Abstract
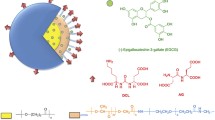
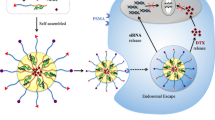
Prostate cancer is a global disease that negatively affects the quality of life. Although various strategies against prostate cancer have been developed, only a few achieved tumor-specific targeting. Therefore, a special emphasis has been placed on the treatment of cancer using nano-carrier-encapsulated chemotherapeutic agents conjugated with tumor-homing peptides. The targeting strategy coupling the drugs with nanotechnology helps to overcome the most common barriers, such as high toxicity and side effects. Prostate-specific membrane antigen has emerged as a promising target molecule for prostate cancer and shown to be targeted with high affinity by GRFLTGGTGRLLRIS peptide known as peptide 563 (P563). Here, we aimed to assess the in vitro and in vivo targeting efficiency, safety, and efficacy of P563-conjugated, docetaxel (DTX)-loaded polymeric micelle nanoparticles (P563-PEtOx-co-PEI30%-b-PCL-DTX) against prostate cancer. To this end, we analyzed the cytotoxic activity of P563-PEtOx-co-PEI30%-b-PCL and P563-PEtOx-co-PEI30%-b-PCL-DTX by a cell proliferation assay using PNT1A and 22Rv1 cells. We have also determined the targeting selectivity of P563-PEtOx-co-PEI30%-b-PCL-FITC by flow cytometry and assessed the induction of cell death by western blot and TUNEL assays for P563-PEtOx-co-PEI30%-b-PCL-DTX in 22Rv1 cells. To investigate the in vivo efficacy, we administered DTX in the free form or in polymeric micelle nanoparticles to athymic CD-1 nu/nu mice 22Rv1 xenograft models and performed histopathological analyses. Our study showed that targeting prostate cancer with P563-conjugated PEtOx-co-PEI30%-b-PCL polymeric micelles could exert a potent anti-cancer activity with low side effects.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Adams N, Schubert US (2007) Poly(2-oxazolines) in biological and biomedical application contexts. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:1504–1520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.08.018
Alven S, Aderibigbe BA (2020) The therapeutic efficacy of dendrimer and micelle formulations for breast cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics 12:1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121212
Barrio M, Fendler WP, Czernin J, Herrmann K (2016) Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) ligands for diagnosis and therapy of prostate cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 16:1177–1188. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737159.2016.1243057
Bhatia NM, Kulkarni PK, Ashtekar SS, Mahuli DV, Bhatia MS (2018) Synthesis, characterization, pharmacokinetics and evaluation of cytotoxicity for docetaxel-oleate conjugate targeting MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Pharm Chem J 51:1005–1013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-018-1730-8
Bhattacharjee S (2016) DLS and zeta potential–what they are and what they are not? J of Control Release 235:337–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.06.017
Bill-Axelson A, Holmberg L, Ruutu M, Garmo H, Stark JR, Busch C, Nordling S, Häggman M, Andersson SO, Bratell S, Spångberg A, Palmgren J, Steineck G, Adami HO, Johansson JE, SPCG-4 Investigators (2011) Radical prostatectomy versus watchful waiting in early prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 364:1708–1717. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1011967
Bourzat JD, Lavelle F, Commerçon A (1995) Synthesis and biological activity of Para-substituted 3′-phenyl docetaxel analogs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5:809–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-894X(95)00118-D
Carter RE, Feldman AR, Coyle JT (1996) Prostate-specific membrane antigen is a hydrolase with substrate and pharmacologic characteristics of a neuropeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:749–753. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.2.749
Chishti N, Jagwani S, Dhamecha D, Jalalpure S, Dehghan MH (2019) Preparation, optimization, and in vivo evaluation of nanoparticle-based formulation for pulmonary delivery of anticancer drug. Medicina (Kaunas) 55:294. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060294
