Abstract
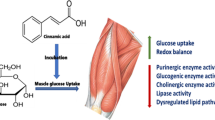
The antidiabetic effect of l-leucine has been attributed to its modulatory effect on glucose uptake and lipid metabolism in muscles. However, there is a dearth on its effect on glucose metabolism in muscles. Thus, the present study investigated the effect of l-leucine – stimulated glucose uptake on glucose metabolism, dysregulated lipid metabolic pathways, redox and bioenergetic homeostasis, and proteolysis in isolated psoas muscle from Sprague Dawley male rats. Isolated psoas muscles were incubated with l-leucine (30–240 μg/mL) in the presence of 11.1 mMol glucose at 37 ˚C for 2 h. Muscles incubated in only glucose served as the control, while muscles not incubated in l-leucine and/or glucose served as the normal control. Metformin (6.04 mM) was used as the standard antidiabetic drug. Incubation with l-leucine caused a significant increase in muscle glucose uptake, with an elevation of glutathione levels, superoxide dismutase, catalase, E-NTPDase and 5’nucleotidase activities. It also led to the depletion of malondialdehyde and nitric oxide levels, ATPase, chymotrypsin, acetylcholinesterase, glycogen phosphorylase, glucose-6-phosphatase, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and lipase activities. There was an alteration in lipid metabolites, with concomitant activation of glycerolipid metabolism, fatty acid metabolism, and fatty acid elongation in mitochondria in the glucose-incubated muscle (negative control). Incubation with l-leucine reversed these alterations, and concomitantly deactivated the pathways. These results indicate that l-leucine-enhanced muscle glucose uptake involves improved redox and bioenergetic homeostasis, with concomitant suppressed proteolytic, glycogenolytic and gluconeogenetic activities, while modulating glucose – lipid metabolic switch.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ademiluyi AO, Ogunsuyi OB, Oboh G (2016) Alkaloid extracts from Jimson weed (Datura stramonium L.) modulate purinergic enzymes in rat brain. Neurotoxicology 56:107–117
Adewoye O, Bolarinwa A, Olorunsogo O (2000) Ca++, Mg++-ATPase activity in insulin-dependent and non-insulin dependent diabetic Nigerians. Afr J Med Med Sci 29(3–4):195–199
Aird TP, Davies RW, Carson BP (2018) Effects of fasted vs fed-state exercise on performance and post-exercise metabolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports 28(5):1476–1493
Akinyemi AJ, Onyebueke N, Faboya OA, Onikanni SA, Fadaka A, Olayide I (2017) Curcumin inhibits adenosine deaminase and arginase activities in cadmium-induced renal toxicity in rat kidney. J Food Drug Anal 25(2):438–446
Aoi W, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T (2013) Role of oxidative stress in impaired insulin signaling associated with exercise-induced muscle damage. Free Radic Biol Med 65:1265–1272
Aragno M, Mastrocola R, Catalano MG, Brignardello E, Danni O, Boccuzzi G (2004) Oxidative stress impairs skeletal muscle repair in diabetic rats. Diabetes 53(4):1082–1088
Bailey CJ, Turner RC (1996) Metformin. N Engl J Med 334(9):574–579
Balogun F, Ashafa A (2017) Aqueous root extracts of Dicoma anomala (Sond.) extenuates postprandial hyperglycaemia in vitro and its modulation on the activities of carbohydrate-metabolizing enzymes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats. S Afr J Bot 112:102–111
Bianco AC, McAninch EA (2013) The role of thyroid hormone and brown adipose tissue in energy homoeostasis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 1(3):250–258
Boersma GJ, Johansson E, Pereira MJ et al (2018) Altered glucose uptake in muscle, visceral adipose tissue, and brain predict whole-body insulin resistance and may contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes: a combined PET/MR study. Horm Metab Res 50(08):627–639
Bornø A, Ploug T, Bune L, Rosenmeier J, Thaning P (2012) Purinergic receptors expressed in human skeletal muscle fibres. Purinergic Signal 8(2):255–264
