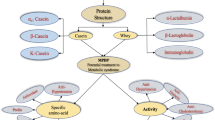
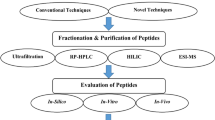
Abstract
Bioactive peptides consist of small protein fragments, which are inactive in their original conformation, and they become active when released from these through enzymatic hydrolysis or fermentation processes. The bioactivity of such peptides has been extensively reported in the literature as contributors to organic homeostasis processes, as well as in immunomodulation, organism defense against oxidative processes, among others. In this study, reports of the activity of BPs isolated from milk with the potential glycemic control, antihypertensive activity, and inhibitors of uric acid formation were compiled. A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis were conducted, using the PICO strategy for the research. The temporal analysis of publications revealed a growing interest in the investigation of bioactive peptides with potential antidiabetic, antihypertensive, and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities, using dairy sources as products for their extraction. The literature analysis also revealed an increase in research involving non-bovine dairy products for bioactive peptide extraction. The collaboration network among authors exhibited weaknesses in scientific cooperation. Regarding the analysis of keywords, the usage of terms such as “bioactive peptides”, “antioxidant”, “antihypertensive”, and “diabetes” was evident, constituting the main research clusters. Peptides with low molecular weight, typically < 10 kDa, of hydrophobic nature with aliphatic and aromatic chains, have significant implications in molecular interactions for the required activities. Although there is a growing interest in the industry regarding the utilization of bioactive peptides as potential drugs, there is a need to address gaps related to elucidating their interactions with cellular targets and their use in human therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated and/or analyzed during this research are included in this published article and its supplementary material.
References
Abedin MM, Chourasia R, Phukon LC, Singh SP, Rai AK (2022) Characterization of ACE inhibitory and antioxidant peptides in yak and cow milk hard chhurpi cheese of the Sikkim Himalayan region. Food Chem X 13:10023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100231
Acquah C, Dzuvor CKO, Tosh S, Agyei D (2022) Anti-diabetic effects of bioactive peptides: recent advances and clinical implications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 63(19):3664–3682. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1851168
Ahmed AS, El-Bassiony T, Elmalt LM, Ibrahim HR (2015) Identification of potent antioxidant bioactive peptides from goat milk proteins. Food Res Int 74:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.04.032
Ahn C-B, Je J-Y (2019) Bone health-promoting bioactive peptides. J Food Biochem 43:e12529. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFBC.12529
Alam F, Giglou HB, Malik KM (2023) Automated clinical knowledge graph generation framework for evidence based medicine. Expert Syst Appl 233:120964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120964
Aluko RE (2019) Food protein-derived renin-inhibitory peptides: in vitro and in vivo properties. J Food Biochem 43:e12648. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFBC.12648
Alvarez-Bueno C, Cavero-Redondo I, Martinez-Vizcaino V, Sotos-Prieto M, Ruiz JR, Gil A (2019) Effects of milk and dairy product consumption on type 2 Diabetes: overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Adv Nutr 10(2):S154–S163. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmy107
Amorim FG, Coitinho LB, Dias AT, Friques AGF, Monteiro BL, Rezende LCD, Pereira TMC, Campagnaro BP, Pauw ED, Vasquez EC, Quinton L (2019) Identification of new bioactive peptides from Kefir milk through proteopeptidomics: bioprospection of antihypertensive molecules. Food Chem 282(109):119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.010
Ashraf A, Mudgil P, Palakkott A, Iratni R, Gan C-Y, Maqsood S, Ayoub MA (2021) Molecular basis of the anti-diabetic properties of camel milk through profiling of its bioactive peptides on dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) and insulin receptor activity. J Dairy Sci 104(1):61–77. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2020-18627
Baba WN, Baby B, Mudgil P, Gan C-Y, Vijayan R, Maqsood S (2021) Pepsin generated camel whey protein hydrolysates with potential antihypertensive properties: identification and molecular docking of antihypertensive peptides. LWT 143:111135. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LWT.2021.111135
Castro RJS, Sato HH (2015) Biologically active peptides: processes for their generation, purification and identification and applications as natural additives in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Food Res Int 74:185–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2015.05.013
Chaudhary A, Bhalla S, Patiyal S, Raghava GPS, Sahni G (2021) FermFooDb: a database of bioactive peptides derived from fermented foods. Heliyon 7(4):E06668. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HELIYON.2021.E06668
Ciau-Solís NA, Acevedo-Fernández JJ, Betancur-Ancona D (2018) In vitro renin–angiotensin system inhibition and in vivo antihypertensive activity of peptide fractions from lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.). J Sci Food Agric 98:781–786. https://doi.org/10.1002/JSFA.8543
Clemente-Suárez VJ, Beltrán-Velasco AI, Redondo-Flórez L, Martín-Rodríguez A, Tornero-Aguilera JF (2023) Global impacts of western diet and its effects on metabolism and health: a narrative review. Nutrients 15(12):2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU15122749
