Abstract
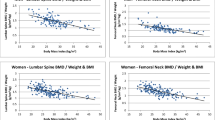
In the general population, low body weight and body mass index (BMI) are significant risk factors for any fracture, but the specific association between body weight, BMI, and prevalence of vertebral fractures in osteoporotic women is not fully recognized. Hence, the association between body weight, BMI, and prevalent vertebral fractures was investigated in 362 women with never-treated postmenopausal osteoporosis. All participants underwent measurement of BMI, bone mineral density (BMD), and semiquantitative assessment of vertebral fractures. Thirty percent of participants had ≥1 vertebral fracture. Body weight and BMI were associated with L1–L4 BMD (R = 0.29, P < 0.001 and R = 0.17, P = 0.009, respectively). In logistic regression analysis, BMI was positively associated with the presence of vertebral fractures independent of age and other traditional risk factors for fractures. Including weight and height instead of BMI in the multivariate model, showed weight as a positive and significant covariate of the presence of vertebral fractures (OR = 1.045; P = 0.016; 95% CI 1.008–1.084). BMI was associated with the number of vertebral fractures (rho = 0.18; P = 0.001), this association being confirmed also in the multivariate analysis (β = 0.14; P = 0.03) after correction for smoking, early menopause, family history of fragility fractures and BMD. In conclusion, among postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, body weight and BMI are associated with a higher likelihood of having a vertebral fracture, irrespective of the positive association between weight and BMD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnell O, Kanis J (2005) Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int 16:3–7
van Staa TP, Dennison EM, Leufkens HG, Cooper C (2001) Epidemiology of fractures in England and Wales. Bone 29:517–522
Briggs AM, Greig AM, Wark JD (2007) The vertebral fracture cascade in osteoporosis: a review of aetiopathogenesis. Osteoporos Int 18:575–584
NIH Consensus Development Panel on Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, Therapy (2001) Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis and therapy. JAMA 285:785–795
Felson DT, Zhang Y, Hannan MT, Anderson JJ (1993) Effects of weight and body mass index on bone mineral density in men and women: the Framingham study. J Bone Miner Res 8:567–573
Svendsen OL, Hassager C, Christiansen C (1993) Effect of an energy-restrictive diet, with or without exercise, on lean tissue mass, resting metabolic rate, cardiovascular risk factors, and bone in overweight postmenopausal women. Am J Med 95:131–140
Compston JE, Laskey MA, Croucher PI, Coxon A, Kreitzman S (1992) Effect of diet-induced weight loss on total body bone mass. Clin Sci (Lond) 82:429–432
Espallargues M, Sampietro-Colom L, Estrada MD, Solà M, del Rio L, Setoain J, Granados A (2001) Identifying bone-mass-related risk factors for fracture to guide bone densitometry measurements: a systematic review of the literature. Osteoporos Int 12:811–822
De Laet C, Kanis JA, Odén A, Johanson H, Johnell O, Delmas P, Eisman JA, Kroger H, Fujiwara S, Garnero P, McCloskey EV, Mellstrom D, Melton LJ 3rd, Meunier PJ, Pols HA, Reeve J, Silman A, Tenenhouse A (2005) Body mass index as a predictor of fracture risk: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 16:1330–1338
van der Klift M, de Laet CE, McCloskey EV, Johnell O, Kanis JA, Hofman A, Pols HA (2004) Risk factors for incident vertebral fractures in men and women: the Rotterdam Study. J Bone Miner Res 19:1172–1180
Finigan J, Greenfield DM, Blumsohn A, Hannon RA, Peel NF, Jiang G, Eastell R (2008) Risk factors for vertebral and nonvertebral fracture over 10 years: a population-based study in women. J Bone Miner Res 23:75–85
Crepaldi G, Romanato G, Tonin P, Maggi S (2007) Osteoporosis and body composition. J Endocrinol Invest 30:42–47
Rubin CT, Lanyon LE (1985) Regulation of bone mass by mechanical strain magnitude. Calcif Tissue Int 37:411–417
Zhao LJ, Jiang H, Papasian CJ, Maulik D, Drees B, Hamilton J, Deng HW (2008) Correlation of obesity and osteoporosis: effect of fat mass on the determination of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 23:17–29
LaFleur J, McAdam-Marx C, Kirkness C, Brixner DI (2008) Clinical risk factors for fracture in postmenopausal osteoporotic women: a review of the recent literature (March). Ann Pharmacother 29 (Epub ahead of print)
Papaioannou A, Joseph L, Ioannidis G, Berger C, Anastassiades T, Brown JP, Hanley DA, Hopman W, Josse RG, Kirkland S, Murray TM, Olszynski WP, Pickard L, Prior JC, Siminoski K, Adachi JD (2005) Risk factors associated with incident clinical vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in postmenopausal women: the Canadian Multicentre Osteoporosis Study (CaMos). Osteoporos Int 16:568–578
