Abstract
Introduction
To investigate the role of LncRNA PVT1 (plasmacytoma variant translocation 1) in hyperglycemia-triggered cartilage damage using the diabetic osteoarthritis (OA) mice model.
Materials and methods
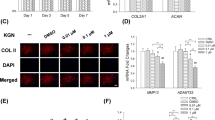
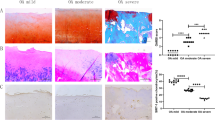
Streptozotocin (STZ) was used to induce mouse diabetes. Knee OA model was induced through transection of anterior cruciate ligament (ACLT). Severity of arthritis was assessed histologically by Safranin O-Fast Green Staining using Mankin Scores. LncRNA PVT1 and miR-146a were detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in cartilage tissue. Moreover, the interaction among PVT1, miR-146a, and SMAD4 was examined by luciferase reporter assays. Mice were injected intra-articularly with ad-siRNA-PVT1 and ad-siRNA scramble control. Articular concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6 and TGF-β1 were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Levels of type II Collagen (COL2A1), TGF-β1, p-SMAD2, SMAD2, p-SMAD3, SMAD3, SMAD4 and nuclear SMAD4 were detected by western blot analysis.
Results
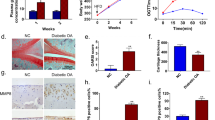
PVT1 expression was significantly increased, whereas miR-146a was markedly decreased in diabetic OA mice than in non-diabetic OA and control. Increased PVT1 expression in diabetic OA mice was significantly associated with Mankin score and reduced miR-146a as well as Collagen alpha-1(II) (COL2A1) expressions. In vivo, intra-articular injection of ad-siRNA-PVT1 efficiently increased miR-146a and COL2A1 expressions, alleviated joint inflammation, decreased the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators, and suppressed TGF-β/SMAD4 pathway in diabetic OA mice.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrate LncRNA PVT1 is involved in cartilage degradation in diabetic OA and correlated with disease severity. Efficiency of ad-siRNA-PVT1 in controlling joint inflammation in diabetic OA mice is associated with the suppression of the expression of miR-146a, pro-inflammatory cytokines and activation of TGF-β/SMAD4 pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van den Bussche H, Koller D, Kolonko T, Hansen H et al (2011) Which chronic diseases and disease combinations are specific to multimorbidity in the elderly? Results of a claims data based cross-sectional study in Germany. BMC Public Health 11:101
Kalra S, Dutta D (2019) The diabetic knee. J Pak Med Assoc 69:1568–1569
Louati K, Vidal C, Berenbaum F et al (2015) Association between diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis: systematic literature review and meta-analysis. RMD Open 1:e000077
Mueller MJ (2016) Musculoskeletal impairments are often unrecognized and underappreciated complications from diabetes. Phys Therapy Sport 96:1861–1864
Alikhani M, Alikhani Z, Boyd C et al (2007) Advanced glycation end products stimulate osteoblast apoptosis via the MAP kinase and cytosolic apoptotic pathways. Bone 40:345–353
Birney E, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A et al (2007) Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the encode pilot project. Nature 447:799–816
Wang KC, Chang HY (2011) Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell 43:904–914
Boloix A, Masanas M, Jiménez C et al (2019) Long Non-coding RNA PVT1 as a prognostic and therapeutic target in pediatric cancer. Front Oncol 9:1173
Bao X, Duan J, Yan Y et al (2017) Upregulation of long noncoding RNA PVT1 predicts unfavorable prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark 21:55–63
Zhan J, Hu P, Wang Y (2019) LncRNA PVT1 aggravates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting the miR-187-3p/AGO1 axis. Mol Cell Probes 28:101490
Alwohhaib M, Alwaheeb S, Alyatama N et al (2014) Single nucleotide polymorphisms at erythropoietin, superoxide dismutase 1, splicing factor, arginine/serin-rich 15 and plasmacytoma variant translocation genes association with diabetic nephropathy. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 25:577–81
Liu DW, Zhang JH, Liu FX et al (2019) Silencing of long noncoding RNA PVT1 inhibits podocyte damage and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy by upregulating FOXA1. Exp Mol Med 51:88
Li Y, Li S, Luo Y et al (2017) LncRNA PVT1 regulates chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by acting as a sponge for miR-488-3p. DNA Cell Biol 36:571–580
Marques-Rocha JL, Samblas M, Milagro FI et al (2015) Noncoding RNAs, cytokines, and inflammation-related diseases. FASEB J. 29:3595–611