da Silva GH, Fernandes MA, Trevizan LNF, de Lima FT, Eloy JO, Chorilli MA (2018) Critical review of properties and analytical methods for the determination of docetaxel in biological and pharmaceutical matrices. Crit Rev Anal Chem 48:517–527. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2018.1456315
Danaei M, Dehghankhold M, Ataei S, Hasanzadeh Davarani F, Javanmard R, Dokhani A, Khorasani S, Mozafari MR (2018) Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 10:57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020057
Denmeade SR, Isaacs JT (2002) A history of prostate cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer 2:389–396. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc801
Gao Y, Li Y, Li Y, Yuan L, Zhou Y, Li J, Zhao L, Zhang C, Li X, Liu Y (2015) PSMA-mediated endosome escape-accelerating polymeric micelles for targeted therapy of prostate cancer and the real time tracing of their intracellular trafficking. Nanoscale 7:597–612. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr05738d
Gao N, Xing C, Wang H, Feng L, Zeng X, Mei L (2019) pH-responsive dual drug-loaded nanocarriers based on poly (2-Ethyl-2-Oxazoline) modified black phosphorus nanosheets for cancer chemo/photothermal therapy. Front Pharmacol 10:270. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00270
Gulyuz S, Ozkose UU, Kocak P, Telci D, Yilmaz O, Tasdelen MA (2018) In-vitro cytotoxic activities of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)-based amphiphilic block copolymers prepared by CuAAC click chemistry. Express Polym Lett 12:146–158. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2018.13
Gulyuz S, Ozkose UU, Khalily MP, Kesici MS, Kocak P, Bolat ZB, Kara A, Ozturk N, Ozcubukcu S, Bozkir A, Alpturk O, Telci D, Sahin F, Vural I, Yilmaz O (2021) Poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline-co-ethyleneimine)-block-poly (ε-caprolactone) based micelles: synthesis, characterization, peptide conjugation and cytotoxic activity. New J Chem 45:14532–14547. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ01647D
Haberkorn U, Eder M, Kopka K, Babich JW, Eisenhut M (2016) New strategies in prostate cancer: prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) ligands for diagnosis and therapy. Clin Cancer Res 22:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0820
Hassan S, Buchanan M, Jahan K, Aguilar-Mahecha A, Gaboury L, Muller WJ, Alsawafi Y, Mourskaia AA, Siegel PM, Salvucci O, Basik M (2011) CXCR4 peptide antagonist inhibits primary breast tumor growth, metastasis and enhances the efficacy of anti-VEGF treatment or docetaxel in a transgenic mouse model. Int J Cancer 2:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25665
Huggins C (1942) Effect of orchiectomy and irradiation on cancer. Ann Surg 115:1192–1200. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-194206000-00030
Imran M, Saleem S, Chaudhuri A, Ali J, Baboota S (2020) Docetaxel: an update on its molecular mechanisms, therapeutic trajectory and nanotechnology in the treatment of breast, lung and prostate cancer. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec 60:101959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101959
Jennings D, Hatton BN, Guo J, Philippe J, Trouard TP, Raghunand N, Marshall J, Gillies RJ (2002) Early response of prostate carcinoma xenografts to docetaxel chemotherapy monitored with diffusion MRI. Neoplasia 4:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.neo.7900225
Kara A, Ozturk N, Esendagli G, Ozkose UU, Gulyuz S, Yilmaz O, Telci D, Bozkir A, Vural I (2018) Development of novel self-assembled polymeric micelles from partially hydrolysed poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline )-co-PEI-b-PCL block copolymer as non-viral vectors for plasmid DNA in vitro transfection. Artif Cell Nanomed B 46:S264–S273. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1491478
Kiess AP, Banerjee SR, Mease RC, Rowe SP, Rao A, Foss CA, Chen Y, Yang X, Cho SY, Nimmagadda S, Pomper MG (2015) Prostate-specific membrane antigen as a target for cancer imaging and therapy. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 59:241–268 (PMID: 26213140)
