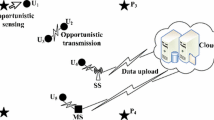
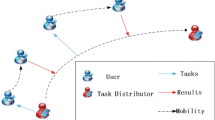
Abstract
The appearance of smart mobile devices with communication, computation and sensing capability and increasing popularity of various mobile applications have caused the explosion of mobile data recently. In the same time, mobile sensing has been emerging as a new sensing paradigm where vast numbers of mobile devices are used for sensing and collecting huge amounts of mobile data in cities. One of the challenges faced by mobile sensing is how to efficiently collect the huge amount of mobile data beyond the existing capacity of 4G networks. In this paper, we investigate the feasibility of collecting data packets from mobile devices through device-to-device communications by carefully selecting the subset of relaying (or/and sensing) devices. We formulate these problems as optimization problems and propose a set of solutions to solve them. Our experiments over a real-life mobile trace confirm the effectiveness of the proposed idea.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cisco visual networking index: global mobile data traffic forecast update, 2015–2020 (February 3, 2016). http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/mobile-white-paper-c11-520862.html
Guo B, Wang Z, Yu Z, Wang Y, Yen N, Huang R, Zhou X (2015) Mobile crowd sensing and computing: the review of an emerging human-powered sensing paradigm. ACM Comput Surv 48(1):7
Bengtsson L, Xin Lu, Thorson A, Garfield R, Schreeb JV (2011) Improved response to disasters and outbreaks by tracking population movements with mobile phone network data: A post-earthquake geospatial study in Haiti. PLoS Med 8(8):e1001083
Bo C, Jian X, Jung TJ, Han X-Y, Li Mao X, Wang Y (2016) Detecting driver’s smartphone usage via non-intrusively sensing driving dynamics. IEEE Internet Things J (99):1. doi:10.1109/JIOT.2016.2552399
Zhou P, Zheng Y, Li M (2012) How long to wait? Predicting bus arrival time with mobile phone based participatory sensing. In: Proceedings of ACM MobiSys
Nawaz S, Efstratiou C, Mascolo C (2013) Parksense: a smartphone based sensing system for on-street parking. In: Proceedings of ACM Mobicom
Gao R, Zhao M, Ye T, Ye F, Wang Y, Bian K, Wang T, Li X (2014) Jigsaw: indoor floor plan reconstruction via mobile crowdsensing. In: Proceedings of ACM MobiCom
Bo C, Jung T, Mao X, Li X-Y, Wang Y (2016) SmartLoc: sensing landmarks silently for smartphone based metropolitan localization. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 2016:e111
Rana RK, Chou CT, Kanhere SS, Bulusu N, Hu W (2010) Ear-phone: an end-to-end participatory urban noise mapping system. In: Proceedings of ACM/IEEE IPSN
Mun M, Reddy S, Shilton K, Yau N, Burke J, Estrin D, Hansen M, Howard E, West R, Boda P (2009) PEIR, the personal environmental impact report, as a platform for participatory sensing systems research. In: Proceedings of ACM MobiSys
Lathia N, Pejovic V, Rachuri KK, Mascolo C, Musolesi M, Rentfrow PJ (2013) Smartphones for large-scale behavior change interventions. IEEE Pervasive Comput 12(3):66–73
Noulas A, Scellato S, Lambiotte R, Pontil M, Mascolo C (2012) A tale of many cities: universal patterns in human urban mobility. PLoS ONE 7(5):e37027
Balasubramanian A, Mahajan R, Venkataramani A (2010) Augmenting mobile 3G using WiFi. In: ACM MobiSys 2010
Dimatteo S, Hui P, Han B, Li VOK (2011) Cellular traffic offloading through WiFi networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE MASS
Chandrasekhar V, Andrews JG, Gatherer A (2008) Femtocell networks: a survey. IEEE Commun Mag 46(9):59–67
Han B, Hui P, Kumar VSA, Marathe MV, Shao J, Srinivasan A (2012) Mobile data offloading through opportunistic communications and social participation. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 11(5):821–834
Li Y, Qian M, Jin D, Hui P, Wang Z, Chen S (2014) Multiple mobile data offloading through disruption tolerant networks. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 13(7):1579–1596
Zhu Y, Zhang C, Wang Y (2013) Mobile data delivery through opportunistic communications among cellular users: a case study for the D4D challenge. In: Proceedings of NetMob
Xiong H, Zhang D, Wang L, Chaouchi H (2015) EMC\(^3\): energy-efficient data transfer in mobile crowdsensing under full coverage constraint. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 14(7):1355–1368
Xiong H, Zhang D, Chen G, Wang L, Gauthier V (2015) Crowdtasker: maximizing coverage quality in piggyback crowdsensing under budget constraint. In: Proceedings of IEEE Percom