Burnstock G, Arnett TR, Orriss IR (2013) Purinergic signalling in the musculoskeletal system. Purinergic Signal 9(4):541–572
Cahova M, Vavřínková H, Kazdova L (2007) Glucose-fatty acid interaction in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue in insulin resistance. Physiol Res 56(1):1–15
Campbell I (2007) Oral antidiabetic drugs: their properties and recommended use. Prescriber 18(6):56–74
Chong J, Soufan O, Li C et al (2018) MetaboAnalyst 4.0: towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 46(1W):W486–W494
Chowdhury P, Soulsby M (2002) Lipid peroxidation in rat brain is increased by simulated weightlessness and decreased by a soy-protein diet. Ann Clin Lab Sci 32(2):188–192
Chukwuma CI, Islam MS (2015) Effects of xylitol on carbohydrate digesting enzymes activity, intestinal glucose absorption and muscle glucose uptake: a multi-mode study. Food Funct 6(3):955–962
Cornblath M, Randle P, Parmeggiani A, Morgan H (1963) Regulation of glycogenolysis in muscle effects of glucagon and anoxia on lactate production, glycogen content, and phosphorylase activity in the perfused isolated rat heart. J Biol Chem 238(5):1592–1597
Debard C, Laville M, Berbe V et al (2004) Expression of key genes of fatty acid oxidation, including adiponectin receptors, in skeletal muscle of Type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 47(5):917–925
Devries MC, McGlory C, Bolster DR et al (2018) Leucine, not total protein, content of a supplement is the primary determinant of muscle protein anabolic responses in healthy older women. J Nutr 148(7):1088–1095
Di Virgilio F, Adinolfi E (2017) Extracellular purines, purinergic receptors and tumor growth. Oncogene 36(3):293–303
Doleski PH, Leal DB, Machado VS et al (2017) Diphenyl diselenide modulates nucleotidases, reducing inflammatory responses in the liver of Toxoplasma gondii-infected mice. Purinergic Signal 13(4):489–496
Donato J Jr, Pedrosa RG, Cruzat VF, de Oliveira Pires IS, Tirapegui J (2006) Effects of leucine supplementation on the body composition and protein status of rats submitted to food restriction. Nutrition 22(5):520–527
Duan Y, Li F, Li Y et al (2016) The role of leucine and its metabolites in protein and energy metabolism. Amino Acids 48(1):41–51
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–95
Erukainure OL, Mopuri R, Oyebode OA, Koorbanally NA, Islam MS (2017) Dacryodes edulis enhances antioxidant activities, suppresses DNA fragmentation in oxidative pancreatic and hepatic injuries; and inhibits carbohydrate digestive enzymes linked to type 2 diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother 96:37–47
Erukainure OL, Salau VF, Xiao X, Matsabisa MG, Koorbanally NA, Islam MS (2020) Bioactive compounds of African star apple (Chrysophyllum albidum G. Don) and its modulatory effect on metabolic activities linked to type 2 diabetes in isolated rat psoas muscle. J Food Biochem 45(1):e13576
Filhiol TM (2012) The effects of leucine on mitochondrial biogenesis and cell cycle in A-375 melanoma cells. The University of Tennessee, Knoxville
Frampton J, Murphy KG, Frost G, Chambers ES (2020) Short-chain fatty acids as potential regulators of skeletal muscle metabolism and function. Nat Metab 2(9):840–848
Frontera WR, Ochala J (2015) Skeletal muscle: a brief review of structure and function. Calcif Tissue Int 96(3):183–195
Gancedo JM, Gancedo C (1971) Fructose-1, 6-diphosphatase, phosphofructokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from fermenting and non fermenting yeasts. Arch Mikrobiol 76(2):132–138
Görgens SW, Benninghoff T, Eckardt K et al (2017) Hypoxia in combination with muscle contraction improves insulin action and glucose metabolism in human skeletal muscle via the HIF-1α pathway. Diabetes 66(11):2800–2807
Guo K, Yu Y-H, Hou J, Zhang Y (2010) Chronic leucine supplementation improves glycemic control in etiologically distinct mouse models of obesity and diabetes mellitus. Nutr Metab 7:57
