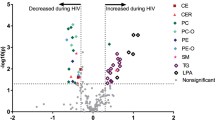
Abstract
Amino acid metabolic profile, particularly its association with clinical characteristics, remains unclear in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) combined with metabolic disorders. In this study, we performed targeted metabolomic analyses on 64 patients with HIV/AIDS and 21 healthy controls. Twenty-four amino acids and selected intermediate metabolites in the serum were quantitatively detected using high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry, and characteristic changes and metabolic pathways were analyzed in HIV-infected patients with different degrees of abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism. Spearman’s partial correlation was used to analyze the association between amino acids, biochemical parameters, and inflammatory cytokines. The results showed that the main metabolic pathways of the eighteen differential metabolites involved were arginine biosynthesis and metabolism, methionine cycle, and tryptophan metabolism. Fourteen differential amino acid metabolites were positively correlated with nine inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, C-reactive protein, IL-1β, and galectin-3 (FDR < 0.1). Kynurenine, ornithine, and homocysteine were positively correlated with fasting blood glucose and insulin resistance index (FDR < 0.1). Our study revealed a multi-pathway imbalance in amino acid metabolism in patients with HIV/AIDS, which was significantly correlated with inflammation and insulin resistance.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adams SH (2011) Emerging perspectives on essential amino acid metabolism in obesity and the insulin-resistant state. Adv Nutr 2(6):445–456. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.111.000737
Alonso A, Barnes AE, Guest JL, Shah A, Shao IY, Marconi V (2019) HIV infection and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: an analysis of a large healthcare database. J Am Heart Assoc 8(14):e012241. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.119.012241
Babu H, Sperk M, Ambikan AT, Rachel G, Viswanathan VK, Tripathy SP, Nowak P, Hanna LE, Neogi U (2019) Plasma metabolic signature and abnormalities in HIV-infected individuals on long-term successful antiretroviral therapy. Metabolites 9(10):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100210
Betene ADC, De Wit S, Neuhaus J, Palfreeman A, Pepe R, Pankow JS, Neaton JD, Insight S, Groups ES (2014) Interleukin-6, high sensitivity C-reactive protein, and the development of type 2 diabetes among HIV-positive patients taking antiretroviral therapy. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 67(5):538–546. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAI.0000000000000354
Blantz RC, Satriano J, Gabbai F, Kelly C (2000) Biological effects of arginine metabolites. Acta Physiol Scand 168(1):21–25. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-201x.2000.00646.x
Bourgi K, Wanjalla C, Koethe JR (2018) Inflammation and metabolic complications in HIV. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 15(5):371–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11904-018-0411-2
Chen S, Akter S, Kuwahara K, Matsushita Y, Nakagawa T, Konishi M, Honda T, Yamamoto S, Hayashi T, Noda M, Mizoue T (2019) Serum amino acid profiles and risk of type 2 diabetes among Japanese adults in the Hitachi Health Study. Sci Rep 9(1):7010. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43431-z
Debnath S, Velagapudi C, Redus L, Thameem F, Kasinath B, Hura CE, Lorenzo C, Abboud HE, O’Connor JC (2017) Tryptophan metabolism in patients with chronic kidney disease secondary to type 2 diabetes: relationship to inflammatory markers. Int J Tryptophan Res 10:1178646917694600. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178646917694600
Deme P, Rubin LH, Yu D, Xu Y, Nakigozi G, Nakasujja N, Anok A, Kisakye A, Quinn TC, Reynolds SJ, Mayanja R, Batte J, Wawer MJ, Sacktor NC, Saylor D, Haughey NJ (2022) Immunometabolic reprogramming in response to HIV infection is not fully normalized by suppressive antiretroviral therapy. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061313
Duncan AD, Goff LM, Peters BS (2018) Type 2 diabetes prevalence and its risk factors in HIV: a cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 13(3):e0194199. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194199
Gar C, Rottenkolber M, Prehn C, Adamski J, Seissler J, Lechner A (2018) Serum and plasma amino acids as markers of prediabetes, insulin resistance, and incident diabetes. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 55(1):21–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408363.2017.1414143
Hamaya R, Mora S, Lawler PR, Cook NR, Ridker PM, Buring JE, Lee IM, Manson JE, Tobias DK (2021) Association of plasma branched-chain amino acid with biomarkers of inflammation and lipid metabolism in women. Circ Genom Precis Med 14(4):e003330. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCGEN.121.003330
Hart BB, Nordell AD, Okulicz JF, Palfreeman A, Horban A, Kedem E, Neuhaus J, Jacobs DR Jr, Duprez DA, Neaton JD, Insight S, Groups E (2018) Inflammation-related morbidity and mortality among hiv-positive adults: how extensive is it? J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 77(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAI.0000000000001554
Hsu DC, Sereti I (2016) Serious non-AIDS events: therapeutic targets of immune activation and chronic inflammation in HIV infection. Drugs 76(5):533–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0546-7
Hunt PW (2012) HIV and inflammation: mechanisms and consequences. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 9(2):139–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11904-012-0118-8
Lercher A, Bhattacharya A, Popa AM, Caldera M, Schlapansky MF, Baazim H, Agerer B, Gurtl B, Kosack L, Majek P, Brunner JS, Vitko D, Pinter T, Genger JW, Orlova A, Pikor N, Reil D, Ozsvar-Kozma M, Kalinke U, Ludewig B, Moriggl R, Bennett KL, Menche J, Cheng PN, Schabbauer G, Trauner M, Klavins K, Bergthaler A (2019) Type I interferon signaling disrupts the hepatic urea cycle and alters systemic metabolism to suppress T cell function. Immunity 51(6):1074–10871079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2019.10.014
Li H, Lu H, Tang W, Zuo J (2017) Targeting methionine cycle as a potential therapeutic strategy for immune disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2017.1370454