Daliri EB-M, Lee BH, Park B-J, Kim S-H, Oh D-H (2018) Antihypertensive peptides from whey proteins fermented by lactic acid bacteria. Food Sci Biotechnol 27:1781–1789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0423-0
Derosa G, D’Angelo A, Maffioli P (2020) Change of some oxidative stress parameters after supplementation with whey protein isolate in patients with type 2 diabetes. Nutrition 73:110700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2019.110700
FitzGerald RJ, Cermeño M, Khalesi M, Kleekayai T, Amigo-Benavent M (2020) Application of in silico approaches for the generation of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides. J Funct Foods 64:103636. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFF.2019.103636
Gao Y-F, Liu M-Q, Li Z-H, Zhang H-L, Hao J-Q, Liu B-H, Li X-Y, Yin Y-Q, Wang X-H, Zhou Q, Xu D, Shi B-M, Zhang Y-H (2023) Purification and identification of xanthine oxidase inhibitory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysate of α-lactalbumin and bovine colostrum casein. Food Res Int 169:112882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112882
Gong H, Gao J, Wang Y, Luo QW, Guo KR, Ren FZ, Mao XY (2020) Identification of novel peptides from goat milk casein that ameliorate high-glucose-induced insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. J Dairy Sci 103(6):4907–4918. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2019-17513
Guha S, Sharma H, Deshwal GK, Rao PS (2021) A comprehensive review on bioactive peptides derived from milk and milk products of minor dairy species. Food Prod Process Nutr 3:2661–8974. https://doi.org/10.1186/S43014-020-00045-7
Guo Q, Chen P, Chen X (2023) Bioactive peptides derived from fermented foods: preparation and biological activities. J Funct Foods 101:105422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2023.105422
Iglesias MJ, de la Fuente Layos MÁ, Alonso JF (2015) The nutrients of the milk on cardiovascular health. Nutr Hosp 31(2):26–32. https://doi.org/10.3305/NH.2015.31.SUP2.8679
Izadi A, Khedmat L, Mojtahedi SY (2019) Nutritional and therapeutic perspectives of camel milk and its protein hydrolysates: a review on versatile biofunctional properties. J Funct Foods 60:103441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.103441
Jahandideh F, Bourque SL, Wu J (2022) A comprehensive review on the glucoregulatory properties of food-derived bioactive peptides. Food Chem X 30:100222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100222
Khalesi M, Salami M, Moslehishad M, Winterburn J, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2017) Biomolecular content of camel milk: a traditional superfood towards future healthcare industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 62:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.02.004
Lacroix IME, Li-Chan ECY (2014) Isolation and characterization of peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity from pepsin-treated bovine whey proteins. Peptides 54:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2014.01.002
Lammi C, Aiello G, Boschin G, Arnoldi A (2019) Multifunctional peptides for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: a new concept in the area of bioactive food-derived peptides. J Funct Foods 55:135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFF.2019.02.016
Li J, Zhao J, Wang X, Qayum A, Hussain MA, Liang G, Hou J, Jiang Z, Li A (2019) Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides from fermented bovine milk started by Lactobacillus helveticus KLDS.31 and Lactobacillus casei KLDS.105: purification, identification, and interaction mechanisms. Front Microbiol 10:2643. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02643
Liu M, Wang Y, Liu Y, Ruan R (2016) Bioactive peptides derived from traditional Chinese medicine and traditional Chinese food: a review. Food Res Int 89:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.08.009
Liu L, Li S, Zheng J, Bu T, He G, Wu J (2020) Safety considerations on food protein-derived bioactive peptides. Trends Food Sci Technol 96:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2019.12.022
Manzoor M, Singh J, Gani A (2022) Exploration of bioactive peptides from various origin as promising nutraceutical treasures: In vitro, in silico and in vivo studies. Food Chem 373:131395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131395
Martínez-Sánchez SM, Gabaldón-Hernández JA, Montoro-García S (2020) Unravelling the molecular mechanisms associated with the role of food-derived bioactive peptides in promoting cardiovascular health. J Funct Foods 64:103645. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFF.2019.103645
Mazorra-Manzano MA, Robles-Porchas GR, González-Velázquez DA, Torres-Llanez MJ, Martínez-Porchas M, García-Sifuentes CO, González-Córdova AF, Vallejo-Córdoba B (2020) Cheese whey fermentation by its native microbiota: proteolysis and bioactive peptides release with ACE-inhibitory activity. Fermentation 6(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6010019
Minj J, Chandra P, Paul C, Sharma RK (2020) Bio-functional properties of probiotic Lactobacillus: current applications and research perspectives. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 61(13):2207–2224. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1774496
Mirzapour-Kouhdasht A, Garcia-Vaquero M (2022) Cardioprotective peptides from milk processing and dairy products: from bioactivity to final products including commercialization and legislation. Foods 11(9):1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/FOODS11091270
Monteiro BL, Dias AT, Wanderkoke SC, Yokota R, Casarini DE, Leal MAS, Nogueira BV, Meyrelles SS, Campos-Toimil M, Campagnaro BP, Campos RR, Pereira TMC, Vasquez EC (2020) Protective effects of kefir in the angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. J Funct Foods 75:104260. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFF.2020.104260
