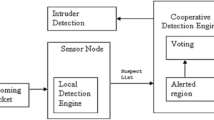
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks consist of some sensor nodes that have a minimum operational capability, with less memory capacity for storing data and limited energy sources. The deployment of these nodes or sensors takes place randomly in the dynamic or static environment. This type of placement of nodes in a hostile environment can be charged by the malicious nodes in a wireless sensor network (WSN). This vulnerability in nodes makes the wireless sensor network unstable and leads to many types of demerits like limited battery lifetime, less computing and limited memory space. To avoid these attacks and to reduce the impact created by the malicious nodes, we suggest a simple and effective way of detecting and removing unhealthy nodes in the environment. We proposed a simple scheme by using the artificial bee colony algorithm which is known as the soldier bee defence mechanism to provide proper security from the impersonate of node attack algorithm in detecting the malicious node present in the network. The malicious nodes will be intimated to the base station and the changes in the position of the estimated node should be monitored continuously. To develop an enriched swarm intelligence algorithm-based secured artificial bee colony optimizer gives a global exploration of multiple paths for carrying data transmission from the sensor to sink nodes in the absence of malicious nodes. Here, we are using the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm for secured communication between the nodes in a wireless network. The novelty of this algorithm is to detect a compromised node and to reduce the authentication delay and packet loss. The theme of a scheme is to find the unhealthy or malicious cluster head nodes in the network and removing that particular node without creating any harm to the other nodes in the environment. It also helps to improve the energy efficiency and packet delivery ratio with maximum throughput in WSN.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
24 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-021-01658-6
References
Abirami R, Premalatha G (2014) Depletion of vampire attacks in medium access control level using interior gateway routing protocol." Information Communication and Embedded Systems (ICICES), 2014 International Conference on. IEEE
Achuthan E, Kishore R (2014) A novel anti jamming technique for wireless sensor networks." Communications and Signal Processing (ICCSP), 2014 International Conference on. IEEE
Amish Parmar, Vaghela VB (2016) Detection and prevention of wormhole attack in wireless sensor network using AOMDV protocol. Procedia Comput Sci 79:700–707
Amudha P, Karthik S, Sivakumari S (2015) A hybrid swarm intelligence algorithm for intrusion detection using significant features. Sci World J 2015
Amudhavel J et al (2016) Recursive ant colony optimization routing in wireless mesh network. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Computer and Communication Technologies, Springer India
Di Pietro R et al (2011) Intrusion-resilient integrity in data-centric unattended WSNs. Pervasive Mob Comput 7(4):495–508
Dimitriou T et al (2016) Imposter detection for replication attacks in mobile sensor networks. Comput Netw 108:210–222
Dongare SP, Mangrulkar RS (2015) Implementing energy efficient technique for defense against Gray-Hole and Black-Hole attacks in wireless sensor networks. Computer Engineering and Applications (ICACEA), 2015 International Conference on Advances in. IEEE
Elhoseny M et al (2016) A secure data routing schema forWSN using Elliptic Curve Cryptography and homomorphic encryption. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 28(3):262–275
Gambhir A, Payal A, Arya R (2018) Performance analysis of artificial bee colony optimization based clustering protocol in various scenarios of WSN. Procedia Comput Sci 132:183–188
Hancer E et al (2015) A binary ABC algorithm based on advanced similarity scheme for feature selection. Appl Soft Comput 36:334–348
Isa MAM et al (2014) Cryptographic key exchange protocol with message authentication codes (mac) using finite state machine. Procedia Comput Sci 42:263–270
Jadidoleslamy H, Aref MR, Bahramgiri H (2016) A fuzzy fully distributed trust management system in wireless sensor networks. AEU-Int J Electron Commun 70(1):40–49
Kumari S, Om H (2016) Authentication protocol for wireless sensor networks applications like safety monitoring in coal mines. Comput Netw 104:137–154
Lee YS, Alasaarela E, Lee HJ (2014) Secure key management scheme based on ECC algorithm for patient's medical information in healthcare system. Information Networking (ICOIN), 2014 International Conference on. IEEE
Lichman M (2013) UCI Machine Learning Repository [http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml]. Irvine, CA: University of California, School of Information and ComputerScience. http://kdd.ics.uci.edu/databases/kddcup99/kddcup.data10.percent.gz
Maerien J et al (2015) SecLooCI: a comprehensive security middleware architecture for shared wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw 25:141–169
Mehmood A, Umar MM, Song H (2017) ICMDS: Secure inter-cluster multiple-key distribution scheme for wireless sensor networks.". Ad Hoc Netw 55:97–106