Kolluru LP, Chandran T, Shastri PN, Rizvi SAA, D’Souza MJ (2020) Development and evaluation of polycaprolactone based docetaxel nanoparticle formulation for targeted breast cancer therapy. J Nanopart Res 22:372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05096-y
Kondo E, Iioka H, Saito K (2021) Tumor-homing peptide and its utility for advanced cancer medicine. Cancer Sci 112:2118–2125. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14909
Kyrylkova K, Kyryachenko S, Leid M, Kioussi C (2012) Detection of apoptosis by TUNEL assay. Methods Mol Biol 887:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-860-3
Litwin MS, Tan HJ (2017) The diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer: a review. JAMA 317:2532–2542. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.7248
Mahmood MA, Madni A, Rehman M, Rahim MA, Jabar A (2019) Ionically cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles for sustained delivery of docetaxel: fabrication, post-formulation and acute oral toxicity evaluation. Int J Nanomedicine 14:10035–10046. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S232350
Makhov P, Golovine K, Canter D, Kutikov A, Simhan J, Uzzo CMM, RG, Kolenko VM, (2012) Co-administration of piperine and docetaxel results in improved anti-tumor efficacy via inhibition of CYP3A4 activity. Prostate 72:661–667. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.21469
Mandracchia D, Tripodo G, Latrofa A, Dorati R (2014) Amphiphilic inulin-d-α-tocopherol succinate (INVITE) bioconjugates for biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym 103:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.11.056
Matsumura Y, Kataoka K (2009) Preclinical and clinical studies of anticancer agent-incorporating polymer micelles. Cancer Sci 100:572–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01103.x
Mudalige T, Qu H, Van Haute D, Ansar SM, Paredes A, Ingle T (2019) Characterization of nanomaterials: tools and challenges. In: López Rubio A (ed) Nanomaterials for food applications. Elsevier, pp 313–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814130-4.00011-7
Narvekar M, Xue HY, Eoh JY, Wong HL (2014) Nanocarrier for poorly water-soluble anticancer drugs—barriers of translation and solutions. AAPS PharmSciTech 15:822–833. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-014-0107-x
Nayman AH, Siginc H, Zemheri E, Yencilek F, Yildirim A, Telci D (2019) Dual-inhibition of mTOR and Bcl-2 enhances the anti-tumor effect of everolimus against renal cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. J Cancer 10:1466–1478. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.29192
Nezir AE, Khalily MP, Gulyuz S, Ozcubukcu S, Kucukguzel SG, Yilmaz O, Telci D (2021) Synthesis and evaluation of tumor-homing peptides for targeting prostate cancer. Amino Acids 53:645–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02971-3
Ozturk N, Kara A, Gulyuz S, Ozkose UU, Tasdelen MA, Bozkir A, Yilmaz O, Vural I (2020) Exploiting ionisable nature of PEtOx-co-PEI to prepare pH sensitive, doxorubicin-loaded micelles. J Microencapsul 37:467–480. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652048.2020.1792566
Salji MJ, Ahmad I, Slater S, Poon FW, Alhasso A, Melquiot NV, Bekarma H, Hendry J, Leung HY (2019) Prostate neoplasm. In: Aboumarzouk OM (ed) Blandy’s urology, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118863343.ch28
Shen D, Xie F, Edwards WB (2013) Evaluation of phage display discovered peptides as ligands for prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA). PLoS One 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068339
Tan Q, Liu X, Fu X, Li Q, Dou J, Zhai G (2012) Current development in nanoformulations of docetaxel. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 9:975–990. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2012.696606
Thambiraj S, Vijayalakshmi R, Shankaran DR (2021) An effective strategy for development of docetaxel encapsulated gold nanoformulations for treatment of prostate cancer. Sci Rep 11:2802. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80529-1
