Abstract
Introduction
Human umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs (hUC-MSCs) have the potential to differentiate into osteoblasts. This study investigated the function and potential mechanisms of a novel lncRNA LINC02381 in hUC-MSC osteogenic differentiation.
Materials and methods
hUC-MSCs were maintained in osteogenic differentiation medium. RT-qPCR assay was performed to assess LINC02381 expression. Alizarin Red S (ARS) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining were performed to evaluate osteogenic differentiation. The interaction between miR-21 and LINC0238/KLF12 was determined by luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay was used to confirm the transcriptional regulation of KLF12 on Wnt4 promoter. The nuclear translocation of β-catenin was evaluated using immunofluorescence. hUC-MSCs seeded on Bio-Oss Collagen scaffolds were transplanted into nude mice to assess in vivo osteogenesis. Bone formation was observed by H&E and Masson's trichrome staining. OSX and OPN levels were assessed by immunohistochemistry.
Results
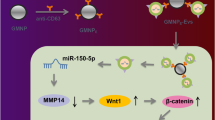
LINC02381 was up-regulated in the clinical samples of osteoporotic patients. However, LINC02381 expression was reduced during osteogenic differentiation of hUC-MSCs. Enforced expression of LINC02381 suppressed the osteogenic differentiation of hUC-MSCs. Mechanistically, LINC02381 sponged miR-21 to enhance KLF12 expression, which led to the inactivation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Furthermore, miR-21 mimics or KLF12 silencing counteracted LINC02381-induced inhibition of osteogenic differentiation, whereas IWP-4 (an inhibitor of Wnt pathway) abolished this effect.
Conclusion
In summary, LINC02381 repressed osteogenic differentiation of hUS-MSCs through sponging miR-21 to enhance KLF12-mediated inactivation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway, indicating that LINC02381 might be a therapeutic target for osteoporosis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- hUC-MSCs:
-
Human umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs
- lncRNAs:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- sh-LINC02381:
-
ShRNA targeting LINC02381
- KLF12:
-
Kruppel-like factor 12
- sh-KLF12:
-
ShRNA targeting KLF12
- sh-NC:
-
Negative control shRNA
- ARS:
-
Alizarin red staining
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- RUNX2:
-
Runt-related transcription factor 2
- OPN:
-
Osteopontin
- OSX:
-
Osterix
- WT:
-
Wild type
- MUT:
-
Mutant
- RIP:
-
RNA immunoprecipitation
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
References
Yang L, Li Y, Gong R, Gao M, Feng C et al (2019) The long non-coding RNA-ORLNC1 regulates bone mass by directing mesenchymal stem cell fate. Mol Ther 27:394–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.11.019
Tang P, Xiong Q, Ge W, Zhang L (2014) The role of microRNAs in osteoclasts and osteoporosis. RNA Biol 11:1355–1363. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2014.996462
Ko NY, Chen LR, Chen KH (2020) The role of micro RNA and long-non-coding RNA in osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144886
Mora-Raimundo P, Lozano D, Manzano M, Vallet-Regi M (2019) Nanoparticles to knockdown osteoporosis-related gene and promote osteogenic marker expression for osteoporosis treatment. ACS Nano 13:5451–5464. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b00241
Griffin M, Iqbal SA, Bayat A (2011) Exploring the application of mesenchymal stem cells in bone repair and regeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93:427–434. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.93B4.25249
Bougioukli S, Saitta B, Sugiyama O, Tang AH, Elphingstone J, Evseenko D, Lieberman JR (2019) Lentiviral gene therapy for bone repair using human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Hum Gene Ther 30:906–917. https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2018.054
Wang Y, You C, Wei R, Zu J, Song C, Li J, Yan J (2017) Modification of human umbilical cord blood stem cells using polyethylenimine combined with modified TAT peptide to enhance BMP-2 production. Biomed Res Int 2017:2971413. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2971413
Hong B, Lee S, Shin N, Ko Y, Kim D, Lee J, Lee W (2018) Bone regeneration with umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in femoral defects of ovariectomized rats. Osteoporos Sarcopenia 4:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afos.2018.08.003