Hadwan MH, Abed HN (2016) Data supporting the spectrophotometric method for the estimation of catalase activity. Data Brief 6:194–199
Hänninen O, Atalay M (1998) Oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle. In: Reznick AZ (ed) Oxidative stress in skeletal muscle. Springer, Switzerland, pp 29–42
Kakkar P, Das B, Viswanathan P (1984) A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase. Indian J Biochem Biophys 21:130–132
Kim MS, Lee J, Ha J et al (2002) ATP stimulates glucose transport through activation of P2 purinergic receptors in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 401(2):205–214
Kim YS, Lee YM, Kim H et al (2010) Anti-obesity effect of Morus bombycis root extract: anti-lipase activity and lipolytic effect. J Ethnopharmacol 130(3):621–624
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T et al (2019) PubChem 2019 update: improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D1102–D1109
Koren D, Palladino A (2016) Hypoglycemia. In: Weiss RE, Refetoff S (eds) Genetic diagnosis of endocrine disorders. Elsevier, London, pp 31–75
Levinger I, Lin X, Zhang X et al (2016) The effects of muscle contraction and recombinant osteocalcin on insulin sensitivity ex vivo. Osteoporos Int 27(2):653–663
Liu H, Liu R, Xiong Y et al (2014) Leucine facilitates the insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and insulin signaling in skeletal muscle cells: involving mTORC1 and mTORC2. Amino Acids 46(8):1971–1979
Liu Z, Apontes P, Fomenko EV et al (2018) Mangiferin accelerates glycolysis and enhances mitochondrial bioenergetics. Int J Mol Sci 19(1):201
Luo X, Wu J, Jing S, Yan L-J (2016) Hyperglycemic stress and carbon stress in diabetic glucotoxicity. Aging Dis 7(1):90–110
Mahato AK, Bhattacharya S, Shanthi N (2011) Design, synthesis and Glucose-6-Phosphatase inhibitory activity of diaminoguanidine analogues of 3-Guanidinopropionic acid and amino substituted (Pyridin-2-Yl) thiourea derivatives. J Pharm Sci Res 3:896–902
Marı́n-Garcı́a J, Goldenthal MJ (2002) Fatty acid metabolism in cardiac failure: biochemical, genetic and cellular analysis. Cardiovasc Res 54(3):516–527
Maritim A, Sanders R, Watkins J III (2003) Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 17(1):24–38
Mastrocola R, Reffo P, Penna F et al (2008) Muscle wasting in diabetic and in tumor-bearing rats: role of oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 44(4):584–593
Mazibuko-Mbeje SE, Dludla PV, Nkambule BB, Obonye N, Louw J (2018) The role of glucose and fatty acid metabolism in the development of insulin resistance in skeletal muscle Muscle cell and tissue-current status of research field. IntechOpen, London, UK
Messina S, Altavilla D, Aguennouz Mh et al (2006) Lipid peroxidation inhibition blunts nuclear factor-κB activation, reduces skeletal muscle degeneration, and enhances muscle function in mdx mice. Am J Pathol 168(3):918–926
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W et al (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30(16):2785–2791
Mortensen SP, González-Alonso J, Bune LT, Saltin B, Pilegaard H, Hellsten Y (2009) ATP-induced vasodilation and purinergic receptors in the human leg: roles of nitric oxide, prostaglandins, and adenosine. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296(4):R1140–R1148
Nishitani S, Matsumura T, Fujitani S, Sonaka I, Miura Y, Yagasaki K (2002) Leucine promotes glucose uptake in skeletal muscles of rats. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 299(5):693–696
Oizel K, Tait-Mulder J, Fernandez-de-Cossio-Diaz J et al (2020) Formate induces a metabolic switch in nucleotide and energy metabolism. Cell Death Dis 11(5):1–14
Oliveira-Batista Rd, Silva A, Passos KMRd, Nogueira RMB, Seraphim PM (2015) Six-week anaerobic training improves proteolytic profile of diabetic rats. Arch Endocrinol Metab 59(5):400–406
Pasiakos SM, Carbone JW (2014) Assessment of skeletal muscle proteolysis and the regulatory response to nutrition and exercise. IUBMB Life 66(7):478–484