Messai M-L, Seba H (2016) A survey of key management schemes in multi-phase wireless sensor networks. Comput Netw 105:60–74
Mishra AK, Turuk AK (2016) A comparative analysis of node replica detection schemes in wireless sensor networks. J Netw Comput Appl 61:21–32
Moon AH, Iqbal U, MohiuddinBhat G (2016) Mutual Entity Authentication Protocol Based on ECDSA for WSN. Procedia Comput Sci 89:187–192
Moon PS, Ingole PK (2015) "An overview on: intrusion detection system with secure hybrid mechanism in wireless sensor network." Computer Engineering and Applications (ICACEA), 2015 International Conference on Advances in. IEEE
Muhammad S, Di Caro GA, M Farooq (2011) Swarm intelligence based routing protocol for wireless sensor networks: Survey and future directions. Inf Sci 181:4597–4624
Murphy FE et al (2015) Development of an heterogeneous wireless sensor network for instrumentation and analysis of beehives." Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), 2015 IEEE International. IEEE
Pang C, Xu G, Zhang Yunpu (2020) A new energy efficient management approach for wireless sensor networks in target tracking. Def Technol
Patil A, Gaikwad R (2015) comparative analysis of the prevention techniques of Denial of Service attacks in wireless sensor network. Procedia Comput Sci 48:387–393
Patil S, Chaudhari S (2016) DoS attack prevention technique in wireless sensor networks. Procedia Comput Sci 79:715–721
Raghav RS, Thirugnansambandam Kalaipriyan, Anguraj Dinesh Kumar (2020) Beeware routing scheme for detecting network layer attacks in wireless sensor networks. Wirel Pers Commun 112(4):2439–2459
Raghav RS et al (2021) Cuddle death algorithm using ABC for detecting unhealthy nodes in wireless sensor networks. Evol Intell 1–13
Rambabu BA, Reddy V, Janakiraman S (2019) Hybrid Artificial Bee Colony and Monarchy Butterfly Optimization Algorithm (HABC-MBOA)-based cluster head selection for WSNs. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci
Saad E, Elhosseini MA, Haikal AY (2019) Culture-based artificial bee colony with heritage mechanism for optimization of wireless sensors network. Appl Soft Comput 79:59–73
Sajjad Syed Muhammad, Bouk SafdarHussain, Yousaf Muhammad (2015) Neighbor node trust based intrusion detection system for wsn. Procedia Comput Sci 63:183–188
Salunke A, Ambawade D (2015) Dynamic Sequence Number Thresholding protocol for detection of blackhole attack in Wireless Sensor Network." Communication, Information & Computing Technology (ICCICT), 2015 International Conference on. IEEE
Shankar SK, Tomar AS, Tak GK (2015) Secure medical data transmission by using ECC with mutual authentication in WSNs. Procedia Comput Sci 70:455–461
Tanabe N, Kohno E, Kakuda Y (2012) An impersonation attack detection method using bloom filters and dispersed data transmission for wireless sensor networks. Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom), 2012 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE
Taylor C, Johnson T (2015) Strong authentication countermeasures using dynamic keying for sinkhole and distance spoofing attacks in smart grid networks. Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), 2015 IEEE. IEEE
Thenmozhi R, Karthikeyan P, Vijayakumar V, Keerthana M, Amudhavel J (2015) Backtracking performance analysis of Internet protocol for DDoS flooding detection. In Circuit, Power and Computing Technologies (ICCPCT), 2015 International Conference on (pp. 1–4). IEEE
Tripathi M, Gaur MS, Laxmi V (2013) Comparing the impact of black hole and gray hole attack on LEACH in WSN. Procedia Comput Sci 19:1101–1107
Upadhyay Raksha, Bhatt Uma Rathore, Tripathi Harendra (2016) DDOS Attack Aware DSR Routing Protocol in WSN. Procedia Comput Sci 78:68–74
Verma D, Singh G, Patidar K (2015) Detection of vampire attack in wireless sensor networks. Int J Comput Sci Inf Technol 6(4):3313–3317
Vijayalakshmi V, Sharmila R, Shalini R (2015) Hierarchical key management scheme using Hyper EllipticCurve Cryptography in Wireless Sensor Networks." Signal Processing, Communication and Networking (ICSCN), 2015 3rd International Conference on. IEEE
Wang D, Wang P (2014) Understanding security failures of two-factor authentication schemes for real-time applications in hierarchical wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw 20:1–15
Yadav AS et al (2020) Increasing Efficiency of Sensor Nodes by Clustering in Section Based Hybrid Routing Protocol with Artificial Bee Colony. Procedia Comput Sci 171:887–896
Zade AV, Tugnayat RM. A honey bee swarm intelligence algorithm for communication networks. Int J Eng Sci Res Technol ISSN: 2277–9655
Zhang X, Zhang X, Wang L (2017) Antenna design by an adaptive variable differential artificial bee colony algorithm. IEEE Trans Magn 54(3):1–4
Zhang X, Lu X, Zhang X (2020) Mobile wireless sensor network lifetime maximization by using evolutionary computing methods. Ad Hoc Networks 101:102094
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised due to changes in second affiliation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghav, R.S., Bhattacharyya, D., Anguraj, D.K. et al. A soldier bee defence mechanism for detecting impersonate sensor node in wireless sensor networks. Pers Ubiquit Comput 27, 889–906 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-021-01653-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-021-01653-x