Abstract.
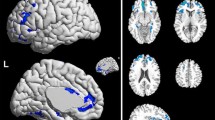
Using magnetoencephalography (MEG) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (f-MRI), we investigated the areas of the cerebral cortex that were activated when patients with brachial plexus injuries performed elbow flexion, a motion re-acquired through nerve transfer surgery. In all patients, elbow flexion on the operated side and on the unaffected side led to the activation of an area in the motor cortex, with these areas being located almost symmetrically on either side of the sagittal midline. These findings suggest that the activity center for the transferred intercostal nerves shifted to the motor cortex for the elbow, from the original intercostal nerve site.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: October 10, 2000 / Accepted: April 26, 2001
About this article
Cite this article
Iwase, Y., Mashiko, T., Ochiai, N. et al. Postoperative changes on functional mapping of the motor cortex in patients with brachial plexus injury: comparative study of magnetoencephalography and functional magnetic resonance imaging. J Orthop Sci 6, 397–402 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007760170005
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007760170005