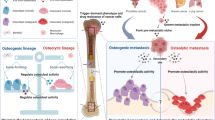
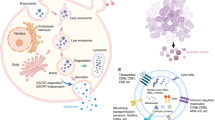
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are phospholipid membrane-enclosed entities containing specific proteins, RNA, miRNA, and lncRNA. EVs are released by various cells and play a vital role in cell communication by transferring their contents from the host cells to the recipient cells. The role of EVs has been characterized in a wide range of physiological and pathophysiological processes. In this context, we highlight recent advances in our understanding of the regulatory effects of EVs, with a focus on bone metabolism and the bone microenvironment. The roles of EVs in cell communication among bone-related cells, stem cells, tumor cells, and other cells under physiological or pathological conditions are also discussed. In addition, promising applications for EVs in treating bone-related diseases are proposed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qin Y, Sun R, Wu C, Wang L, Zhang C (2016) Exosome: a novel approach to stimulate bone regeneration through regulation of osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 17:712. doi:10.3390/ijms17050712
Nolte-’t Hoen E, Cremer T, Gallo RC, Margolis LB (2016) Extracellular vesicles and viruses: are they close relatives?. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:9155–9161. doi:10.1073/pnas.1605146113
Morhayim J, Baroncelli M, van Leeuwen JP (2014) Extracellular vesicles: specialized bone messengers. Arch Biochem Biophys 561:38–45. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2014.05.011
Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Meldolesi J (2009) Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol 19:43–51. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2008.11.003
Simons M, Raposo G (2009) Exosomes–vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:575–581. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007
Hristov M, Erl W, Linder S, Weber PC (2004) Apoptotic bodies from endothelial cells enhance the number and initiate the differentiation of human endothelial progenitor cells in vitro. Blood 104:2761–2766. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-10-3614
Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, Cantaluppi V, Biancone L (2010) Exosomes/microvesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication. Kidney Int 78:838–848. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.278
van der Pol E, Boing AN, Harrison P, Sturk A, Nieuwland R (2012) Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev 64:676–705. doi:10.1124/pr.112.005983
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:654–659. doi:10.1038/ncb1596
Hannafon BN, Carpenter KJ, Berry WL, Janknecht R, Dooley WC, Ding WQ (2015) Exosome-mediated microRNA signaling from breast cancer cells is altered by the anti-angiogenesis agent docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Mol Cancer 14:133. doi:10.1186/s12943-015-0400-7
Shurtleff MJ, Temoche-Diaz MM, Karfilis KV, Ri S, Schekman R (2016) Y-box protein 1 is required to sort microRNAs into exosomes in cells and in a cell-free reaction. eLife. doi:10.7554/eLife.19276
Nakamachi Y, Kawano S, Takenokuchi M, Nishimura K, Sakai Y, Chin T, Saura R, Kurosaka M, Kumagai S (2009) MicroRNA-124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 60:1294–1304. doi:10.1002/art.24475
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H, Spector DL (2009) Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev 23:1494–1504. doi:10.1101/gad.1800909
Sims NA, Walsh NC (2012) Intercellular cross-talk among bone cells: new factors and pathways. Curr Osteoporos Rep 10:109–117. doi:10.1007/s11914-012-0096-1
Chiu YH, Ritchlin CT (2016) DC-STAMP: a key regulator in osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Physiol 231:2402–2407. doi:10.1002/jcp.25389
Deng L, Wang Y, Peng Y, Wu Y, Ding Y, Jiang Y, Shen Z, Fu Q (2015) Osteoblast-derived microvesicles: a novel mechanism for communication between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Bone 79:37–42. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2015.05.022
Bronisz A, Godlewski J, Chiocca EA (2016) Extracellular vesicles and microRNAs: their role in tumorigenicity and therapy for brain tumors. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36:361–376. doi:10.1007/s10571-015-0293-4
Kosaka N, Yoshioka Y, Fujita Y, Ochiya T (2016) Versatile roles of extracellular vesicles in cancer. J Clin Investig 126:1163–1172. doi:10.1172/JCI81130