Hollaender R, Hartl F, Krieg MA, Tyndall A, Geuckel C, Buitrago-Tellez C, Manghani M, Kraenzlin M, Theiler R, Hans D (2009) Prospective evaluation of risk of vertebral fractures using quantitative ultrasound measurements and bone mineral density in a population-based sample of postmenopausal women: results of the Basel Osteoporosis Study. Ann Rheum Dis 68:391–396
Albrand G, Munoz F, Sornay-Rendu E, DuBoeuf F, Delmas PD (2003) Independent predictors of all osteoporosis-related fractures in healthy postmenopausal women: the OFELY study. Bone 32:78–85
Takata S, Yasui N (2002) Effects of constitution, atraumatic vertebral fracture and aging on bone mineral density and soft tissue composition in women. J Med Invest 49:18–24
Genant HK, Grampp S, Glüer CC, Faulkner KG, Jergas M, Engelke K, Hagiwara S, Van Kuijk C (1994) Universal standardization for dual X-ray absorptiometry: patient and phantom cross-calibration results. J Bone Miner Res 9:1503–1514
Looker AC, Orwoll ES, Johnston CC Jr, Lindsay RL, Wahner HW, Dunn WL, Calvo MS, Harris TB, Heyse SP (1997) Prevalence of low femoral bone density in older U.S. adults from NHANES III. J Bone Miner Res 12:1761–1768
Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC (1993) Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8:1137–1148
Huang C, Ross PD, Lydick E, Davis JW, Wasnich RD (1996) Contributions of vertebral fractures to stature loss among elderly Japanese–American women in Hawaii. J Bone Miner Res 11:408–411
Siminoski K, Jiang G, Adachi JD, Hanley DA, Cline G, Ioannidis G, Hodsman A, Josse RG, Kendler D, Olszynski WP, Ste Marie LG, Eastell R (2005) Accuracy of height loss during prospective monitoring for detection of incident vertebral fractures. Osteoporos Int 16:403–410
Sugiyama T, Yamaguchi A, Kawai S (2002) Effects of skeletal loading on bone mass and compensation mechanism in bone: a new insight into the “mechanostat” theory. J Bone Miner Metab 20:196–200
Finkelstein EA, Chen H, Prabhu M, Trogdon JG, Corso PS (2007) The relationship between obesity and injuries among U.S. adults. Am J Health Promot 21:460–468
Tchernof A, Calles-Escandon J, Sites CK, Poehlman ET (1998) Menopause, central body fatness, and insulin resistance: effects of hormone-replacement therapy. Coron Artery Dis 9:503–511
Justesen J, Stenderup K, Ebbesen EN, Mosekilde L, Steiniche T, Kassem M (2001) Adipocyte tissue volume in bone marrow is increased with aging and in patients with osteoporosis. Biogerontology 2:165–171
Riggs BL, Khosla S, Melton LJ 3rd (1998) A unitary model for involutional osteoporosis: estrogen deficiency causes both type I and type II osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and contributes to bone loss in aging men. J Bone Miner Res 13:763–773
Jensen LB, Vestergaard P, Hermann AP, Gram J, Eiken P, Abrahamsen B, Brot C, Kolthoff N, Sørensen OH, Beck-Nielsen H, Nielsen SP, Charles P, Mosekilde L (2003) Hormone replacement therapy dissociates fat mass and bone mass, and tends to reduce weight gain in early postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled 5-year clinical trial of the Danish Osteoporosis Prevention Study. J Bone Miner Res 8:333–342
Rossouw JE, Anderson GL, Prentice RL, LaCroix AZ, Kooperberg C, Stefanick ML, Jackson RD, Beresford SA, Howard BV, Johnson KC, Kotchen JM, Ockene J, Writing Group for the Women’s Health Initiative Investigators (2002) Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: principal results from the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA 288:321–333
Fabris de Souza SA, Faintuch J, Valezi AC, Sant’Anna AF, Gama-Rodrigues JJ, de Batista Fonseca IC, de Melo RD (2005) Postural changes in morbidly obese patients. Obes Surg 15:1013–1016
Keller TS, Harrison DE, Colloca CJ, Harrison DD, Janik TJ (2003) Prediction of osteoporotic spinal deformity. Spine 28:455–462
Riedt CS, Cifuentes M, Stahl T, Chowdhury HA, Schlussel Y, Shapses SA (2005) Overweight postmenopausal women lose bone with moderate weight reduction and 1 g/day calcium intake. J Bone Miner Res 2005:455–463
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Iliana Lega, MD, for her assistance in the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Pirro, M., Fabbriciani, G., Leli, C. et al. High weight or body mass index increase the risk of vertebral fractures in postmenopausal osteoporotic women. J Bone Miner Metab 28, 88–93 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-009-0108-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-009-0108-0