Abstract
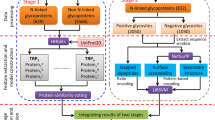
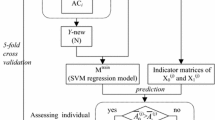
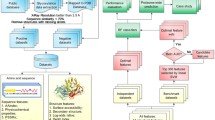
N-Glycosylation is a common post-translational modification that plays an important role in the proper folding and function of many proteins. This modification is largely dependent on the presence of a sequence motif called a “sequon” defined as Asn-Xxx-Ser/Thr. However, evidence has shown that the presence of such a “sequon” is insufficient to determine the occurrence of N-glycosylation with high precision. This study aims to elucidate patterns that can more accurately predict N-glycosylation sites in human proteins. The novel motifs are evaluated using benchmarking data from 188 organisms. Performance is largely sustained compared to the human data, which validates the robustness of the novel extracted “extended sequons”. We, therefore, introduce new knowledge about sequence-related factors that control N-glycosylation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caragea C, Sinapov J, Silvescu A, Dobbs I, Honaver V (2007) Glycosylation site prediction using ensembles of support vector machines classifiers. BMC Bioinformatics 8:438
Chen K, Kurgan LA, Ruan J (2007) Prediction of flexible/rigid regions from protein sequences using k-spaced amino acid pairs. BMC Struct Biol 7(1):1–13. doi:10.1186/1472-6807-7-25
Chi YH, Koo YD, Dai SY, Ahn JE, Yun DJ, Lee SY, Zhu-Salzman K (2010) N-glycosylation at non-canonical Asn-X-Cys sequence of an insect recombinant cathepsin B-like counter-defense protein. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 156(1):40–47. doi:10.1016/j.cbpb.2010.01.017
Cohen WW (1995) Fast Effective Rule Induction. Paper presented at the Twelfth International Conference on Machine Learning
Collantes ER, Dunn-III WJ (1995) Amino acid side chain descriptors for quantitative structure-activity relationship studies of peptide analogues. J Med Chem 38:2705–2713
Dell A, Galadari A, Sastre F, Hitchen P (2010) Similarities and differences in the glycosylation mechanisms in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Int J Microbiol 2010:14. doi:10.1155/2010/148178
García-Jacas CR, Marrero-Ponce Y, Acevedo-Martínez L, Barigye SJ, Valdés-Martiní JR, Contreras-Torres E (2014) QuBiLS-MIDAS: a parallel free-software for molecular descriptors computation based on multi-linear algebraic maps. J Comput Chem 35:1395–1409
Gavel Y, von Heijne G (1990) Sequence differences between glycosylated and non-glycosylated Asn-X-Thr/Ser acceptor sites: implications for protein engineering. Protein Eng 3(5):433–442
Gupta R, Brunak S (2002) Prediction of glycosylation across the human proteome and the correlation to protein function. Pac Symp Biocomput 2002:310–322
Hall M, Frank E, Holmes G, Pfahringer B, Reutemann P, Witten IH (2009) The WEKA data mining software: an update. SIGKDD Explor 11(1):10–18
Hamby S, Hirst J (2008) Prediction of glycosylation sites using random forests. BMC Bioinformatics 9(1):500
Hart G (1992) Glycosylation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 4:1017–1023
Helenius A, Aebi M (2004) Roles of N-linked glycans in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem 73:1019–1049
Hellberg S, Sjostrom M, Skagerberg B, Wold S (1987) Peptide quantitative structure-activity relationships, a multivariate approach. J Med Chem 30:1126–1135
Kasturi L, Chen H, Shakin-Eshleman SH (1997) Regulation of N-linked core glycosylation: use of a site-directed mutagenesis approach to identify Asn-Xaa-Ser/Thr sequons that are poor oligosaccharide acceptors. Biochem J 323(Pt 2):415–419
Kasturi L, Eshleman JR, Wunner WH, Shakin-Eshleman SH (1995a) The hydroxy amino acid in an Asn-X-Ser/Thr sequon can influence N-linked core glycosylation efficiency and the level of expression of a cell surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem 270(24):14756–14761
Kasturi L, Eshleman JR, Wunner WH, Shakin-Eshleman SH (1995b) The hydroxy amino acid in an Asn-X-Ser/Thr sequon can influence N-linked core glycosylation efficiency and the level of expression of a cell surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem 270(24):14756–14761. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.24.14756
Katrin S, Karelson M, Järv J (1999) Modeling of the amino acid side chain effects on peptide conformation. Bioorg Chem 27:434–442
Kawashima S, Kanehisa M (2000) AAindex: amino acid index database. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):374
Kelleher DJ, Gilmore R (2006) An evolving view of the eukaryotic oligosaccharyltransferase. Glycobiology 16(4):47r–62r. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwj066
Kowarik M, Young NM, Numao S, Schulz BL, Hug I, Callewaert N, Mills DC, Watson DC, Hernandez M, Kelly JF, Wacker M, Aebi M (2006) Definition of the bacterial N-glycosylation site consensus sequence. EMBO J 25(9):1957–1966. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601087
