Abstract
Background
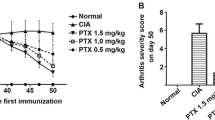
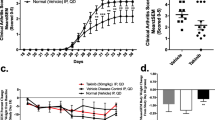
We have previously reported that recombinant human plasminogen-related protein B (rPRP-B), a putative 9-kDa protein that closely resembles the activation peptide of plasminogen, has shown significant inhibition of tumor growth through inhibition of angiogenesis. Based on recent reports suggesting a close relationship between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and angiogenesis, we hypothesized that this compound would regulate inflammatory conditions in RA. The present study therefore tested the effects of rPRP-B in the treatment of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) to elucidate the mechanisms underlying these effects.
Methods
DBA/1J mice immunized with type II collagen to induce CIA were monitored to assess the effects of rPRP-B on clinical severity of the disease. Pathological changes in joints, including vessel formation and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production, were examined histologically. Bone destruction was radiologically evaluated. In vitro studies on the effects of rPRP-B on cell proliferation and production of VEGF in interleukin (IL)-1β or basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)-stimulated human synoviocytes were also performed.
Results
Development of CIA was effectively inhibited by rPRP-B. Radiological examinations revealed that the protein reduced bone destruction in CIA. CIA-induced vessel formation and VEGF expression in vivo were also reduced. In vitro mechanistic studies demonstrated that rPRP-B affected human synoviocyte proliferation and VEGF production stimulated by IL-1β and bFGF.
Conclusions
Given the ability to effectively promote multistep anti-angiogenic activities, including cell growth inhibition and cytokine regulation, rPRP-B represents a promising candidate for a novel therapeutic agent against RA.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weissbach L, Treadwell BV. A plasminogen-related gene is expressed in cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;186:1108–14.
Morioka H, Weissbach L, Vogel T, Nielsen GP, Faircloth GT, Shao L, Hornicek FJ. Antiangiogenesis treatment combined with chemotherapy produces chondrosarcoma necrosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:1211–7.
Lewis VO, O’Reilly MS, Gehrmann M, Llinas M, Schaller J, Weissbach L. Inhibition of tumor growth by plasminogen-related protein-B. Anticancer Res. 2001;21:2287–91.
Morioka H, Morii T, Vogel T, Hornicek FJ, Weissbach L. Interaction of plasminogen-related protein B with endothelial and smooth muscle cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 2003;287:166–77.
Tateno T, Ichinose A. Expression of plasminogen-related gene B varies among normal tissues and increases in cancer tissues. FEBS Lett. 1999;445:31–5.
Sone H, Sakauchi M, Takahashi A, Suzuki H, Inoue N, Iida K, Shimano H, Toyoshima H, Kawakami Y, Okuda Y, Matsuo K, Yamada N. Elevated levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis correlation with disease activity. Life Sci. 2001;69:1861–9.
Salliot C, Dougados M, Gossec L. Risk of serious infections during rituximab, abatacept and anakinra treatments for rheumatoid arthritis: meta-analyses of randomised placebo-controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:25–32.
Lewis VO, Gehrmann M, Weissbach L, Hyman JE, Rielly A, Jones DG, Llinas M, Schaller J. Homologous plasminogen N-terminal and plasminogen-related gene A and B peptides: characterization of cDNAs and recombinant fusion proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1999;259:618–25.
Guo YL, Wang S, Colman RW. Kininostatin, an angiogenic inhibitor, inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:1427–33.
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J. Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell. 1997;88:277–85.
Rosloniec EF, Cremer M, Kang A, Myers LK. Collagen-induced arthlitis. In: Coligan JE, Kruisbeek AM, Argulies DH, Shevach EM, Strober W, editors. Current protocols in immunology. New York: Wiley; 2001. p. 15.5.1.
Hildner KM, Schirmacher P, Atreya I, Dittmayer M, Bartsch B, Galle PR, Wirtz S, Neurath MF. Targeting of the transcription factor STAT4 by antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotides suppresses collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2007;178:3427–36.
Chu CQ, Field M, Allard S, Abney E, Feldmann M, Maini RN. Detection of cytokines at the cartilage/pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: implications for the role of cytokines in cartilage destruction and repair. Br J Rheumatol. 1992;31:653–61.
Kurosaka D, Yoshida K, Yasuda J, Yokoyama T, Kingetsu I, Yamaguchi N, Joh K, Matsushima M, Saito S, Yamada A. Inhibition of arthritis by systemic administration of endostatin in passive murine collagen induced arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:677–9.
Choi ST, Kim JH, Seok JY, Park YB, Lee SK. Therapeutic effect of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor I antibody in the established collagen-induced arthritis mouse model. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28:333–7.
Morii T, Weissbach L. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and cell migration: resistance to angiogenesis inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;310:884–8.
Storgard CM, Stupack DG, Jonczyk A, Goodman SL, Fox RI, Cheresh DA. Decreased angiogenesis and arthritic disease in rabbits treated with an alphavbeta3 antagonist. J Clin Invest. 1999;103:47–54.
Wilder RL. Integrin alpha V beta 3 as a target for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and related rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 2002;61(Suppl2):96–9.
Jain RK. Tumor angiogenesis and accessibility: role of vascular endothelial growth factor. Semin Oncol. 2002;29:3–9.
Ferrara N. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol. 2002;29:10–4.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–76.
Nagashima M, Asano G, Yoshino S. Imbalance in production between vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:2339–42.
Bergers G, Hanahan D. Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:592–603.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance of Miyuki Murayama and Mizuho Kosuge. Financial support for this study was provided by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, K., Morii, T., Weissbach, L. et al. Treatment of collagen-induced arthritis with recombinant plasminogen-related protein B: a novel inhibitor of angiogenesis. J Orthop Sci 16, 443–450 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-011-0091-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-011-0091-x