Abstract:
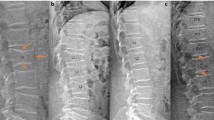
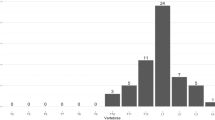
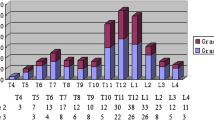
The most typical fracture that occurs in osteoporotic patients is a vertebral fracture, whereas hip fractures are thought to occur in the most severe osteoporotic patients. The purpose of this study was to compare the degree of osteoporosis between patients with vertebral fractures and patients with hip fracture by examining bone mineral density, biochemical markers of bone metabolism, and the incidence of vertebral fractures. Subjects were 50 female patients with vertebral fractures (VX) and 60 female patients with hip fracture (HX). Bone mineral densities (BMD) of the lumbar spine, femoral neck (Neck), and one-third of the radius were determined by DXA. Total and bone alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin, N-MID osteocalcin, PICP, free deoxypyridinoline, and CTx were measured. All z-scores of BMD in the three areas of VX and HX patients were negative, meaning those BMDs were lower in VX and HX than a decade-matched normal reference. The z-score of Neck BMD was significantly lower in HX than in VX. Deoxypyridinoline and CTx were significantly higher in HX than in VX. N-MID osteocalcin was significantly lower in HX than in VX. VX and HX patients were divided into four subgroups according to the number of their vertebral fractures: VX, with a single fracture; VX, with multiple fractures; HX, without vertebral fractures; and HX, with vertebral fractures. VX with multiple fractures and HX with vertebral fractures had lower z-scores at all skeletal sites. HX with vertebral fractures had the lowest median z-score at spine and Neck, whereas HX without vertebral fractures had a low z-score only at Neck compared to VX with a single fracture. There was no significant difference in markers among the subgroups. The number of vertebral fractures was negatively correlated with z-scores of BMD at all three sites. We concluded that uncoupling between bone formation and resorption is greater in hip fractures than in vertebral fractures. Vertebral fractures are associated with general osteopenia of the total skeleton. We suggest that there are two types of osteoporosis in patients with hip fractures: one is that the bone mass of the femoral neck is specifically reduced, and the other is a terminal stage of osteoporosis which follows osteoporosis with vertebral fractures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: Aug. 24, 1998 / Accepted: Dec. 4, 1998
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, M., Kushida, K. & Naitou, K. The degree of osteoporosis in patients with vertebral fracture and patients with hip fracture: Relationship to incidence of vertebral fracture. J Bone Miner Metab 17, 187–194 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007740050083
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007740050083