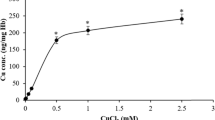
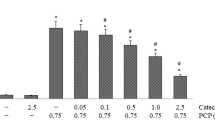
Abstract
Hexavalent chromium [(Cr(VI)] is widely used in several industries, but human exposure results in multiple organ toxicity. Enhanced generation of free radicals and reactive species is thought to play a key role in Cr(VI)-induced toxicity. We have examined the effect of taurine, a simple sulphur-containing amino acid and an antioxidant, on potassium dichromate [K2Cr2O7, a Cr(VI) compound]-induced cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in human blood cells. Erythrocytes were treated with K2Cr2O7, either alone or after incubation with different concentrations of taurine. Treatment of erythrocytes with K2Cr2O7 alone led to marked increase in generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, lipid and protein oxidation. This was accompanied by decrease in total sulfhydryl and glutathione content and lowered antioxidant power of the cells. This suggests that Cr(VI) induces oxidative stress in the cells. Incubation of erythrocytes with taurine prior to addition of K2Cr2O7, resulted in a concentration-dependent decrease in the generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, mitigation of oxidative stress and amelioration of antioxidant power of these cells. It also restored the activities of several metabolic, antioxidant and membrane-bound enzymes. Cr(VI)-induced damage to erythrocyte membrane and lymphocyte DNA was also significantly attenuated by prior administration of taurine. These results suggest that taurine can function as a chemoprotectant against Cr(VI)-induced oxidative injury and can be potentially used to mitigate the toxic effects of this transition metal ion.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adedara IA, Ojuade TJD, Olabiyi BF et al (2017) Taurine ameliorates renal oxidative damage and thyroid dysfunction in rats chronically exposed to fluoride. Biol Trace Elem Res 175:388–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0784-2
Adedara IA, Alake SE, Adeyemo MO et al (2018) Taurine enhances spermatogenic function and antioxidant defense mechanisms in testes and epididymis of L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats. Biomed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother 97:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.095
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Antonelou MH, Kriebardis AG, Velentzas AD et al (2011) Oxidative stress-associated shape transformation and membrane proteome remodeling in erythrocytes of end stage renal disease patients on hemodialysis. J Proteomics 74:2441–2452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2011.04.009
Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Hoey BM, Butler J (1988) The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their metabolic precursors. Biochem J 256:251–255
Avron M, Shavit N (1963) A sensitive and simple method for determination of ferrocyanide. Anal Biochem 6:549–554
Balachandar V, Arun M, Mohana Devi S et al (2010) Evaluation of the genetic alterations in direct and indirect exposures of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] in leather tanning industry workers North Arcot District, South India. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 83:791–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-010-0562-y
Benesch RE, Benesch R, Yung S (1973) Equations for the spectrophotometric analysis of hemoglobin mixtures. Anal Biochem 55:245–248
Benzie IF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1996.0292
Bonting SL, Simon KA, Hawkins NM (1961) Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. I. Quantitative distribution in several tissues of the cat. Arch Biochem Biophys 95:416–423
Bucolo C, Fidilio A, Platania CBM et al (2018) Antioxidant and osmoprotecting activity of taurine in dry eye models. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther Off J Assoc Ocul Pharmacol Ther 34:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1089/jop.2017.0008
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Bukowska B, Rychlik B, Krokosz A, Michałowicz J (2008) Phenoxyherbicides induce production of free radicals in human erythrocytes: oxidation of dichlorodihydrofluorescine and dihydrorhodamine 123 by 2,4-D-Na and MCPA-Na. Food Chem Toxicol Int J Publ Br Ind Biol Res Assoc 46:359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.08.011
Buttner B, Beyersmann D (1985) Modification of the erythrocyte anion carrier by chromate. Xenobiotica Fate Foreign Compd Biol Syst 15:735–741. https://doi.org/10.3109/00498258509047435
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1985) Glutathione reductase. Methods Enzymol 113:484–490
Casadevall M, da Cruz Fresco P, Kortenkamp A (1999) Chromium(VI)-mediated DNA damage: oxidative pathways resulting in the formation of DNA breaks and abasic sites. Chem Biol Interact 123:117–132
Çekiç SD, Kara N, Tütem E et al (2012) Protein–incorporated serum total antioxidant capacity measurement by a modified CUPRAC (CUPRIC Reducing Antioxidant Capacity) method. Anal Lett 45:754–763
