Abstract
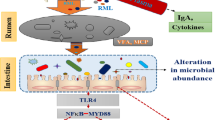
Glycine is an amino acid with a diverse array of health benefits regarding metabolism, immunity, and development. The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that glycine supplementation alters the intestinal microbial composition and improves the intestinal mucosal immunity of weaned piglets. One hundred and twenty-eight weaned piglets divided into 4 groups were fed with a corn- and soybean meal-based diet supplemented with 0 (control), 0.5, 1, or 2% glycine for 7 days. The intestinal microbiota and tissue samples from the control and the 2% glycine-supplemented piglets were collected for determination of the composition of microbial community and the intestinal mucosal barrier function. Piglets fed with diet containing 2% glycine, instead of 0.5% or 1% glycine, presented elevated average daily gain and feed conversion ratio, as compared with the control. 2% glycine enhanced the abundance of mucins in the jejunum and ileum and mRNA level of porcine β-defensin (pBD) 2 and pBD-3, as well as the protein level of secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) in the jejunum. The mRNA expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6, and the protein level of phosphorylated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65, and claudin-2 in the jejunum were lower in the 2% glycine group than that in the control. In addition, an elevated ratio of CD4+/CD8+ T lymphocytes was observed in the jejunum of piglets receiving diet supplemented with 2% glycine. The colon content of piglets fed with 2% glycine exhibited a reduction in abundance of pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia–Shigella, Clostridium, and Burkholderiales) and an increase in short-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria (Blautia, Lachnospiraceae, Anaerostipes, and Prevotella) in comparison with the control. We conclude that dietary supplementation with 2% glycine improves the intestinal immunological barrier function and the microbial composition, therefore, contributing to the growth performance of weaned piglets.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeola O, King DE (2006) Developmental changes in morphometry of the small intestine and jejunal sucrase activity during the first nine weeks of postnatal growth in pigs. J Anim Sci 84(1):112–118. https://doi.org/10.2527/2006.841112x
Al-Sadi R, Ye D, Boivin M, Guo S, Hashimi M, Ereifej L, Ma TY (2014) Interleukin-6 modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability is mediated by JNK pathway activation of claudin-2 gene. PLoS ONE 9(3):e85345. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085345
Alves A, Bassot A, Bulteau AL, Pirola L, Morio B (2019) Glycine metabolism and its alterations in obesity and metabolic diseases. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061356
Ananthakrishnan AN, Luo C, Yajnik V, Khalili H, Garber JJ, Stevens BW, Cleland T, Xavier RJ (2017) Gut microbiome function predicts response to anti-integrin biologic therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Cell Host Microbe 21(5):603-610 e603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2017.04.010
Atay O, Skotheim JM (2017) Spatial and temporal signal processing and decision making by MAPK pathways. J Cell Biol 216(2):317–330. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201609124
Baxter NT, Schmidt AW, Venkataraman A, Kim KS, Waldron C, Schmidt TM (2019) Dynamics of human gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in response to dietary interventions with three fermentable fibers. MBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02566-18
Bien J, Palagani V, Bozko P (2013) The intestinal microbiota dysbiosis and Clostridium difficile infection: is there a relationship with inflammatory bowel disease? Therap Adv Gastroenterol 6(1):53–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756283X12454590
Chelakkot C, Ghim J, Ryu SH (2018) Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp Mol Med 50(8):103. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0126-x
D’Acquisto F, Crompton T (2011) CD3+CD4-CD8- (double negative) T cells: saviours or villains of the immune response? Biochem Pharmacol 82(4):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2011.05.019
de Picanco Aguiar E, Lopes-Paulo F, Marques RG, Diestel CF, Caetano CE, de Souza MV, Moscoso GM, Pazos HM (2011) L-arginine and glycine supplementation in the repair of the irradiated colonic wall of rats. Int J Colorectal Dis 26(5):561–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1154-3
Dupont A, Heinbockel L, Brandenburg K, Hornef MW (2014) Antimicrobial peptides and the enteric mucus layer act in concert to protect the intestinal mucosa. Gut Microbes 5(6):761–765. https://doi.org/10.4161/19490976.2014.972238