Ciardiello C, Cavallini L, Spinelli C, Yang J, Reis-Sobreiro M, de Candia P, Minciacchi VR, Di Vizio D (2016) Focus on extracellular vesicles: new frontiers of cell-to-cell communication in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 17:175. doi:10.3390/ijms17020175
Lopatina T, Gai C, Deregibus MC, Kholia S, Camussi G (2016) Cross talk between cancer and mesenchymal stem cells through extracellular vesicles carrying nucleic acids. Front Oncol 6:125. doi:10.3389/fonc.2016.00125
Desrochers LM, Antonyak MA, Cerione RA (2016) Extracellular vesicles: satellites of information transfer in cancer and stem cell biology. Dev Cell 37:301–309. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2016.04.019
Kramer-Albers EM, Hill AF (2016) Extracellular vesicles: interneural shuttles of complex messages. Curr Opin Neurobiol 39:101–107. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2016.04.016
Zappulli V, Friis KP, Fitzpatrick Z, Maguire CA, Breakefield XO (2016) Extracellular vesicles and intercellular communication within the nervous system. J Clin Investig 126:1198–1207. doi:10.1172/JCI81134
Teixeira JH, Silva AM, Almeida MI, Barbosa MA, Santos SG (2016) Circulating extracellular vesicles: their role in tissue repair and regeneration. Transfus Apheresis Sci 55:53–61. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2016.07.015
Koniusz S, Andrzejewska A, Muraca M, Srivastava AK, Janowski M, Lukomska B (2016) Extracellular vesicles in physiology, pathology, and therapy of the immune and central nervous system, with focus on extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutic tools. Front Cell Neurosci 10:109. doi:10.3389/fncel.2016.00109
Robbins PD, Dorronsoro A, Booker CN (2016) Regulation of chronic inflammatory and immune processes by extracellular vesicles. J Clin Investig 126:1173–1180. doi:10.1172/JCI81131
Merino-Gonzalez C, Zuniga FA, Escudero C, Ormazabal V, Reyes C, Nova-Lamperti E, Salomon C, Aguayo C (2016) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote angiogenesis: potencial clinical application. Front Physiol 7:24. doi:10.3389/fphys.2016.00024
Kinoshita T, Yip KW, Spence T, Liu FF (2017) MicroRNAs in extracellular vesicles: potential cancer biomarkers. J Hum Genet 62:67–74. doi:10.1038/jhg.2016.87
Gillet V, Hunting DJ, Takser L (2016) Turing revisited: decoding the microRNA messages in brain extracellular vesicles for early detection of neurodevelopmental disorders. Curr Environ Health Rep 3:188–201. doi:10.1007/s40572-016-0093-0
Vader P, Mol EA, Pasterkamp G, Schiffelers RM (2016) Extracellular vesicles for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 106:148–156. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2016.02.006
Anderson HC, Garimella R, Tague SE (2005) The role of matrix vesicles in growth plate development and biomineralization. Front Biosci: J Virtual Libr 10:822–837
Nahar NN, Missana LR, Garimella R, Tague SE, Anderson HC (2008) Matrix vesicles are carriers of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and noncollagenous matrix proteins. J Bone Miner Metab 26:514–519. doi:10.1007/s00774-008-0859-z
Proff P, Romer P (2009) The molecular mechanism behind bone remodelling: a review. Clin Oral Investig 13:355–362. doi:10.1007/s00784-009-0268-2
Ge M, Ke R, Cai T, Yang J, Mu X (2015) Identification and proteomic analysis of osteoblast-derived exosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 467:27–32. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.09.135
Valenti MT, Dalle Carbonare L, Mottes M (2016) Hypophosphatasia and mesenchymal stem cells: a therapeutic promise. Int J Stem Cell Res Ther 3:1–3. doi:10.3390/ijms18010041
Cui Y, Luan J, Li H, Zhou X, Han J (2016) Exosomes derived from mineralizing osteoblasts promote ST2 cell osteogenic differentiation by alteration of microRNA expression. FEBS Lett 590:185–192. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.12024
Morhayim J, van de Peppel J, Demmers JA, Kocer G, Nigg AL, van Driel M, Chiba H, van Leeuwen JP (2015) Proteomic signatures of extracellular vesicles secreted by nonmineralizing and mineralizing human osteoblasts and stimulation of tumor cell growth. FASEB J 29:274–285. doi:10.1096/fj.14-261404
Morhayim J, van de Peppel J, Braakman E, Rombouts EW, Ter Borg MN, Dudakovic A, Chiba H, van der Eerden BC, Raaijmakers MH, van Wijnen AJ, Cornelissen JJ, van Leeuwen JP (2016) Osteoblasts secrete miRNA-containing extracellular vesicles that enhance expansion of human umbilical cord blood cells. Sci Rep 6:32034. doi:10.1038/srep32034
