., Schöneich, M., Draenert, F.G. et al. Retrospective analysis of orbital floor fractures—complications, outcome, and review of literature. Clin Oral Invest 15, 305–313 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-010-0385-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-010-0385-y