Antebi B, Pelled G, Gazit D (2014) Stem cell therapy for osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep 12:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-013-0184-x
Xiao T, Liu L, Li H, Sun Y, Luo H, Li T, Wang S, Dalton S, Zhao RC, Chen R (2021) Long noncoding RNA ADINR regulates adipogenesis by transcriptionally activating C/EBPalpha. Stem Cell Rep 16:1006–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.03.024
Zhang J, Jiang T, Liang X, Shu S, Xiang X, Zhang W, Guo T, Xie W, Deng W, Tang X (2019) lncRNA MALAT1 mediated high glucose-induced HK-2 cell epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and injury. J Physiol Biochem 75:443–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-019-00688-2
Xu Q, Cheng D, Liu Y, Pan H, Li G, Li P, Li Y, Sun W, Ma D, Ni C (2021) LncRNA-ATB regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression in pulmonary fibrosis via sponging miR-29b-2-5p and miR-34c-3p. J Cell Mol Med 25:7294–7306. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16758
Han Y, Kang C, Kang M, Quan W, Gao H, Zhong Z (2019) Long non-coding RNA Mirt2 prevents TNF-alpha-triggered inflammation via the repression of microRNA-101. Int Immunopharmacol 76: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105878
Liu J, Wu M, Feng G, Li R, Wang Y, Jiao J (2020) Downregulation of LINC00707 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrowderived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating DKK1 via targeting miR103a3p. Int J Mol Med 46:1029–1038. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2020.4672
Jin C, Jia L, Tang Z, Zheng Y (2020) Long non-coding RNA MIR22HG promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via PTEN/ AKT pathway. Cell Death Dis 11:601. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02813-2
Jafarzadeh M, Soltani BM, Soleimani M, Hosseinkhani S (2020) Epigenetically silenced LINC02381 functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Biochimie 171–172:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2020.02.009
Chen X, Zhang Z, Ma Y, Su H, Xie P, Ran J (2020) LINC02381 promoted cell viability and migration via targeting miR-133b in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Manag Res 12:3971–3979. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S237285
Yang SE, Ha CW, Jung M, Jin HJ, Lee M, Song H, Choi S, Oh W, Yang YS (2004) Mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells developed in cultures from UC blood. Cytotherapy 6:476–486. https://doi.org/10.1080/14653240410005041
Cao L, Liu W, Zhong Y, Zhang Y, Gao D, He T, Liu Y, Zou Z, Mo Y, Peng S, Shuai C (2020) Linc02349 promotes osteogenesis of human umbilical cord-derived stem cells by acting as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-25-3p and miR-33b-5p. Cell Prolif 53: https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12814
Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan CW, Wei S, Hao W, Kilgore J, Williams NS, Roth MG, Amatruda JF, Chen C, Lum L (2009) Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol 5:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.137
Xiaoling G, Shuaibin L, Kailu L (2020) MicroRNA-19b-3p promotes cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by interacting with lncRNA H19. BMC Med Genet 21:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-020-0948-y
Vescini F, Attanasio R, Balestrieri A, Bandeira F, Bonadonna S et al (2016) Italian association of clinical endocrinologists (AME) position statement: drug therapy of osteoporosis. J Endocrinol Investig 39:807–834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0434-8
Mi B, Yan C, Xue H, Chen L, Panayi AC, Hu L, Hu Y, Cao F, Sun Y, Zhou W, Xiong Y, Liu G (2020) Inhibition of circulating miR-194-5p reverses osteoporosis through Wnt5a/beta-catenin-dependent induction of osteogenic differentiation. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 21:814–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.07.023
Feng L, Zhang JF, Shi L, Yang ZM, Wu TY, Wang HX, Lin WP, Lu YF, Lo JHT, Zhu DH, Li G (2020) MicroRNA-378 suppressed osteogenesis of MSCs and impaired bone formation via inactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 21:1017–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.07.018