Fan X, Li S, Wu Z, Dai Z, Li J, Wang X, Wu G (2019) Glycine supplementation to breast-fed piglets attenuates post-weaning jejunal epithelial apoptosis: a functional role of CHOP signaling. Amino Acids 51(3):463–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2681-9
Fuchs SA, Peeters-Scholte CM, de Barse MM, Roeleveld MW, Klomp LW, Berger R, de Koning TJ (2012) Increased concentrations of both NMDA receptor co-agonists D-serine and glycine in global ischemia: a potential novel treatment target for perinatal asphyxia. Amino Acids 43(1):355–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1086-9
Grotz MR, Pape HC, van Griensven M, Stalp M, Rohde F, Bock D, Krettek C (2001) Glycine reduces the inflammatory response and organ damage in a two-hit sepsis model in rats. Shock 16(2):116–121
Hartog A, Leenders I, van der Kraan PM, Garssen J (2007) Anti-inflammatory effects of orally ingested lactoferrin and glycine in different zymosan-induced inflammation models: evidence for synergistic activity. Int Immunopharmacol 7(13):1784–1792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2007.09.019
Hu CH, Xiao K, Luan ZS, Song J (2013) Early weaning increases intestinal permeability, alters expression of cytokine and tight junction proteins, and activates mitogen-activated protein kinases in pigs. J Anim Sci 91(3):1094–1101. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2012-5796
Hussain T, Kulshreshtha KK, Yadav VS, Katoch K (2015) CD4+, CD8+, CD3+ cell counts and CD4+/CD8+ ratio among patients with mycobacterial diseases (leprosy, tuberculosis), HIV infections, and normal healthy adults: a comparative analysis of studies in different regions of India. J Immunoassay Immunochem 36(4):420–443. https://doi.org/10.1080/15321819.2014.978082
Johansson ME, Hansson GC (2016) Immunological aspects of intestinal mucus and mucins. Nat Rev Immunol 16(10):639–649. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.88
Le N, Mazahery C, Nguyen K, Levine AD (2021) Regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier and immune function by activated T Cells. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(1):55–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2020.07.004
Li X, Bradford BU, Wheeler MD, Stimpson SA, Pink HM, Brodie TA, Schwab JH, Thurman RG (2001) Dietary glycine prevents peptidoglycan polysaccharide-induced reactive arthritis in the rat: role for glycine-gated chloride channel. Infect Immun 69(9):5883–5891
Li W, Sun K, Ji Y, Wu Z, Wang W, Dai Z, Wu G (2016) Glycine regulates expression and distribution of claudin-7 and ZO-3 proteins in intestinal porcine epithelial cells. J Nutr 146(5):964–969. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.115.228312
Lopez-Pedrosa JM, Torres MI, Fernandez MI, Rios A, Gil A (1998) Severe malnutrition alters lipid composition and fatty acid profile of small intestine in newborn piglets. J Nutr 128(2):224–233. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/128.2.224
Luu M, Pautz S, Kohl V, Singh R, Romero R, Lucas S, Hofmann J, Raifer H, Vachharajani N, Carrascosa LC, Lamp B, Nist A, Stiewe T, Shaul Y, Adhikary T, Zaiss MM, Lauth M, Steinhoff U, Visekruna A (2019) The short-chain fatty acid pentanoate suppresses autoimmunity by modulating the metabolic-epigenetic crosstalk in lymphocytes. Nat Commun 10(1):760. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08711-2
Ma EH, Bantug G, Griss T, Condotta S, Johnson RM, Samborska B, Mainolfi N, Suri V, Guak H, Balmer ML, Verway MJ, Raissi TC, Tsui H, Boukhaled G, Henriques da Costa S, Frezza C, Krawczyk CM, Friedman A, Manfredi M, Richer MJ, Hess C, Jones RG (2017) Serine is an essential metabolite for effector T cell expansion. Cell Metab 25(2):345–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.12.011
Mantis NJ, Rol N, Corthesy B (2011) Secretory IgA’s complex roles in immunity and mucosal homeostasis in the gut. Mucosal Immunol 4(6):603–611. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2011.41
Martinez-Medina M, Garcia-Gil LJ (2014) Escherichia coli in chronic inflammatory bowel diseases: an update on adherent invasive Escherichia coli pathogenicity. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 5(3):213–227. https://doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v5.i3.213
Mauriz JL, Matilla B, Culebras JM, Gonzalez P, Gonzalez-Gallego J (2001) Dietary glycine inhibits activation of nuclear factor kappa B and prevents liver injury in hemorrhagic shock in the rat. Free Radic Biol Med 31(10):1236–1244
McCarty MF, O’Keefe JH, DiNicolantonio JJ (2018) Dietary glycine is rate-limiting for glutathione synthesis and may have broad potential for health protection. Ochsner J 18(1):81–87