Mudgil P, Baba WN, Alneyadi M, Redha AA, Maqsood S (2022) Production, characterization, and bioactivity of novel camel milk-based infant formula in comparison to bovine and commercial sources. LWT 154:112813. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LWT.2021.112813
Nongonierma AB, FitzGerald RJ (2012) Tryptophan-containing milk protein-derived dipeptides inhibit xanthine oxidase. Peptides 37(2):263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2012.07.030
Nongonierma AB, FitzGerald RJ (2016) Strategies for the discovery, identification and validation of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides. Trends Food Sci Technol 50:26–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2016.01.022
Patil P, Mandal S, Tomar SK, Anand S (2015) Food protein-derived bioactive peptides in management of type 2 diabetes. Eur J Nutr 54:863–880. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-0974-2
Punia H, Tokas J, Malik A, Sangwan S, Baloda S, Singh N, Singh S, Bhuker A, Singh P, Yashveer S, Agarwal S, Mor VS (2020) Identification and detection of bioactive peptides in milk and dairy products: remarks about agro-foods. Molecules 25(15):3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES25153328
Qi X, Chen H, Guan K, Sun Y, Wang R, Ma Y (2022) Identification, inhibitory mechanism and transepithelial transport of xanthine oxidase inhibitory peptides from whey protein after simulated gastrointestinal digestion and intestinal absorption. Food Res Int 162:111959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111959
Rosa LS, Santos ML, Abreu JP, Rocha RS, Esmerino EA, Freitas MQ, Mársico ET, Campelo PH, Pimentel TC, Silva MC, Souza AA, Nogueira FCS, Cruz AG, Teodoro AJ (2023) Probiotic fermented whey-milk beverages: effect of different probiotic strains on the physicochemical characteristics, biological activity, and bioactive peptides. Food Res Int 164:112396. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2022.112396
Samtiya M, Samtiya S, Badgujar PC, Puniya AK, Dhewa T, Aluko RE (2022) Health-promoting and therapeutic attributes of milk-derived bioactive peptides. Nutrients 14(15):3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU14153001
Shivanna SK, Nataraj BH (2020) Revisiting therapeutic and toxicological fingerprints of milk-derived bioactive peptides: an overview. Food Biosci 38:100771. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FBIO.2020.100771
Shukla P, Sakure A, Pipaliya R, Basaiawmoit B, Maurya R, Bishnoi M, Kondepudi KK, Hati S (2022) Exploring the potential of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei M11 on antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and ACE inhibitory effects of fermented dromedary camel milk (Camelus dromedaries) and the release of antidiabetic and anti-hypertensive peptides. J Food Biochem 46:e14449. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFBC.14449
Singh BP, Aluko RE, Hati S, Solanki D (2021) Bioactive peptides in the management of lifestyle-related diseases: current trends and future perspectives. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 62(17):4593–4606. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1877109
Solieri L, Valentini M, Cattivelli A, Sola L, Helal A, Martini S, Tagliazucchi D (2022) Fermentation of whey protein concentrate by Streptococcus thermophilus strains releases peptides with biological activities. Process Biochem 121:590–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2022.08.003
Thaha A, Wang B-S, Chang Y-W, Hsia S-M, Huang T-C, Shiau C-Y, Hwang D-F, Chen T-Y (2021) Food-derived bioactive peptides with antioxidative capacity, xanthine oxidase and tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Processes 9(5):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050747
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84:523538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Vargas-Bello-Pérez E, Márquez-Hernández RI, Hernández-Castellano LE (2019) Bioactive peptides from milk: animal determinants and their implications in human health. J Dairy Res 86(2):136–144. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022029919000384
Yilmaz B, Sharma H, Melekoglu E, Ozogul F (2022) Recent developments in dairy kefir-derived lactic acid bacteria and their health benefits. Food Biosci 46:101592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101592
Zhang Y, Chen R, Ma H, Chen S (2015) Isolation and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV-inhibitory peptides from trypsin/chymotrypsin-treated goat milk casein hydrolysates by 2D-TLC and LC–MS/MS. J Agric Food Chem 63(40):8819–8828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03062
Zhou X, Chai L, Wu Q, Wang Y, Li S, Chen J (2021) Anti-diabetic properties of bioactive components from fish and milk. J Funct Foods 85:104669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2021.104669
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC – Termos de outorga 2021TR1757; 2023TR564). Aniela Pinto Kempka is granted a fellowship (PQ2) from CNPq – Brazil (303915/2022–6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EHB: writing (original draft preparation, methodology, validation and data curation, formal analysis and investigation); APK: supervision and writing (review and editing).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Handling editor: S. Broer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bellaver, E.H., Kempka, A.P. Potential of milk-derived bioactive peptides as antidiabetic, antihypertensive, and xanthine oxidase inhibitors: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis and updated review. Amino Acids 55, 1829–1855 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03351-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03351-9