Nair R, Santos L, Awasthi S, von Erlach T, Chow LW, Bertazzo S, Stevens MM (2014) Extracellular vesicles derived from preosteoblasts influence embryonic stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells Dev 23:1625–1635. doi:10.1089/scd.2013.0633
Burgess TL, Qian Y, Kaufman S, Ring BD, Van G, Capparelli C, Kelley M, Hsu H, Boyle WJ, Dunstan CR, Hu S, Lacey DL (1999) The ligand for osteoprotegerin (OPGL) directly activates mature osteoclasts. J Cell Biol 145:527–538
Huynh N, VonMoss L, Smith D, Rahman I, Felemban MF, Zuo J, Rody WJ Jr, McHugh KP, Holliday LS (2016) Characterization of regulatory extracellular vesicles from osteoclasts. J Dent Res 95:673–679. doi:10.1177/0022034516633189
Shapiro IM, Landis WJ, Risbud MV (2015) Matrix vesicles: are they anchored exosomes?. Bone 79:29–36. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2015.05.013
Kagiya T, Taira M (2013) Expression of microRNAs in the extracellular microvesicles of murine osteoclasts. J Oral Tissue Eng 10:142–150
Kagiya T, Nakamura S (2013) Expression profiling of microRNAs in RAW264.7 cells treated with a combination of tumor necrosis factor alpha and RANKL during osteoclast differentiation. J Periodontal Res 48:373–385. doi:10.1111/jre.12017
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH, Yang BB (2007) MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:20350–20355. doi:10.1073/pnas.0706901104
Fasanaro P, Greco S, Lorenzi M, Pescatori M, Brioschi M, Kulshreshtha R, Banfi C, Stubbs A, Calin GA, Ivan M, Capogrossi MC, Martelli F (2009) An integrated approach for experimental target identification of hypoxia-induced miR-210. J Biol Chem 284:35134–35143. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.052779
Tsuchiya S, Fujiwara T, Sato F, Shimada Y, Tanaka E, Sakai Y, Shimizu K, Tsujimoto G (2011) MicroRNA-210 regulates cancer cell proliferation through targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 (FGFRL1). J Biol Chem 286:420–428. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.170852
Sugatani T, Hruska KA (2007) MicroRNA-223 is a key factor in osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Biochem 101:996–999. doi:10.1002/jcb.21335
Papaioannou G, Inloes JB, Nakamura Y, Paltrinieri E, Kobayashi T (2013) let-7 and miR-140 microRNAs coordinately regulate skeletal development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E3291–E3300. doi:10.1073/pnas.1302797110
Shi K, Lu J, Zhao Y, Wang L, Li J, Qi B, Li H, Ma C (2013) MicroRNA-214 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblast cells by targeting Osterix. Bone 55:487–494. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.04.002
Wang X, Guo B, Li Q, Peng J, Yang Z et al (2013) miR-214 targets ATF4 to inhibit bone formation. Nat Med 19:93–100. doi:10.1038/nm.3026
Zhao C, Sun W, Zhang P, Ling S, Li Y, Zhao D, Peng J, Wang A, Li Q, Song J, Wang C, Xu X, Xu Z, Zhong G, Han B, Chang YZ (2015) miR-214 promotes osteoclastogenesis by targeting Pten/PI3k/Akt pathway. RNA Biol 12:343–353. doi:10.1080/15476286.2015.1017205
Li D, Liu J, Guo B, Liang C, Dang L et al (2016) Osteoclast-derived exosomal miR-214-3p inhibits osteoblastic bone formation. Nat Commun 7:10872. doi:10.1038/ncomms10872
Sun W, Zhao C, Li Y, Wang L, Nie G et al (2016) Osteoclast-derived microRNA-containing exosomes selectively inhibit osteoblast activity. Cell Discov 2:16015. doi:10.1038/celldisc.2016.15
Zhang B, Yeo RW, Tan KH, Lim SK (2016) Focus on extracellular vesicles: therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Int J Mol Sci 17:174. doi:10.3390/ijms17020174
Phinney DG, Prockop DJ (2007) Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair—current views. Stem Cells 25:2896–2902. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2007-0637
Ronne WYY, Ruenn CL, Kok HT, Sai KL (2013) Exosome: a novel and safer therapeutic refinement of mesenchymal stem cell. J Circ Biomark 1:1–12. doi:10.5772/57460
Thery C (2011) Exosomes: secreted vesicles and intercellular communications. F1000 Biol Rep 3:15. doi:10.3410/B3-15
Baglio SR, Pegtel DM, Baldini N (2012) Mesenchymal stem cell secreted vesicles provide novel opportunities in (stem) cell-free therapy. Front Physiol 3:359. doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00359
Yeo RW, Lai RC, Zhang B, Tan SS, Yin Y, Teh BJ, Lim SK (2013) Mesenchymal stem cell: an efficient mass producer of exosomes for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:336–341. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.07.001
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Maumus M, Guerit D, Toupet K, Jorgensen C, Noel D (2011) Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies in regenerative medicine: applications in rheumatology. Stem Cell Res Ther 2:14. doi:10.1186/scrt55