McCracken BA, Spurlock ME, Roos MA, Zuckermann FA, Gaskins HR (1999) Weaning anorexia may contribute to local inflammation in the piglet small intestine. J Nutr 129(3):613–619
Meade KG, O’Farrelly C (2018) beta-defensins: farming the microbiome for homeostasis and health. Front Immunol 9:3072. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.03072
Moeser AJ, Klok CV, Ryan KA, Wooten JG, Little D, Cook VL, Blikslager AT (2007) Stress signaling pathways activated by weaning mediate intestinal dysfunction in the pig. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292(1):G173-181. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00197.2006
National Research Council (NRC) (2012) Nutrient requirements of swine. 11th rev. ed. National Academy Press, Washington, DC, USA
Ospina-Rojas IC, Murakami AE, Oliveira CAL, Guerra AFQG (2013) Supplemental glycine and threonine effects on performance, intestinal mucosa development, and nutrient utilization of growing broiler chickens. Poultry Sci 92(10):2724–2731. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2013-03171
Parada Venegas D, De la Fuente MK, Landskron G, Gonzalez MJ, Quera R, Dijkstra G, Harmsen HJM, Faber KN, Hermoso MA (2019) Short chain fatty acids (SCFAs)-mediated gut epithelial and immune regulation and its relevance for inflammatory bowel diseases. Front Immunol 10:277. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00277
Pelaseyed T, Bergstrom JH, Gustafsson JK, Ermund A, Birchenough GM, Schutte A, van der Post S, Svensson F, Rodriguez-Pineiro AM, Nystrom EE, Wising C, Johansson ME, Hansson GC (2014) The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol Rev 260(1):8–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12182
Pie S, Lalles JP, Blazy F, Laffitte J, Seve B, Oswald IP (2004) Weaning is associated with an upregulation of expression of inflammatory cytokines in the intestine of piglets. J Nutr 134(3):641–647
Powell S, Bidner TD, Payne RL, Southern LL (2011) Growth performance of 20- to 50-kilogram pigs fed low-crude-protein diets supplemented with histidine, cystine, glycine, glutamic acid, or arginine. J Anim Sci 89(11):3643–3650. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2010-3757
Rock KL, Kono H (2008) The inflammatory response to cell death. Annu Rev Pathol 3:99–126. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.151456
Rogier EW, Frantz AL, Bruno ME, Kaetzel CS (2014) Secretory IgA is concentrated in the outer layer of colonic mucus along with gut bacteria. Pathogens 3(2):390–403. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3020390
Rom O, Villacorta L, Zhang J, Chen YE, Aviram M (2018) Emerging therapeutic potential of glycine in cardiometabolic diseases: dual benefits in lipid and glucose metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol 29(5):428–432. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOL.0000000000000543
Rom O, Liu Y, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Wu J, Ghrayeb A, Villacorta L, Fan Y, Chang L, Wang L, Liu C, Yang D, Song J, Rech JC, Guo Y, Wang H, Zhao G, Liang W, Koike Y, Lu H, Koike T, Hayek T, Pennathur S, Xi C, Wen B, Sun D, Garcia-Barrio MT, Aviram M, Gottlieb E, Mor I, Liu W, Zhang J, Chen YE (2020) Glycine-based treatment ameliorates NAFLD by modulating fatty acid oxidation, glutathione synthesis, and the gut microbiome. Sci Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz2841
Rowland I, Gibson G, Heinken A, Scott K, Swann J, Thiele I, Tuohy K (2018) Gut microbiota functions: metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur J Nutr 57(1):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1445-8
Schaumann T, Kraus D, Winter J, Wolf M, Deschner J, Jager A (2013) Potential immune modularly role of glycine in oral gingival inflammation. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:808367. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/808367
Schilling T, Eder C (2004) A novel physiological mechanism of glycine-induced immunomodulation: Na+-coupled amino acid transporter currents in cultured brain macrophages. J Physiol 559(Pt 1):35–40. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.070763
Suzuki T (2013) Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol Life Sci 70(4):631–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1070-x
Suzuki T, Yoshinaga N, Tanabe S (2011) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) regulates claudin-2 expression and tight junction permeability in intestinal epithelium. J Biol Chem 286(36):31263–31271. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.238147
Takiishi T, Fenero CIM, Camara NOS (2017) Intestinal barrier and gut microbiota: shaping our immune responses throughout life. Tissue Barriers 5(4):e1373208. https://doi.org/10.1080/21688370.2017.1373208