Wei F, Liu D, Feng C, Zhang F, Yang S, Hu Y, Ding G, Wang S (2015) microRNA-21 mediates stretch-induced osteogenic differentiation in human periodontal ligament stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 24:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2014.0191
Meng YB, Li X, Li ZY, Zhao J, Yuan XB, Ren Y, Cui ZD, Liu YD, Yang XJ (2015) microRNA-21 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by the PI3K/beta-catenin pathway. J Orthop Res 33:957–964. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.22884
Sun X, Li X, Qi H, Hou X, Zhao J, Yuan X, Ma X (2020) MiR-21 nanocapsules promote early bone repair of osteoporotic fractures by stimulating the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Transl 24:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jot.2020.04.007
Wu T, Wang S, Wang L, Zhang W, Chen W, Lv X, Li Y, Hussain Z, Sun W (2020) Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) CTTN-IT1 elevates skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by acting as ceRNA for YAP1 through absorbing miR-29a in Hu sheep. Front Genet 11:843. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00843
Zhang L, Xie H, Li S (2020) LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 controls osteogenic and adipocytic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis through regulating the miR-196a-5p/Hmga2 axis. J Bone Miner Metab. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-020-01123-z
Wu D, Yin L, Sun D, Wang F, Wu Q, Xu Q, Xin B (2020) Long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cell through sponging microRNA-222-3p to negatively regulate Smad2/7. Arch Oral Biol 117: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104814
Yan Q, Yan G, Zhang C, Wang Z, Huang C, Wang J, Zhou J, Liu Y, Ding L, Zhang Q, Zhen X, Jiang Y, Sun H (2019) miR-21 reverses impaired decidualization through modulation of KLF12 and NR4A1 expression in human endometrial stromal cellsdagger. Biol Reprod 100:1395–1405. https://doi.org/10.1093/biolre/ioz026
Takai H, van Wijnen AJ, Ogata Y (2019) Induction of chondrogenic or mesenchymal stem cells from human periodontal ligament cells through inhibition of Twist2 or Klf12. J Oral Sci 61:313–320. https://doi.org/10.2334/josnusd.18-0224
Yang C, Wang C, Zhou J, Liang Q, He F, Li F, Li Y, Chen J, Zhang F, Han C, Liu J, Li K, Tang Y (2020) Fibronectin 1 activates WNT/beta-catenin signaling to induce osteogenic differentiation via integrin beta1 interaction. Lab Investig. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-020-0451-2
Shen J, Sun Y, Liu X, Zhu Y, Bao B, Gao T, Chai Y, Xu J, Zheng X (2021) EGFL6 regulates angiogenesis and osteogenesis in distraction osteogenesis via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther 12:415. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02487-3
Huang Y, Xiao D, Huang S, Zhuang J, Zheng X, Chang Y, Yin D (2020) Circular RNA YAP1 attenuates osteoporosis through up-regulation of YAP1 and activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 129: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110365
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Kunming Medical University Applied Basic Research Joint Special Fund Project [2017FE468(-060)]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
(1) JS made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; W-DL, HT and YY the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data; FL the creation of new software used in the work; (2) H-BC and HT drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content; (3) L-MG and J-JM approved the version to be published; (4) GZ agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The experimental procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. All subjects provided written informed consents. All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethical Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
774_2021_1277_MOESM1_ESM.tif
(A) The effects of LINC02381 overexpression on theTCF/LEF reporter activity. (B) The KLF12 binding sites in the Wnt4 promoter. **p <0.01. (TIF 1731 kb)
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Luo, WD., Yuan, Y. et al. LINC02381, a sponge of miR-21, weakens osteogenic differentiation of hUC-MSCs through KLF12-mediated Wnt4 transcriptional repression. J Bone Miner Metab 40, 66–80 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-021-01277-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-021-01277-4