Choi EJ, Tang Y, Lee CB et al (2015) Investigation of antioxidant and anticancer potential of taurine by means of multiple chemical and biological assays. Adv Exp Med Biol 803:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15126-7_16
Coogan TP, Squibb KS, Motz J et al (1991) Distribution of chromium within cells of the blood. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 108:157–166
Cozzi R, Ricordy R, Bartolini F et al (1995) Taurine and ellagic acid: two differently-acting natural antioxidants. Environ Mol Mutagen 26:248–254
Crane RK, Sols A (1953) The association of hexokinase with particulate fractions of brain and other tissue homogenates. J Biol Chem 203:273–292
Dalle-Donne I, Aldini G, Carini M et al (2006) Protein carbonylation, cellular dysfunction, and disease progression. J Cell Mol Med 10:389–406
Dayan AD, Paine AJ (2001) Mechanisms of chromium toxicity, carcinogenicity and allergenicity: review of the literature from 1985 to 2000. Hum Exp Toxicol 20:439–451. https://doi.org/10.1191/096032701682693062
De Luca A, Pierno S, Camerino DC (2015) Taurine: the appeal of a safe amino acid for skeletal muscle disorders. J Transl Med 13:243. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-015-0610-1
del Castillo-Olivares A, Núñez de Castro I, Medina MA (2000) Dual role of plasma membrane electron transport systems in defense. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 35:197–220. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409230091169203
Domingo-Pueyo A, Sanz-Valero J, Wanden-Berghe C (2014) Effects of occupational exposure to chromium and its compounds: a systematic review. Arch Prevencion Riesgos Laborales 17:142–153. https://doi.org/10.12961/aprl.2014.17.3.03
Dubey SK, Rai LC (1989) Toxicity of chromium and tin to Anabaena doliolum. Interaction with sulphur-containing amino acids and thiols. Biol Met 2:55–60
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Erman F, Balkan J, Cevikbaş U et al (2004) Betaine or taurine administration prevents fibrosis and lipid peroxidation induced by rat liver by ethanol plus carbon tetrachloride intoxication. Amino Acids 27:199–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-004-0105-5
Farag MR, Alagawany M (2018) Erythrocytes as a biological model for screening of xenobiotics toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 279:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.11.007
Flohé L, Günzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121
Forman HJ, Zhang H, Rinna A (2009) Glutathione: overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol Aspects Med 30:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.006
Furfaro AL, Nitti M, Marengo B et al (2012) Impaired synthesis contributes to diabetes-induced decrease in liver glutathione. Int J Mol Med 29:899–905. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.915
Gay C, Gebicki JM (2000) A critical evaluation of the effect of sorbitol on the ferric-xylenol orange hydroperoxide assay. Anal Biochem 284:217–220. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.2000.4696
González-Burgos E, Gómez-Serranillos MP (2012) Terpene compounds in nature: a review of their potential antioxidant activity. Curr Med Chem 19:5319–5341
Gürer H, Ozgünes H, Saygin E, Ercal N (2001) Antioxidant effect of taurine against lead-induced oxidative stress. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 41:397–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010265
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hamaguchi T, Azuma J, Schaffer S (1991) Interaction of taurine with methionine: inhibition of myocardial phospholipid methyltransferase. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 18:224–230
Hare GMT, Tsui AKY, Crawford JH, Patel RP (2013) Is methemoglobin an inert bystander, biomarker or a mediator of oxidative stress—the example of anemia? Redox Biol 1:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2012.12.003
Hassan W, Noreen H, Rehman S et al (2017) Oxidative stress and antioxidant potential of one hundred medicinal plants. Curr Top Med Chem 17:1336–1370. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026617666170102125648
Heller-Stilb B, van Roeyen C, Rascher K et al (2002) Disruption of the taurine transporter gene (taut) leads to retinal degeneration in mice. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 16:231–233. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.01-0691fje
Heppel LA, Hilmore RJ (1951) Purification and properties of 5-nucleotidase. J Biol Chem 188:665–676
Hissin PJ, Hilf R (1976) A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem 74:214–226
Huang JC, Li DJ, Diao JC et al (2007) A novel fluorescent method for determination of peroxynitrite using folic acid as a probe. Talanta 72:1283–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.01.033