Tripodo G, Mandracchia D, Dorati R, Latrofa A, Genta I, Conti B (2013) Nanostructured polymeric functional micelles for drug delivery applications. Macromole Symp 334:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201300099
Tripodo G, Mandracchia D, Collina S, Rui M, Rossi D (2014) New perspectives in cancer therapy: the biotin-antitumor molecule conjugates. Med Chem S1:1–8. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0444.S1-004
van Beek ER, Lowik CWGM, van Wijngaarden J, Ebetino FH, Papapoulos SE (2009) Synergistic effect of bisphosphonate and docetaxel on the growth of bone metastasis in an animal model of established metastatic bone disease. Breast Cancer Res Treat 118:307–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0236-6
Varela-Moreira A, Shi Y, Fens MHAM, Lammers T, Hennink WE, Schiffelers RM (2017) Clinical application of polymeric micelles for the treatment of cancer. Mater Chem Front 1:1485–1501. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6QM00289G
Wang Y, Zuo A, Huang X, Ying Y, Shu X, Chen X, Yang Y, Ma J, Lin G, Wang X, Mei L, Liu G, Zhao Y (2019) Docetaxel-loaded PAMAM-based poly (γ-benzyl-l-glutamate)-b-d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate nanoparticles in human breast cancer and human cervical cancer therapy. J Microencapsul 36:552–565. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652048.2019.1654002
Woodruff MA, Hutmacher DW (2010) The return of a forgotten polymer—polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2010.04.002
Wüstemann T, Haberkorn U, Babich J, Mier W (2018) Targeting prostate cancer: prostate-specific membrane antigen based diagnosis and therapy. Med Res Rev 39:40–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21508
Yokoyama M (2014) Polymeric micelles as drug carriers: their lights and shadows. J Drug Target 22:576–583. https://doi.org/10.3109/1061186X.2014.934688
Zhang L, Zhang N (2013) How nanotechnology can enhance docetaxel therapy. Int J Nanomedicine 8:2927–2941. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S46921
Zhang X, Liu J, Li X, Li F, Lee RJ, Sun F, Li Y, Liu Z, Teng L (2019) Trastuzumab-coated nanoparticles loaded with docetaxel for breast cancer therapy. Dose Response 17:1559325819872583. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559325819872583
Zhang H, Liu X, Xu T, Xu K, Du B, Li Y (2020) Biodegradable reduction and pH dual-sensitive polymer micelles based on poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) for efficient delivery of curcumin. RSC Adv 10:25435–25445. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA02779K
Zhao Y, Dandan S, Shang M, Sun X, Guo L, Meng D, Liu X, Zhou X, Li J (2022) GRP78-targeted and doxorubicin-loaded nanodroplets combined with ultrasound: a potential novel theranostics for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Drug Delivery 29:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2021.2023698
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK, grant numbers 213M726 and 213M728) is gratefully acknowledged. All cell culture and animal experiments were conducted at Yeditepe University. We would like to thank Ayla Burcin Asutay and Murat Ozpolat for their technical support on flow cytometer. We also thank Engin Sumer, Ayse Hande Nayman, Halime Ilhan-Siginc, Selen Tiryaki, and Ipek Bedir for their technical support in the in vivo experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AEN, NO, and DT; Development of methodology: AEN, NO, SG, UUO, IV, OY, AB, and DT; Investigation: AEN, ZBB, PK, IEZ and DT; Writing- Original Draft: AEN, NO, and DT; Writing-Review and Editing: DT and FS; Supervision: DT.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling editor: E. Closs.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nezir, A.E., Bolat, Z.B., Ozturk, N. et al. Targeting prostate cancer with docetaxel-loaded peptide 563-conjugated PEtOx-co-PEI30%-b-PCL polymeric micelle nanocarriers. Amino Acids 55, 1023–1037 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03292-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03292-3