Abstract
Background
Severe disability originating from feet generally requires surgery. In addition to a number of other techniques, triple arthrodesis is still used to treat deformity and instability unresponsive to conservative measures. The aim of this study was to evaluate the results of the triple arthrodesis operation in two groups of patients with different primary etiologies and to identify the possible factors affecting the results.
Methods
During a 4-year period, triple arthrodesis was performed on 25 feet in 20 patients (average age 24.9 years). These patients were divided into two groups according to the primary etiology of the disability: neurogenic and nonneurogenic. Patients were evaluated with pre-and postoperative clinical examinations, American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) Hindfoot and Ankle Scale, radiography, pedobarography, and a general health questionnaire (Short Form 36, SF-36). The need for orthotics and the effect of previous treatments on the end results were also evaluated.
Results
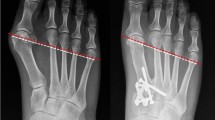
The preoperative average AOFAS score improved from 24 to 71 postoperatively. Preoperative AOFAS values of neurogenic cases were significantly lower than those of nonneurogenic cases. Postoperative AOFAS values were found to be lower in neurogenic cases (64.0 vs. 77.6). Marked improvement was observed for all angular measurements. No relation was found between the AOFAS, changes in angular measurements, and pre-and postoperative plantar pressure analysis results. SF-36 results improved postoperatively in both groups. Triple arthrodesis decreased the use of orthotics postoperatively in both groups. Previous treatments were not found to affect the end results in this series.
Conclusions
Triple arthrodesis operation is a surgical option with limited alternatives in patients with disabilities originating from feet. Both neurogenic and nonneurogenic patient groups improved significantly, and we were unable to show any significant differences in the results of these two groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Heus JA, Marti RK, Besselaar PP, Albers GH. The influence of subtalar and triple arthrodesis on the tibiotalar joint: a long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1997;79:644–647.
Pell RF, Myerson MS, Schon LC. Clinical outcome after primary triple arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000;82:47–57.
Angus PD, Cowell HR. Triple arthrodesis: a critical long-term review. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1986;68:260–265.
Bennett GL, Graham CE, Mauldin DM. Triple arthrodesis in adults. Foot Ankle 1991;12:138–143.
Bibbo C, Anderson RB, Davis WH. Complications of midfoot and hindfoot arthrodesis. Clin Orthop 2001;391:45–58.
Smith RW, Shen W, Dewitt S, Reischl SF. Triple arthrodesis in adults with non-paralytic disease: a minimum ten-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004;86:2707–2713.
Suckel A, Muller O, Herberts T, Langenstein P, Reize P, Wulker N. Talonavicular arthrodesis or triple arthrodesis: peak pressure in the adjacent joints measured in 8 cadaver specimens. Acta Orthop 2007;78:592–597.
Sangeorzan BJ, Smith D, Veith R, Hansen ST Jr. Triple arthrodesis using internal fixation in treatment of adult foot disorders. Clin Orthop 1993;294:299–307.
Saltzman CL, Fehrle MJ, Cooper RR, Spencer EC, Ponseti IV. Triple arthrodesis: twenty-five and forty-four-year average follow-up of the same patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1999;81:1391–1402.
Tenuta J, Shelton YA, Miller F. Long-term follow-up of triple arthrodesis in patients with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop 1993;13:713–716.
Mann DC, Hsu JD. Triple arthrodesis in the treatment of fixed cavovarus deformity in adolescent patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Foot Ankle 1992;13:1–6.
Azmaipairashvili Z, Riddle EC, Scavina M, Kumar SJ. Correction of cavovarus foot deformity in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Pediatr Orthop 2005;25:360–365.
Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M. Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int 1994;15:349–353.
Mäenpää H, Lehto MU, Belt EA. What went wrong in triple arthrodesis? An analysis of failures in 21 patients. Clin Orthop 2001;391:218–223.
Bednarz PA, Monroe MT, Manoli A 2nd. Triple arthrodesis in adults using rigid internal fixation: an assessment of outcome. Foot Ankle Int 1999;20:356–363.
Graves SC, Mann RA, Graves KO. Triple arthrodesis in older adults: results after long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1993;75:355–362.
Charles YP, Axt M, Doderlein L. Dynamic pedobarography in postoperative evaluation of pes cavovarus. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 2001;87:696–705.
Metaxiotis D, Accles W, Pappas A, Doederlein L. Dynamic pedobarography (DPB) in operative management of cavovarus foot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 2000;21:935–947.
Beischer AD, Brodsky JW, Pollo FE, Peereboom J. Functional outcome and gait analysis after triple or double arthrodesis. Foot Ankle Int 1999;20:545–553.
Wu WL, Huang PJ, Lin CJ, Chen WY, Huang KF, Cheng YM. Lower extremity kinematics and kinetics during level walking and stair climbing in subjects with triple arthrodesis or subtalar fusion. Gait Posture 2005;21:263–270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Daglar, B., Deveci, A., Delialioglu, O.M. et al. Results of triple arthrodesis: effect of primary etiology. J Orthop Sci 13, 341–347 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-008-1243-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-008-1243-5