Zhang D, Xiong H, Wang L, Chen G (2014) Crowdrecruiter: selecting participants for piggyback crowdsensing under probabilistic coverage constraint. In: Proceedings of ACM UbiComp
Li H, Li T, Wang Y (2015) Dynamic participant recruitment of mobile crowd sensing for heterogeneous sensing tasks. In: Proceedings of IEEE MASS
Li H, Li T, Li F, Wang W, Wang Y (2016) Enhancing participant selection through caching in mobile crowd sensing. In: Proceedings of ACM/IEEE IWQoS
Wang L, Zhang D, Xiong H (2013) Effsense: energy-efficient and cost-effective data uploading in mobile crowdsensing . In: Proceedings of ACM UbiComp
Karaliopoulos M, Telelis O, Koutsopoulos I (2015) User recruitment for mobile crowdsensing over opportunistic networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM
Li H, Li T, Shi X, Wang Y (2016) Data collection through device-to-device communications for mobile big data sensing. In: Proceedings of 1st workshop of mission-critical big data analytics (MCBDA 2016)
Vahdat A, Becker D (2000) Epidemic routing for partially connected ad hoc networks. Technical Report CS-200006, Duke University, Technical Report
Merugu S, Ammar M, Zegura E (2004) Routing in space and time in networks with predictable mobility. Technical Report GIT-CC-04-07
Huang M, Chen S, Zhu Y, Wang Y (2013) Topology control for time-evolving and predictable delay-tolerant networks. IEEE Trans Comput 62(11):2308–2321
Li F, Chen S, Huang M, Yin Z, Zhang C, Wang Y (2015) Reliable topology design in time-evolving delay-tolerant networks with unreliable links. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 14(6):1301–1314
Agrawal A, Barlow RE (1984) A survey of network reliability and domination theory. Oper Res 32:478–492
Blondel VD, Esch M, Chan C, Clerot F, Deville P, Huens E, Morlot F, Smoreda Z, Ziemlicki C (2013) Data for development: the D4D challenge on mobile phone data. arXiv.1210.0137v2
Pournajaf L, Xiong L, Sunderam VS (2014) Dynamic data driven crowd sensing task assignment. In: Proceedings of ICCS
Zhao D, Ma H, Liu L (2014) Energy-efficient opportunistic coverage for people-centric urban sensing. Wirel Netw 20(6):461–1476
Li F, Tian C, Li T, Wang Y (2016) Energy efficient social routing framework for mobile social sensing networks. Tsinghua Sci Technol 21(4):363–373
Jin H, Su L, Ding B, Nahrstedt K, Borisov N (2016) Enabling privacy-preserving incentives for mobile crowd sensing systems. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICDCS
Yang D, Xue G, Fang X, Tang J (2012) Crowdsourcing to smartphones: incentive mechanism design for mobile phone sensing. In: Proceedings of ACM Mobicom
Liu Y, Li F, Wang Y (2016) Incentives for delay-constrained data query and feedback in mobile opportunistic crowdsensing. Sensors 16(7):1138. doi:10.3390/s16071138
Feng Z, Zhu Y, Zhang Q, Ni LM (2014) Vasilakos AV TRAC: truthful auction for location-aware collaborative sensing in mobile crowdsourcing In: Proceedings of INFOCOM
Zhu Y, Xu B, Shi X, Wang Y (2013) A survey of social-based routing in delay tolerant networks: positive and negative social effects. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 15(1):387–401
Zhu Y, Zhang C, Li F, Wang Y (2015) Geo-social: routing with location and social metrics in mobile opportunistic networks. In: IEEE ICC
Liu Y, Bashar AMAE, Li F, Wang Y, Liu K (2016) Multi-copy data dissemination with probabilistic delay constraint in mobile opportunistic device-to-device networks. In: Proceedings of 17th IEEE international symposium on a world of wireless, mobile and multimedia networks (WOWMOM 2016)
Li Y, Wu H, Xia Y, Wang Y, Li F, Yang P (2016) Optimal online data dissemination for resource constrained mobile opportunistic networks. IEEE Trans Veh Tech (99):1. doi:10.1109/TVT.2016.2616034
Acknowledgements
The work is partially supported by the US National Science Foundation under Grant Nos. CNS-1319915 and CNS-1343355, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61428203 and 61572347. The authors would like to thank Orange and the D4D challenge organizers for providing them the D4D datasets and allowing them to continue working on the datasets after the D4D challenge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Li, H. & Li, T. Participant selection for data collection through device-to-device communications in mobile sensing. Pers Ubiquit Comput 21, 31–41 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-016-0974-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-016-0974-0