Abstract
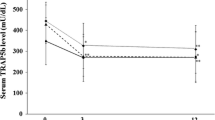
This study was performed to investigate the effects of the co-administration of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) on the efficacy of bisphosphonate (BP) treatment for osteoporosis. A total of 180 women with low bone mineral density were randomly divided into four groups, one in which sodium risedronate was administered with sodium rabeprazole and one in which only risedronate was administered (BP + PPI and BP groups, respectively). The biomarkers were measured at the baseline and every 3 months, inlcuding: N-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen corrected for creatinine, bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BAP), parathyroid hormone, bone mineral density (BMD) of the lumbar spine and physical parameters evaluated according to the SF-36v2™ Health Survey. Statistical comparisons of these parameters were performed after 9 months. Data were available for a total of 137 patients (62 in the BP group and 75 in the BP + PPI group). The Δ % value of increase in BMD and improvement of physical functioning in the BP + PPI group were significantly larger, and its decrease in BAP in the BP + PPI group was significantly smaller than that in the BP group. It is expected that risedronate administration in combination with a PPI may be more effective not only for treating osteoporosis but also improving physical fitness than treatment with risedronate alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris ST, Watts NB, Genant HK, McKeever CD, Hangartner T, Keller M, Chesnut CH III, Brown J, Eriksen EF, Hoseyni MS, Axelrod DW, Mille PD (1999) Effects of risedronate treatment on vertebral and non-vertebral fractures in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 282:1344–1352
Reginster JY, Minne HW, Sorensen OH, Hooper M, Roux C, Brandi ML, Lund B, Ethgen D, Pack S, Roumagnac I, Eastell R (2000) Randomised trial of the effects of risedronate on vertebral fractures in women with established postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 11:83–91
Ettinger B, Pressman A, Schein J, Chan J, Silver P, Connolly N (1998) Alendronate use among 812 women: prevalence of gastrointestinal complaints, noncompliance with patient instructions, and discontinuation. J Manag Care Pharm 4:488–492
Aggart HT, Bolognese MA, Lindsay R, Ettinger MP, Mulder HF, Josse RG, Roberts A, Zippel H, Adami SV, Ernst TF, Stevens KP (2002) Upper gastrointestinal tract safety of risedronate: a pooled analysis of 9 clinical trials. Mayo Clin Proc 77:262–270
Gertz BJ, Holland SD, Kline WF, Matuszewski BK, Freeman A, Quan H, Lasseter KC, Mucklow JC, Porras AG (1995) Studies of the oral bioavailability of alendronate. Clin Pharmacol Ther 58:288–298
Abrahamsen B, Eiken P, Eastell R (2011) Proton pump inhibitor use and the antifracture efficacy of alendronate. Arch Intern Med 171:998–1004
Ito M, Ikeda K, Nishiguchi M, Shindo H, Uetani M, Hosoi T, Orimo H (2005) Multi-detector row CT imaging of vertebral microstructure for evaluation fracture risk. J Bone Miner Res 20:1828–1836
Ivanovich P, Fellows H, Rich C (1967) The absorption of calcium carbonate. Ann Intern Med 66:917–923
Sheikh MS, Santa Ana CA, Nicar MJ, Schiller LR, Fordtran JS (1987) Gastrointestinal absorption of calcium from milk and calcium salts. N Engl J Med 317:532–536
Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, Cauley JA, Thompson DE, Nevitt MC, Bauer DC, Genant HK, Haskell WL, Marcus R, Ott SM, Torner JC, Quandt SA, Reiss TF, Ensrud KE (1996) Randomized trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Lancet 348:1535–1541
Colina RE, Smith M, Kikendall JW, Wong RK (1997) A new probable increasing cause of esophageal ulceration: alendronate. Am J Gastroenterol 92:704–706
Bauer DC, Black D, Ensrud K, Thompson D, Hochberg M, Nevitt M, Musliner T, Freedholm D (2000) Upper gastrointestinal tract safety profile of alendronate: the fracture intervention trial. Arch Intern Med 160:517–525
Leslie WD, Tsang JF, Caetano PA, Lix LM (2007) Effectiveness of bone density measurement for predicting osteoporotic fractures in clinical practice. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:77–81
Fleisch H (1981) Biphosphonate: history and mechanism of action. Metab Bone Dis Rel Res 3:279–287
Conflict of interest
No benefit of any kind will be received either directly or indirectly by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Itoh, S., Sekino, Y., Shinomiya, Ki. et al. The effects of risedronate administered in combination with a proton pump inhibitor for the treatment of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 31, 206–211 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0406-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0406-9