Ranganath SH, Levy O, Inamdar MS, Karp JM (2012) Harnessing the mesenchymal stem cell secretome for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cell Stem Cell 10:244–258. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.02.005
Martin PJ, Haren N, Ghali O, Clabaut A, Chauveau C, Hardouin P, Broux O (2015) Adipogenic RNAs are transferred in osteoblasts via bone marrow adipocytes-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). BMC cell Biol 16:10. doi:10.1186/s12860-015-0057-5
Zhao L, Jiang S, Hantash BM (2010) Transforming growth factor beta1 induces osteogenic differentiation of murine bone marrow stromal cells. Tissue Eng Part A 16:725–733. doi:10.1089/ten.TEA.2009.0495
Narayanan R, Huang CC, Ravindran S (2016) Hijacking the cellular mail: exosome mediated differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int 2016:3808674. doi:10.1155/2016/3808674
Collino F, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, Sterpone L, Aghemo G, Viltono L, Tetta C, Camussi G (2010) Microvesicles derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs. PLoS One 5:e11803. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011803
Baglio SR, Rooijers K, Koppers-Lalic D, Verweij FJ, Perez Lanzon M, Zini N, Naaijkens B, Perut F, Niessen HW, Baldini N, Pegtel DM (2015) Human bone marrow- and adipose-mesenchymal stem cells secrete exosomes enriched in distinctive miRNA and tRNA species. Stem Cell Res Ther 6:127. doi:10.1186/s13287-015-0116-z
Kim HS, Choi DY, Yun SJ, Choi SM, Kang JW, Jung JW, Hwang D, Kim KP, Kim DW (2012) Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. J Proteome Res 11:839–849. doi:10.1021/pr200682z
Xu JF, Yang GH, Pan XH, Zhang SJ, Zhao C, Qiu BS, Gu HF, Hong JF, Cao L, Chen Y, Xia B, Bi Q, Wang YP (2014) Altered microRNA expression profile in exosomes during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One 9:e114627. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0114627
Qin Y, Wang L, Gao Z, Chen G, Zhang C (2016) Bone marrow stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate osteoblast activity and differentiation in vitro and promote bone regeneration in vivo. Sci Rep 6:21961. doi:10.1038/srep21961
Mardones R, Jofre CM, Minguell JJ (2015) Cell therapy and tissue engineering approaches for cartilage repair and/or regeneration. Int J Stem Cells 8:48–53. doi:10.15283/ijsc.2015.8.1.48
Tao SC, Yuan T, Zhang YL, Yin WJ, Guo SC, Zhang CQ (2017) Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics 7:180–195. doi:10.7150/thno.17133
Liu S, Liu D, Chen C, Hamamura K, Moshaverinia A, Yang R, Liu Y, Jin Y, Shi S (2015) MSC transplantation improves osteopenia via epigenetic regulation of notch signaling in lupus. Cell Metab 22:606–618. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2015.08.018
Martins M, Ribeiro D, Martins A, Reis RL, Neves NM (2016) Extracellular vesicles derived from osteogenically induced human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can modulate lineage commitment. Stem Cell Rep 6:284–291. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.01.001
Wang KX, Xu LL, Rui YF, Huang S, Lin SE, Xiong JH, Li YH, Lee WY, Li G (2015) The effects of secretion factors from umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One 10:e0120593. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120593
Omar OM, Graneli C, Ekstrom K, Karlsson C, Johansson A, Lausmaa J, Wexell CL, Thomsen P (2011) The stimulation of an osteogenic response by classical monocyte activation. Biomaterials 32:8190–8204. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.07.055
Ekstrom K, Omar O, Graneli C, Wang X, Vazirisani F, Thomsen P (2013) Monocyte exosomes stimulate the osteogenic gene expression of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One 8:e75227. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075227
Wang Z, Ding L, Zheng XL, Wang HX, Yan HM (2014) [DC-derived exosomes induce osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells] (in Chinese). Zhongguo shi yan xue ye xue za zhi 22:600–604. doi:10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2014.03.005
Raimondi L, De Luca A, Amodio N, Manno M, Raccosta S, Taverna S, Bellavia D, Naselli F, Fontana S, Schillaci O, Giardino R, Fini M, Tassone P, Santoro A, De Leo G, Giavaresi G, Alessandro R (2015) Involvement of multiple myeloma cell-derived exosomes in osteoclast differentiation. Oncotarget 6:13772–13789. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3830