Thoo L, Noti M, Krebs P (2019) Keep calm: the intestinal barrier at the interface of peace and war. Cell Death Dis 10(11):849. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2086-z
Tsune I, Ikejima K, Hirose M, Yoshikawa M, Enomoto N, Takei Y, Sato N (2003) Dietary glycine prevents chemical-induced experimental colitis in the rat. Gastroenterology 125(3):775–785
Utech M, Mennigen R, Bruewer M (2010) Endocytosis and recycling of tight junction proteins in inflammation. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:484987. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/484987
Van den Eynden J, Ali SS, Horwood N, Carmans S, Brone B, Hellings N, Steels P, Harvey RJ, Rigo JM (2009) Glycine and glycine receptor signalling in non-neuronal cells. Front Mol Neurosci 2:9. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.02.009.2009
van’t Land B, Schijf MA, Martin R, Garssen J, van Bleek GM (2011) Influencing mucosal homeostasis and immune responsiveness: the impact of nutrition and pharmaceuticals. Eur J Pharmacol 668(Suppl 1):S101-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.05.082
Vieira CP, De Oliveira LP, Da Re Guerra F, Dos Santos De Almeida M, Marcondes MC, Pimentel ER (2015) Glycine improves biochemical and biomechanical properties following inflammation of the achilles tendon. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 298(3):538–545. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.23041
Wang W, Dai Z, Wu Z, Lin G, Jia S, Hu S, Dahanayaka S, Wu G (2014) Glycine is a nutritionally essential amino acid for maximal growth of milk-fed young pigs. Amino Acids 46(8):2037–2045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1758-3
Wells JM, Brummer RJ, Derrien M, MacDonald TT, Troost F, Cani PD, Theodorou V, Dekker J, Meheust A, de Vos WM, Mercenier A, Nauta A, Garcia-Rodenas CL (2017) Homeostasis of the gut barrier and potential biomarkers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 312(3):G171–G193. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00048.2015
Wu X, Zheng Y, Ma J, Yin J, Chen S (2020) The effects of dietary glycine on the acetic acid-induced mouse model of colitis. Mediators Inflamm 2020:5867627. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5867627
Yang H, Xiong X, Wang X, Tan B, Li T, Yin Y (2016) Effects of weaning on intestinal upper villus epithelial cells of piglets. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0150216. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150216
Zhang L, Tao L, Shi T, Zhang F, Sheng X, Cao Y, Zheng S, Wang A, Qian W, Jiang L, Lu Y (2015) Paeonol inhibits B16F10 melanoma metastasis in vitro and in vivo via disrupting proinflammatory cytokines-mediated NF-kappaB and STAT3 pathways. IUBMB Life 67(10):778–788. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1435
Zhang J, Song L, Wang Y, Liu C, Zhang L, Zhu S, Liu S, Duan L (2019) Beneficial effect of butyrate-producing Lachnospiraceae on stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in rats. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 34(8):1368–1376. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.14536
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Li J, Xing T, Jiang Y, Zhang L, Gao F (2020) Dietary resistant starch modifies the composition and function of caecal microbiota of broilers. J Sci Food Agric 100(3):1274–1284. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10139
Zmora N, Levy M, Pevsner-Fischer M, Elinav E (2017) Inflammasomes and intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 10(4):865–883. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2017.19
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31625025, 31301979), the Zhengzhou 1125 Talent Program, and the Jinxinnong Animal Science Development Foundation.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31625025, 31301979), the Zhengzhou 1125 Talent Program, and the Jinxinnong Animal Science Development Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics statement
The studies were approved by China Agricultural University Institutional Animal Science and Technology College and conducted according to the Guidelines for Experimental Animal Research of the Ministry of Science and Technology (Beijing, China).
Informed consent
All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional information
Handling Editor: F. Blachier.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Y., Fan, X., Zhang, Y. et al. Glycine regulates mucosal immunity and the intestinal microbial composition in weaned piglets. Amino Acids 54, 385–398 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02976-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02976-y