Husain N, Mahmood R (2017) Hexavalent chromium induces reactive oxygen species and impairs the antioxidant power of human erythrocytes and lymphocytes: decreased metal reducing and free radical quenching ability of the cells. Toxicol Ind Health 33:623–635. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233717703892
Husain N, Mahmood R (2018) 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde quenches ROS and RNS and protects human blood cells from Cr(VI)-induced cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. Toxicol Vitro Int J Publ Assoc BIBRA 50:293–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2018.04.004
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) (1990) Chromium, nickel and welding. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 49:1–648
Ito T, Kimura Y, Uozumi Y et al (2008) Taurine depletion caused by knocking out the taurine transporter gene leads to cardiomyopathy with cardiac atrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:927–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.03.001
Ito T, Yoshikawa N, Inui T et al (2014) Tissue depletion of taurine accelerates skeletal muscle senescence and leads to early death in mice. PLoS One 9:e107409. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107409
Ito T, Yoshikawa N, Ito H, Schaffer SW (2015) Impact of taurine depletion on glucose control and insulin secretion in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 129:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2015.08.007
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 283:65–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2011.03.001
Jong CJ, Azuma J, Schaffer S (2012) Mechanism underlying the antioxidant activity of taurine: prevention of mitochondrial oxidant production. Amino Acids 42:2223–2232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0962-7
Kanagaraj G, Elango L (2016) Hydrogeochemical processes and impact of tanning industries on groundwater quality in Ambur, Vellore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:24364–24383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7639-4
Keller A, Mohamed A, Dröse S et al (2004) Analysis of dichlorodihydrofluorescein and dihydrocalcein as probes for the detection of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Res 38:1257–1267. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760400022145
Kesharwani RK, Singh DV, Misra K, Rizvi SI (2012) Plant polyphenols as electron donors for erythrocyte plasma membrane redox system: validation through in silico approach. Org Med Chem Lett 2:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-2858-2-12
Khundmiri SJ, Asghar M, Khan F et al (2004) Effect of ischemia and reperfusion on enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in rat kidney. J Nephrol 17:377–383
Kim SH, Zhong X, Kim W et al (2018) Taurine chloramine potentiates phagocytic activity of peritoneal macrophages through up-regulation of dectin-1 mediated by heme oxygenase-1-derived carbon monoxide. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 32:2246–2257. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201700817R
Kim-Shapiro DB, Schechter AN, Gladwin MT (2006) Unraveling the reactions of nitric oxide, nitrite, and hemoglobin in physiology and therapeutics. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:697–705. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000204350.44226.9a
Kuma F, Ishizawa S, Hirayama K, Nakajima H (1972) Studies on methemoglobin reductase. I. Comparative studies of diaphorases from normal and methemoglobinemic erythrocytes. J Biol Chem 247:550–555
Lambert IH, Hoffmann EK, Pedersen SF (2008) Cell volume regulation: physiology and pathophysiology. Acta Physiol Oxf Engl 194:255–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.2008.01910.x
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN et al (1990) Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186:464–478
Lewalter J, Korallus U, Harzdorf C, Weidemann H (1985) Chromium bond detection in isolated erythrocytes: a new principle of biological monitoring of exposure to hexavalent chromium. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 55:305–318
Liu KJ, Shi X (2001) In vivo reduction of chromium (VI) and its related free radical generation. Mol Cell Biochem 222:41–47
Loschen G, Azzi A, Richter C, Flohé L (1974) Superoxide radicals as precursors of mitochondrial hydrogen peroxide. FEBS Lett 42:68–72
Marcinkiewicz J, Kontny E (2014) Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids 46:7–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1361-4
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
May JM, Qu Z, Cobb CE (2004) Human erythrocyte recycling of ascorbic acid: relative contributions from the ascorbate free radical and dehydroascorbic acid. J Biol Chem 279:14975–14982. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M312548200
Miranda KM, Espey MG, Wink DA (2001) A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 5:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1006/niox.2000.0319