Guan YJ, Li J, Yang X et al (2018) Evidence that miR-146a attenuates aging- and trauma-induced osteoarthritis by inhibiting Notch 1, IL-6, and IL-1 mediated catabolism. Aging Cell 17:e12752
Yang M, Ye L, Wang B et al (2015) Decreased miR-146 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is correlated with ongoing islet autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes patients 1miR-146. J Diabetes 7:158–165
Liu XS, Fan B, Szalad A et al (2017) MicroRNA-146a mimics reduce the peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetic mice. Diabetes 66:3111–3121
Hata Akiko, Chen Ye-Guang (2016) TGF-β Signaling from receptors to Smads. Cold Spring HarbPerspect Biol 8:a022061
Shi Y, Massague J (2003) Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell 113:685–700
Zhai G, Doré J, Rahman P et al (2015) TGF-β signal transduction pathways and osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int 35:1283–1292
Moldovan F, Pelletier JP, Hambor J et al (1997) Collagenase-3 (matrix metalloprotease 13) is preferentially localized in the deep layer of human arthritic cartilage in situ: in vitro mimicking effect by transforming growth factor beta. Arthritis Rheum 40:1653–1661
Cao F, Li Z, Ding WM et al (2019) LncRNA PVT1 regulates atrial fibrosis via miR-128-3p-SP1-TGF-β1-Smad axis in atrial fibrillation. Mol Med 25:7
van der Sluijs JA, Geesink RG, van der Linden AJ et al (1992) The reliability of the Mankin score for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res 10:58–61
Ding LB, Li Y, Liu GY et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA PVT1, a molecular sponge of miR-26b, is involved in the progression of hyperglycemia-induced collagen degradation in human chondrocytes by targeting CTGF/TGF-β signal ways. Innate Immun 26:204–214
Jiang Z, Lu W, Zeng Q et al (2018) High glucose-induced excessive reactive oxygen species promote apoptosis through mitochondrial damage in rat cartilage endplate cells. J Orthop Res 36:2476–2483
Xing Dan, Liang Jin-qian, Li Yan et al (2014) Identification of long noncoding RNA associated with osteoarthritis in humans. Orthop Surg 6:288–293
Leti F, DiStefano JK (2017) Long Noncoding RNAs as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes and related complications. Genes 8:207
Swingler TE, Niu L, Smith P et al (2019) The function of microRNAs in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 120:40–47
Vasu S, Kumano K, Darden CM et al (2019) MicroRNA Signatures as future biomarkers for diagnosis of diabetes states. Cells 8:e1533
Tang LP, Ding JB, Liu ZH et al (2018) LncRNA TUG1 promotes osteoarthritis-induced degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-195/MMP-13 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:8574–8581
Zhu YJ, Jiang DM (2019) LncRNA PART1 modulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via regulating miR-373-3p/SOX4 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:8175–8185
Wang T, He C (2018) Pro-inflammatory cytokines: the link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 44:38–50
Luo S, Shi Q, Chen J et al (2019) Expression and significance of MMPs in synovial fluid, serum and PBMC culture supernatant stimulated by LPS in osteoarthritis patients with or without diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 127:195–202
Khoury M, Louis-Plence P, Escriou V et al (2006) Efficient new cationic liposome formulation for systemic delivery of small interfering RNA silencing tumor necrosis factor alpha in experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54:1867–1877
Inoue A, Takahashi KA, Mazda O et al (2005) Electro-transfer of small interfering RNA ameliorated arthritis in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:903–908
Ventura A, Meissner A, Dillon CP et al (2004) Adenovirus-delivered siRNA. Methods Mol Biol 252:523–532
Funding
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant Number 2016A030313100), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 81601219), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Numbers 2015M582480 and 2017T100660), Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (A2019100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YZ., Yao-Li, Liang, SK. et al. LncPVT1 promotes cartilage degradation in diabetic OA mice by downregulating miR-146a and activating TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling. J Bone Miner Metab 39, 534–546 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-020-01199-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-020-01199-7