Abstract
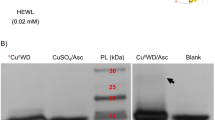
To design soluble artificial proteases that cleave peptide backbones of a wide range of proteins with high reactivity, artificial active sites comprising the Cu(II) complex of 1-oxa-4,7,10-triazacyclodedecane (oxacyclen) and the aldehyde group were synthesized. The aldehyde group was employed as the binding site in view of its ability to reversibly form imine bonds with ammonium groups exposed on the surfaces of proteins, and Cu(II) oxacyclen was exploited as the catalytic group for peptide hydrolysis. The artificial metalloproteases synthesized in the present study cleaved all of the protein substrates examined (albumin, γ-globulin, myoglobin, and lysozyme). In addition, the activity of the best soluble artificial protease was enhanced by up to 190-fold in terms of k cat/K m. When the temperature was raised to 80 °C, the activities of the artificial proteases were significantly enhanced. The activity of the artificial protease was not greatly affected by surfactants, including sodium dodecyl sulfate. The intermediacy of the imine complex formed between the artificial protease and the protein substrate was supported by an experiment using sodium cyanoborohydride. Soluble artificial metalloproteases with broad substrate selectivity, high reactivity, high thermal and chemical stabilities, and small molecular weights were thus synthesized by positioning the aldehyde group in proximity to Cu(II) oxacyclen.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cyclen:
-
1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane
- MALDI:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- Oxacyclen:
-
1-Oxa-4,7,10-triazacyclododecane
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- TOF:
-
Time-of-flight
References
Radzicka A, Wolfenden R (1996) J Am Chem Soc 118:6105–6109
Bryant RAR, Hansen DA (1998) J Am Chem Soc 120:8910–8913
Overall CM, Blobel CP (2007) Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:245–257
Rao MB, Tanksale AP, Ghatge MS, Deshpande VV (1998) Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:597–635
Kirby AJ (1980) Adv Phys Org Chem 17:183–278
Sutton PA, Buckingham DA (1987) Acc Chem Res 20:357–364
Suh J, Park TH, Hwang BK (1992) J Am Chem Soc 114:5141–5146
Chin J (1991) Acc Chem Res 24:145–152
Suh J (2003) Acc Chem Res 36:562–570
Chin J, Jubian V, Mrejen K (1990) J Chem Soc Chem Commun 1326–1328
Zhu L, Qin L, Parac TN, Kostic NM (1994) J Am Chem Soc 116:5218–5224
Hegg EL, Burstyn JN (1995) J Am Chem Soc 117:7015–7016
Jang BB, Lee KP, Min DH, Suh J (1998) J Am Chem Soc 120:12008–12016
Kaminskaia NV, Johnson TW, Kostic NM (1999) J Am Chem Soc 121:8663–8664
Saha MK, Bernal I (2003) J Chem Soc Chem Commun 612–613
Kasai M, Ravi RG, Shealy SJ, Grant KB (2004) Inorg Chem 43:6130–6132
Suh J, Hah SS (1980) J Am Chem Soc 120:10088–10093
Suh J, Oh SJ (2000) Org Chem 65:7534–7540
Oh S, Chang W, Suh J (2001) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11:1469–1472
Kim H, Paik H, Kim M, Chung YS, Suh J (2002) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12:2557–2560
Kim H, Kim M, Paik H, Chung Y-S, Hong IS, Suh J (2002) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12:3247–3250
Chei WS, Suh J (2007) In: Karlin KD (ed) Progress in inorganic chemistry, vol 55. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 79–142
Suh J, Chei WS (2008) Curr Opin Chem Biol 12:207–213
Lee TY, Suh J (2009) Chem Soc Rev 38:1949–1957
Suh J (1992) Acc Chem Res 25:273–279
Rana TM, Meares CF (1991) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10578–10582
Shepartz A, Cuenoud B (1990) J Am Chem Soc 112:3247–3249
Hoyer D, Cho H, Schultz PG (1990) J Am Chem Soc 112:3250–32449
Gallagher J, Zelenko O, Walts AD, Sigman DS (1998) Biochemistry 37:2096–2104
Suh J, Moon S-J (2001) Inorg Chem 40:4890–4895
Moon SJ, Jeon JW, Kim H, Suh MP, Suh J (2000) J Am Chem Soc 122:7742–7749
Yoo CE, Chae PS, Kim JE, Jeong EJ, Suh J (2003) J Am Chem Soc 125:14580–14589
Milovic NM, Badjic JD, Kostic NM (2004) J Am Chem Soc 126:696–697
Yang G, Miao R, Li Y, Hong J, Zhao C, Guo Z, Zhu L (2005) Dalton Trans 1613–1619
Jitsukawa K, Mabuchi T, Einaga H, Masuda H (2006) Eur J Inorg Chem 21:4254–4263
Yashiro M, Kawakami Y, Taya J, Arai S, Fujii Y (2009) Chem Commun 1544–1546
Rajković S, Glisić BD, Zivković MD, Djuran MI (2009) Bioorg Chem 37:173–179
Yoo SH, Lee BJ, Kim H, Suh J (2005) J Am Chem Soc 127:9593–9602
Jang SW, Suh J (2008) Org Lett 10:481–484
Bodwell CE, McClain PE (1971) In: Price JF, Schweigert BS (eds) The science of meat and meat products, 2nd edn. WH Freeman, San Francisco, p 97
Lameli UK (1970) Nature 227:680–685
Hames BD (1990) Chapter 1. In: Hames, BD, Rickwood D (eds) Gel electrophoresis of proteins. IRL, New York
Amorim MTS, Chaves S, Delgado R, Fraústo da Silva JJR (1991) J Chem Soc Dalton Trans 3065–3072
Suckau D, Resemann A, Schuerenberg M, Hufnagel P, Franzen J, Holl A (2003) Anal Bioanal Chem 376:952–965
Jeon JW, Son SJ, Yoo CE, Hong IS, Song JB, Suh J (2002) Org Lett 4:4155–4158
Jeon JW, Son SJ, Yoo CE, Hong IS, Suh J (2003) Bioorg Med Chem 11:2901–2910
Polgár L (1989) Mechanisms of protease action. CRC, Boca Raton
Borch RF, Bernstein MD, Durst HD (1971) J Am Chem Soc 93:2897–2904
Michaux C, Pomroy NC, Privé GG (2008) J Mol Biol 375:1477–1488
Fujie T (2002) Chem Rev 102:4885–4906
Taguchi H, Planque S, Sapparapu G, Boivin S, Hara M, Nishiyama Y, Paul S (2008) J Biol Chem 283:36724–36733
Varadarajan N, Rodriguez S, Hwang B-Y, Georgiou G, Iverson BL (2008) Nat Chem Biol 4:290–294
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MEST) (No. 2009-0072151). This paper is dedicated to the memory of the late Prof. Chi Sun Hahn.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.G., Yoo, S.H., Chei, W.S. et al. Soluble artificial metalloproteases with broad substrate selectivity, high reactivity, and high thermal and chemical stabilities. J Biol Inorg Chem 15, 1023–1031 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-010-0662-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-010-0662-x