Mishra K, Ojha H, Chaudhury NK (2012) Estimation of antiradical properties of antioxidants using DPPH assay: a critical review and results. Food Chem 130:1036–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.127
Nandhini TA, Anuradha CV (2003) Inhibition of lipid peroxidation, protein glycation and elevation of membrane ion pump activity by taurine in RBC exposed to high glucose. Clin Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem 336:129–135
Oja SS, Saransaari P (2007) Pharmacology of taurine. Proc West Pharmacol Soc 50:8–15
Ottenwaelder H, Wiegand HJ, Bolt HM (1988) Uptake of 51Cr(VI) by human erythrocytes: evidence for a carrier-mediated transport mechanism. Sci Total Environ 71:561–566
Owoeye O, Adedara IA, Farombi EO (2018) Pretreatment with taurine prevented brain injury and exploratory behaviour associated with administration of anticancer drug cisplatin in rats. Biomed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother 102:375–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.051
Paiva AN, de Lima JG, de Medeiros ACQ et al (2015) Beneficial effects of oral chromium picolinate supplementation on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical study. J Trace Elem Med Biol Organ Soc Miner Trace Elem GMS 32:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2015.05.006
Panigrahi DC, Pandey JK, Udaybhanu G (2006) Pattern of hexa-valent chromium in air borne respirable dust generated at various workplaces in opencast chromite mines. Environ Monit Assess 114:211–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-3262-z
Peacock A, Martin FH, Carr A (2013) Energy drink ingredients. Contribution of caffeine and taurine to performance outcomes. Appetite 64:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2012.12.021
Pedersen RC, Berry AJ (1977) Sensitive, optimized assay for serum AMP deaminase. Clin Chem 23:1726–1733
Peng M, Yang X (2015) Controlling diabetes by chromium complexes: the role of the ligands. J Inorg Biochem 146:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2015.01.002
Percy MJ, McFerran NV, Lappin TRJ (2005) Disorders of oxidised haemoglobin. Blood Rev 19:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2004.02.001
Prieto P, Pineda M, Aguilar M (1999) Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Anal Biochem 269:337–341. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1999.4019
Proctor DM, Suh M, Campleman SL, Thompson CM (2014) Assessment of the mode of action for hexavalent chromium-induced lung cancer following inhalation exposures. Toxicology 325:160–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2014.08.009
Qiao M, Liu P, Ren X et al (2015) Potential protection of taurine on antioxidant system and ATPase in brain and blood of rats exposed to aluminum. Biotechnol Lett 37:1579–1584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1846-9
Radi R (2013) Peroxynitrite, a stealthy biological oxidant. J Biol Chem 288:26464–26472. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R113.472936
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A et al (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med 26:1231–1237
Redmond HP, Wang JH, Bouchier-Hayes D (1996) Taurine attenuates nitric oxide- and reactive oxygen intermediate-dependent hepatocyte injury. Arch Surg Chic Ill 1960 131:1280–1287 (discussion 1287–1288)
Refsgaard HH, Tsai L, Stadtman ER (2000) Modifications of proteins by polyunsaturated fatty acid peroxidation products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:611–616
Rifkind JM, Zhang L, Heim JM, Levy A (1988) The role of hemoglobin in generating oxyradicals. Basic Life Sci 49:157–162
Rizvi SI, Srivastava N (2010) Erythrocyte plasma membrane redox system in first degree relatives of type 2 diabetic patients. Int J Diabetes Mellit 2:119–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdm.2010.05.005
Rosemberg DB, Kist LW, Etchart RJ et al (2010) Evidence that acute taurine treatment alters extracellular AMP hydrolysis and adenosine deaminase activity in zebrafish brain membranes. Neurosci Lett 481:105–109
Sayato Y, Nakamuro K, Matsui S, Ando M (1980) Metabolic fate of chromium compounds. I. Comparative behavior of chromium in rat administered with Na251CrO4 and 51CrCl3. J Pharmacobiodyn 3:17–23
Schaffer SW, Azuma J, Madura JD (1995) Mechanisms underlying taurine-mediated alterations in membrane function. Amino Acids 8:231–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00806821
Schaffer SW, Jong CJ, Ramila KC, Azuma J (2010) Physiological roles of taurine in heart and muscle. J Biomed Sci 17(Suppl 1):S2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S2
Schuller-Levis GB, Park E (2003) Taurine: new implications for an old amino acid. FEMS Microbiol Lett 226:195–202
Schütt F, Aretz S, Auffarth GU, Kopitz J (2012) Moderately reduced ATP levels promote oxidative stress and debilitate autophagic and phagocytic capacities in human RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:5354–5361. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.12-9845
