Abstract.
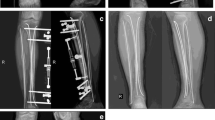
Twenty-four unstable tibial fractures were stabilized with a narrow limited contact-dynamic compression plate inserted using a percutaneous plating technique under fluoroscopic guidance. The major indication for this technique was a tibial fracture for which intramedullary nailing would be difficult. There were 16 proximal or distal metaphyseal fractures and 5 segmental fractures in adults and 3 mid-shaft fractures in adolescents who still had an open physis. Of the 24 fractures, 22 healed without a second procedure; the two failures included one that required an early bone graft for severe comminution and another with a superficial infection that healed after early removal of the plate. There were no other infections. There were three cases of screw breakage, but they did not require a further procedure. At the final follow-up, one patient had healed with 5° varus alignment and another with 10° external rotation. All the patients had good knee or ankle function. We are confident that the percutaneous plating technique to treat unstable tibial fractures for which intramedullary nailing would be difficult will prove to be an alternative stabilization method, as it avoids the risk of infection or soft tissue compromise.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: July 12, 2002 / Accepted: October 25, 2002
Offprint requests to: C-W. Oh, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Alfred I. DuPont Hospital for Children, 1600 Rockland Road, Wilmington, DE 19899, USA
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, CW., Park, BC., Kyung, HS. et al. Percutaneous plating for unstable tibial fractures. J Orthop Sci 8, 166–169 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007760300028
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007760300028