Pereira RM, Moura LPd, Muñoz VR et al (2017) Molecular mechanisms of glucose uptake in skeletal muscle at rest and in response to exercise. Motriz: Rev Ed Fís e101609
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC et al (2004) UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612
Ralston-Hooper K, Jannasch A, Adamec J, Sepúlveda M (2011) The use of two-dimensional gas chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry (gc× gc–tof-ms) for metabolomic analysis of polar metabolites. In: Metz TO (ed) Metabolic Profiling. Springer, Berlin, Germany p, pp 205–211
Randle P, Garland P, Hales C, Newsholme E (1963) The glucose fatty-acid cycle its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 281(7285):785–789
Roden M (2004) How free fatty acids inhibit glucose utilization in human skeletal muscle. Physiology 19(3):92–96
Rolo AP, Palmeira CM (2006) Diabetes and mitochondrial function: role of hyperglycemia and oxidative stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 212(2):167–178
Salau VF, Erukainure OL, Ibeji CU, Koorbanally NA, Islam MS (2020) Umbelliferone stimulates glucose uptake; modulates gluconeogenic and nucleotide-hydrolyzing enzymes activities, and dysregulated lipid metabolic pathways in isolated psoas muscle. J Funct Foods 67:103847
Saleem H, Ahmad I, Ashraf M et al (2016) In vitro studies on anti-diabetic and anti-ulcer potentials of Jatropha gossypifolia (Euphorbiaceae). Trop J Pharm Res 15(1):121–125
Schetinger MRC, Morsch VM, Bonan CD, Wyse AT (2007) NTPDase and 5’-nucleotidase activities in physiological and disease conditions: new perspectives for human health. BioFactors 31(2):77–98
Schnuck JK, Sunderland KL, Gannon NP, Kuennen MR, Vaughan RA (2016) Leucine stimulates PPARβ/δ-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative metabolism with enhanced GLUT4 content and glucose uptake in myotubes. Biochimie 128:1–7
Schrödinger (2020) Release 2020–4: LigPrep. Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY
Shen X, Wang L, Zhou N, Gai S, Liu X, Zhang S (2020) Beneficial effects of combination therapy of phloretin and metformin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and improved insulin sensitivity in vitro. Food Funct 11(1):392–403
Tipton KD, Hamilton DL, Gallagher IJ (2018) Assessing the role of muscle protein breakdown in response to nutrition and exercise in humans. Sports Med 48(1):53–64
Tripathi BK, Srivastava AK (2006) Diabetes mellitus: Complications and therapeutics. Med Sci Monit 12(7):RA130–RA147
Tsikas D (2005) Review Methods of quantitative analysis of the nitric oxide metabolites nitrite and nitrate in human biological fluids. Free Radic Res 39(8):797–815
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Yao X-g et al (2012) (+)-Rutamarin as a dual inducer of both GLUT4 translocation and expression efficiently ameliorates glucose homeostasis in insulin-resistant mice. PLoS ONE 7(2):e31811
Zhang L, Li F, Guo Q et al (2020) Leucine supplementation: a novel strategy for modulating lipid metabolism and energy homeostasis. Nutrients 12(5):1299
Funding
No funding was received for this study
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest relating to this work.
Research involving Human Participants and/or Animals
The study was undertaken in accordance with the approved guidelines of the Animal Ethics Committee of the University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa (Protocol approval number: AREC/022/019D).
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling editor: S. S. Gross.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erukainure, O.L., Salau, V.F., Atolani, O. et al. L-leucine stimulation of glucose uptake and utilization involves modulation of glucose – lipid metabolic switch and improved bioenergetic homeostasis in isolated rat psoas muscle ex vivo. Amino Acids 53, 1135–1151 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03021-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03021-8