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Sharma P, Bihari V, Agarwal SK et al (2012) Groundwater contaminated with hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]: a health survey and clinical examination of community inhabitants (Kanpur, India). PLoS One 7:e47877. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047877
Sheetz MP, Singer SJ (1974) Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:4457–4461
Shonk CE, Boxer GE (1964) Enzyme patterns in human tissues. I. Methods for the determination of glycolytic enzymes. Cancer Res 24:709–721
Singh N, Rajini PS (2008) Antioxidant-mediated protective effect of potato peel extract in erythrocytes against oxidative damage. Chem Biol Interact 173:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2008.03.008
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Soldatow VY, LeCluyse EL, Griffith LG, Rusyn I (2013) In vitro models for liver toxicity testing. Toxicol Res 2:23–39. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2TX20051A
Spengler MI, Svetaz MJ, Leroux MB et al (2014) Lipid peroxidation affects red blood cells membrane properties in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 58:489–495. https://doi.org/10.3233/CH-131716
Standeven AM, Wetterhahn KE (1991) Ascorbate is the principal reductant of chromium (VI) in rat liver and kidney ultrafiltrates. Carcinogenesis 12:1733–1737
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–336
Sunderman FW (1990) The clinical biochemistry of 5′-nucleotidase. Ann Clin Lab Sci 20:123–139
Tamura T, Stadtman TC (1996) A new selenoprotein from human lung adenocarcinoma cells: purification, properties, and thioredoxin reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1006–1011
Tavazzi B, Amorini AM, Fazzina G et al (2001) Oxidative stress induces impairment of human erythrocyte energy metabolism through the oxygen radical-mediated direct activation of AMP-deaminase. J Biol Chem 276:48083–48092. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M101715200
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. EXS 101:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D et al (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Ueno S, Kashimoto T, Susa N et al (2001) Detection of dichromate (VI)-induced DNA strand breaks and formation of paramagnetic chromium in multiple mouse organs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 170:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.2000.9081
Villalba JM, Canalejo A, Burón MI et al (1993) Thiol groups are involved in NADH-ascorbate free radical reductase activity of rat liver plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 192:707–713. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1993.1472
Wang Y, Yang L, Cheng W et al (2009) Scanning electron microscopic observation of erythrocytes and endothelial cells of electrified death rabbits. Leg Med Tokyo Jpn 11(Suppl 1):S244–S247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.legalmed.2009.01.097
Wilbur S, Abadin H, Fay M et al (2012) Toxicological profile for chromium. In: Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (US), Atlanta (GA)
Witt KL, Stout MD, Herbert RA et al (2013) Mechanistic insights from the NTP studies of chromium. Toxicol Pathol 41:326–342. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623312469856
Wojtala A, Bonora M, Malinska D et al (2014) Methods to monitor ROS production by fluorescence microscopy and fluorometry. Methods Enzymol 542:243–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-416618-9.00013-3
Yu J, Kim AK (2009) Effect of taurine on antioxidant enzyme system in B16F10 melanoma cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 643:491–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-75681-3_51
Yuann JM, Liu KJ, Hamilton JW, Wetterhahn KE (1999) In vivo effects of ascorbate and glutathione on the uptake of chromium, formation of chromium(V), chromium-DNA binding and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in liver and kidney of osteogenic disorder shionogi rats following treatment with chromium(VI). Carcinogenesis 20:1267–1275
Acknowledgements
The financial support to the department by the following schemes is gratefully acknowledged. Department of Science & Technology (DST) sanctioned Funds for Improvement of Science & Technology (DST-FIST II), DST sanctioned Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence (DST-PURSE) and University Grants Commission sanctioned Special Assistance Programme -Departmental Research Support (UGC-SAP-DRS III). NH is the recipient of a senior research fellowship from Maulana Azad National Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists in this work.
Additional information
Handling Editor: S. W. Schaffer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Husain, N., Mahmood, R. Taurine attenuates Cr(VI)-induced cellular and DNA damage: an in vitro study using human erythrocytes and lymphocytes. Amino Acids 52, 35–53 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02807-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02807-1