Kyte J, Doolitle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Levitt M (1978) Conformational preferences of amino acids in globular proteins. Biochemistry 17(20):4277–4285
Li F, Li C, Wang M, Webb GI, Zhang Y, Whisstock JC, Song J (2015) GlycoMine: a machine learning-based approach for predicting N-, C- and O-linked glycosylation in the human proteome. Bioinformatics 31(9):1411–1419. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu852
Lu C-T, Huang K-Y, Su M-G, Lee T-Y, Bretaña N, Chang W-C, Chen Y-J, Huang H-D (2013) DbPTM 3.0: an informative resource for investigating substrate site specificity and functional association of protein post-translational modifications. Nucl Acids Res 41(Database issue):D295–305
Miletich JP, Broze GJ Jr (1990) Beta protein C is not glycosylated at asparagine 329. The rate of translation may influence the frequency of usage at asparagine-X-cysteine sites. J Biol Chem 265(19):11397–11404
Obenauer JC, Cantley LC, Yaffe MB (2003) Scansite 2.0: Proteome-wide prediction of cell signaling interactions using short sequence motifs. Nucl Acids Res 31:3635–3641
Rao HB, Zhu F, Yang GB, Li ZR, Chen YZ (2011) Update of PROFEAT: a web server for computing structural and physicochemical features of proteins and peptides from amino acid sequence. Nucl Acids Res 39(Web Server):W385–W390
Ruiz-Blanco YB, Marrero-Ponce Y, García Y, Puris A, Bello R, Green J, Sotomayor-Torres CM (2014) A physics-based scoring function for protein structural decoys: dynamic testing on targets of CASP-ROLL. Chem Phys Lett 610–611:135–140. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2014.07.014
Ruiz-Blanco YB, Marrero-Ponce Y, Paz W, García Y, Salgado J (2013) Global stability of protein folding from an empirical free energy function. J Theor Biol 321:44–53. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.12.023
Ruiz-Blanco YB, Marrero-Ponce Y, Prieto PJ, Salgado J, García Y, Sotomayor-Torres CM (2015a) A Hooke׳ s law-based approach to protein folding rate. J Theor Biol 364:407–417
Ruiz-Blanco YB, Paz W, Green J, Marrero-Ponce Y (2015b) ProtDCal: a program to compute general-purpose-numerical descriptors for sequences and 3D-structures of proteins. BMC Bioinformatics 16:162
Ruiz-Canada C, Kelleher DJ, Gilmore R (2009) Cotranslational and posttranslational N-Glycosylation of polypeptides by distinct mammalian OST isoforms. Cell 136:272–283
Sato C, Kim JH, Abe Y, Saito K, Yokoyama S, Kohda D (2000) Characterization of the N-oligosaccharides attached to the atypical Asn-X-Cys sequence of recombinant human epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biochem 127(1):65–72
Schulz BL (2012) Beyond the Sequon: sites of N-Glycosylation. In: INTECH, Rijeka, pp 21–39. doi:10.5772/50260
Schwarz F, Aebi M (2011) Mechanisms and principles of N-linked protein glycosylation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 21(5):576–582. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2011.08.005
Seitz O (2000) Synthesis and the effects of glycosylation on protein structure and activity. Chem BioChem 1:214–246
Shannon CE (1949) Communication theory of secrecy systems. Bell Syst Tech J 28(4):656–715. doi:10.1002/j.1538-7305.1949.tb00928.x
Shannon CE (2001) A mathematical theory of communication. SIGMOBILE Mob Comput Commun Rev 5(1):3–55. doi:10.1145/584091.584093
Urias RWP, Barigye SJ, Marrero-Ponce Y, García-Jacas CR, Valdes-Martiní JR, Perez-Gimenez F (2015) IMMAN: free software for information theory-based chemometric analysis. Mol Divers 19(2):305–319. doi:10.1007/s11030-014-9565-z
Vance BA, Wu W, Ribaudo RK, Segal DM, Kearse KP (1997) Multiple dimeric forms of human CD69 result from differential addition of N-glycans to typical (Asn-X-Ser/Thr) and atypical (Asn-X-cys) glycosylation motifs. J Biol Chem 272(37):23117–23122
Whitley P, Nilsson I, Gv Heijne (1996) A nascent secretory protein may traverse the ribosome/endoplasmic reticulum translocase complex as an extended chain. J Biol Chem 271:6241–6244
Yu L, Liu H (2003) Feature selection for high-dimensional data: a fast correlation-based filter solution. ICML 3:856–863
Zielinska DF, Gnad F, Wisniewski JR, Mann M (2010) Precision mapping of an in vivo N-glycoproteome reveals rigid topological and sequence constraints. Cell 141(5):897–907. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared. The present report contains no research involving human and/or animals participants.
Additional information
Handling Editor: L. Taher.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Blanco, Y.B., Marrero-Ponce, Y., García-Hernández, E. et al. Novel “extended sequons” of human N-glycosylation sites improve the precision of qualitative predictions: an alignment-free study of pattern recognition using ProtDCal protein features. Amino Acids 49, 317–325 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2362-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2362-5