Anderson HC, Mulhall D, Garimella R (2010) Role of extracellular membrane vesicles in the pathogenesis of various diseases, including cancer, renal diseases, atherosclerosis, and arthritis. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol 90:1549–1557. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2010.152
Ali SY, Griffiths S (1983) Formation of calcium phosphate crystals in normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis 42:45–48
Kato T, Miyaki S, Ishitobi H, Nakamura Y, Nakasa T, Lotz MK, Ochi M (2014) Exosomes from IL-1beta stimulated synovial fibroblasts induce osteoarthritic changes in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 16:R163. doi:10.1186/ar4679
Karlsson T, Lundholm M, Widmark A, Persson E (2016) Tumor cell-derived exosomes from the prostate cancer cell line TRAMP-C1 impair osteoclast formation and differentiation. PLoS One 11:e0166284. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0166284
Inder KL, Ruelcke JE, Petelin L, Moon H, Choi E, Rae J, Blumenthal A, Hutmacher D, Saunders NA, Stow JL, Parton RG, Hill MM (2014) Cavin-1/PTRF alters prostate cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicle content and internalization to attenuate extracellular vesicle-mediated osteoclastogenesis and osteoblast proliferation. J Extracell Vesicles 3:23784. doi:10.3402/jev.v3.23784
Garimella R, Washington L, Isaacson J, Vallejo J, Spence M, Tawfik O, Rowe P, Brotto M, Perez R (2014) Extracellular membrane vesicles derived from 143B osteosarcoma cells contain pro-osteoclastogenic cargo: a novel communication mechanism in osteosarcoma bone microenvironment. Transl Oncol 7:331–340. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2014.04.011
Oliveira MC, Di Ceglie I, Arntz OJ, van den Berg WB, van den Hoogen FH, Ferreira AV, van Lent PL, van de Loo FA (2017) Milk-derived nanoparticle fraction promotes the formation of small osteoclasts but reduces bone resorption. J Cell Physiol 232:225–233. doi:10.1002/jcp.25414
Oliveira MC, Arntz OJ, Blaney Davidson EN, van Lent PL, Koenders MI, van der Kraan PM, van den Berg WB, Ferreira AV, van de Loo FA (2016) Milk extracellular vesicles accelerate osteoblastogenesis but impair bone matrix formation. J Nutr Biochem 30:74–84. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.11.017
Scita G, Di Fiore PP (2010) The endocytic matrix. Nature 463:464–473. doi:10.1038/nature08910
Ludwig AK, Giebel B (2012) Exosomes: small vesicles participating in intercellular communication. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:11–15. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2011.10.005
Fang Y, Wu N, Gan X, Yan W, Morrell JC, Gould SJ (2007) Higher-order oligomerization targets plasma membrane proteins and HIV gag to exosomes. PLoS Biol 5:e158. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050158
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, Rajendran L, Wenzel D, Wieland F, Schwille P, Brugger B, Simons M (2008) Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319:1244–1247. doi:10.1126/science.1153124
Raiborg C, Rusten TE, Stenmark H (2003) Protein sorting into multivesicular endosomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:446–455
Franzen CA, Simms PE, Van Huis AF, Foreman KE, Kuo PC, Gupta GN (2014) Characterization of uptake and internalization of exosomes by bladder cancer cells. Biomed Res Int 2014:619829. doi:10.1155/2014/619829
Mause SF, Weber C (2010) Microparticles: protagonists of a novel communication network for intercellular information exchange. Circ Res 107:1047–1057. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.226456
Schorey JS, Bhatnagar S (2008) Exosome function: from tumor immunology to pathogen biology. Traffic 9:871–881. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00734.x
Oltra E (2014) Relevance of splicing on tumor-released exosome landscape: implications in cancer therapeutics. Front Endocrinol 5:194. doi:10.3389/fendo.2014.00194
van der Pol E, Hoekstra AG, Sturk A, Otto C, van Leeuwen TG, Nieuwland R (2010) Optical and non-optical methods for detection and characterization of microparticles and exosomes. J Thromb Haemost 8:2596–2607. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04074.x
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC; Grant No. 81502465).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Huang, QP., Wang, YL. et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated bone metabolism in the bone microenvironment. J Bone Miner Metab 36, 1–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-017-0860-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-017-0860-5