Li T, Ning N, Li B, Luo D, Qin E, Yu W, Wang J, Yang G, Nan N, He Z, Yang N, Gong S, Li J, Liu A, Sun Y, Li Z, Jia T, Gao J, Zhang W, Huang Y, Hou J, Xue Y, Li D, Wei Z, Zhang L, Li B, Wang H (2021) Longitudinal metabolomics reveals ornithine cycle dysregulation correlates with inflammation and coagulation in COVID-19 severe patients. Front Microbiol 12:723818. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.723818
Marin-Palma D, Castro GA, Cardona-Arias JA, Urcuqui-Inchima S, Hernandez JC (2018) Lower high-density lipoproteins levels during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection are associated with increased inflammatory markers and disease progression. Front Immunol 9:1350. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01350
Monti LD, Galluccio E, Villa V, Fontana B, Spadoni S, Piatti PM (2018) Decreased diabetes risk over 9 year after 18-month oral L-arginine treatment in middle-aged subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and metabolic syndrome (extension evaluation of L-arginine study). Eur J Nutr 57(8):2805–2817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1548-2
Non LR, Escota GV, Powderly WG (2017) HIV and its relationship to insulin resistance and lipid abnormalities. Transl Res 183:41–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2016.12.007
Pedro MN, Rocha GZ, Guadagnini D, Santos A, Magro DO, Assalin HB, Oliveira AG, Pedro RJ, Saad MJA (2018) Insulin resistance in HIV-patients: causes and consequences. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 9:514. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00514
Peltenburg NC, Schoeman JC, Hou J, Mora F, Harms AC, Lowe SH, Bierau J, Bakker JA, Verbon A, Hankemeier T, Boonstra A (2018) Persistent metabolic changes in HIV-infected patients during the first year of combination antiretroviral therapy. Sci Rep 8(1):16947. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35271-0
Ren Y, Li Z, Li W, Fan X, Han F, Huang Y, Yu Y, Qian L, Xiong Y (2022) Arginase: biological and therapeutic implications in diabetes mellitus and its complications. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:2419412. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2419412
Saez-Cirion A, Sereti I (2021) Immunometabolism and HIV-1 pathogenesis: food for thought. Nat Rev Immunol 21(1):5–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-020-0381-7
Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB (2006) Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116(7):1793–1801. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI29069
Strasser B, Sperner-Unterweger B, Fuchs D, Gostner JM (2017) Mechanisms of inflammation-associated depression: immune influences on tryptophan and phenylalanine metabolisms. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 31:95–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/7854_2016_23
Tadesse BT, Foster BA, Chala A, Chaka TE, Bizuayehu T, Ayalew F, H/Meskel G, Tadesse S, Jerene D, Makonnen E, Aklillu E (2019) HIV and cART-associated dyslipidemia among HIV-infected children. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040430
Vos AG, Chersich MF, Klipstein-Grobusch K, Zuithoff P, Moorhouse MA, Lalla-Edward ST, Kambugu A, Kumarasamy N, Grobbee DE, Barth RE, Venter WD (2018) Lipid levels, insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk over 96 weeks of antiretroviral therapy: a randomised controlled trial comparing low-dose stavudine and tenofovir. Retrovirology 15(1):77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12977-018-0460-z
Wang X, Mehra S, Kaushal D, Veazey RS, Xu H (2021) Abnormal tryptophan metabolism in HIV and Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. Front Microbiol 12:666227. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.666227
Webel AR, Jenkins T, Vest M, Oliveira VHF, Longenecker CT, Liu J, Currie J, Sattar A, Josephson R (2019) Cardiorespiratory fitness is associated with inflammation and physical activity in HIV+ adults. AIDS 33(6):1023–1030. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000002154
Yaribeygi H, Farrokhi FR, Butler AE, Sahebkar A (2019) Insulin resistance: review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. J Cell Physiol 234(6):8152–8161. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27603
Zangerle R, Kurz K, Neurauter G, Kitchen M, Sarcletti M, Fuchs D (2010) Increased blood phenylalanine to tyrosine ratio in HIV-1 infection and correction following effective antiretroviral therapy. Brain Behav Immun 24(3):403–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2009.11.004
Zhang X, Qu YY, Liu L, Qiao YN, Geng HR, Lin Y, Xu W, Cao J, Zhao JY (2021) Homocysteine inhibits pro-insulin receptor cleavage and causes insulin resistance via protein cysteine-homocysteinylation. Cell Rep 37(2):109821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109821
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFC2304800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82072265), the Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou (20220020285, 20220020276, 202201010874 and 2023A03J0813), the Project of Health Science and Technology of Guangzhou (20191A011039), the Medical Science and Technology Foundation of Guangdong (A2023219), the YIWEN Talent Project of The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University (2021#9) and the Medical Key Discipline Program of Guangzhou-Viral Infectious Diseases (2021–2023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: SZ, ZY, JZ. Methodology: ZY, JZ, YC. Formal analysis and investigation: JZ, YC, MW, LZ, ZY. Writing—original draft preparation: JZ, YC. Writing—review and editing: LL, ZY, SZ. Funding acquisition: LL, ZY, JZ, YC. Resources: LL. Supervision: SZ.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Commission of Guangzhou Eighth People’s Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University (ref. no. 201913126), and written informed consent was obtained from all the subjects.
Additional information
Handling editor: S. Broeer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Chen, Y., Wang, M. et al. Amino acid metabolism dysregulation associated with inflammation and insulin resistance in HIV-infected individuals with metabolic disorders. Amino Acids 55, 1545–1555 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03325-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03325-x