Abstract
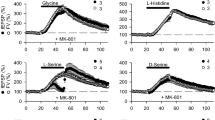
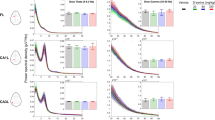
Taurine is especially abundant in rodent brain where it appears to be involved in osmoregulation and synaptic plasticity mechanisms. The demonstration of a physiological role for taurine has been hampered by the difficulty in modifying taurine levels in most tissues, including the brain. We used an experimental strategy to reduce taurine levels, involving treatment with guanidinoethyl sulfonate (GES), a structural analogue of taurine that, among other properties, acts as a competitive inhibitor of taurine transport. GES delivered in the drinking water of rats for 1 month effectively reduced taurine levels in brain structures (hippocampus, cerebellum and cortex) and outside the brain (heart, muscle, kidney, liver and plasma) by between 50 and 80 %, depending on the tissue. This partial taurine depletion did not affect either basal synaptic transmission or the late phase of long-term potentiation (late-LTP) in hippocampal slices. In vivo microdialysis studies in the hippocampus revealed that GES treatment reduced extracellular taurine levels and the magnitude of taurine released in response to the application of either N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) or a hypoosmotic solution, without affecting release mechanisms. Finally, we demonstrated in hippocampal slices that a brief GES application can mimic taurine action on the conversion of a decremental LTP into a perdurable late-LTP, concluding that GES might replace taurine function in some mechanisms such as those implicated in synaptic plasticity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson CH, Howard A, Walters JRF, Ganapathy V, Thwaites DT (2009) Taurine uptake across the human intestinal brush-border membrane is via two transporters: H+-coupled PAT1 (SLC36A1) and Na+- and Cl-dependent TauT (SLC6A6). J Physiol 587:731–744
Baker DA, Xi Z-X, Shen H, Swanson CJ, Kalivas P (2002) The origin and neuronal function of in vivo nonsynaptic glutamate. J Neurosci 22:9134–9141
Barakat L, Wang D, Bordey A (2002) Carrier-mediated uptake and release of taurine from Bergmann glia in rat cerebellar slices. J Physiol 541:753–767
Borden LA (1996) GABA transporter heterogeneity: pharmacology and cellular localization. Neurochem Int 29:335–356
Chaudhry FA, Schmitz D, Reimer RJ, Larsson P, Gray AT, Nicoll R, Kavanaugh Edwards RH (2002) Glutamine uptake by neurons: interaction of protons with system A transporters. J Neurosci 22:62–72
Chepkova AN, Doreulee N, Yanovsky Y, Mukhopadhyay D, Haas HL, Sergeeva OA (2002) Long-lasting enhancement of corticostriatal neurotransmission by taurine. Eur J Neurosci 16:1523–1530
del Olmo N, Bustamante J, Martín del Río R, Solís JM (2000) Taurine activates GABAA but not GABAB receptors in rat hippocampal CA1 area. Brain Res 864:298–307
del Olmo N, Handler A, Alvarez L, Bustamante J, Martín del Río R, Solís JM (2003) Taurine-induced synaptic potentiation and the late phase of long-term potentiation are related mechanistically. Neuropharmacology 44:26–39
del Olmo N, Suárez LM, Orensanz LM, Suárez F, Bustamante J, Duarte JM, Martín del Río R, Solís JM (2004) Role of taurine uptake on the induction of long-term synaptic potentiation. Eur J Neurosci 19:1875–1886
Dutton GR, Rogers KL (1992) Evoked endogenous taurine release from cultured cerebellar neurons. Adv Exp Med Biol 315:269–276
El Idrissi A, Shen CH, L’Amoreaux WJ (2013) Neuroprotective role of taurine during aging. Amino Acids 45:735–750
Eppler B, Dawson R Jr (2001) Dietary taurine manipulations in aged male Fischer 344 rat tissue: taurine concentration, taurine biosynthesis, and oxidative markers. Biochem Pharmacol 62:29–39
Galarreta M, Bustamante J, Martín del Río R, Solís JM (1996) Taurine induces a long-lasting increase of synaptic efficacy and axon excitability in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 16:92–102
Haskew-Layton RE, Rudkouskaya A, Jin Y, Feustel PJ, Kimelberg HK, Mongin AA (2008) Two distinct modes of hypoosmotic medium-induced release of excitatory amino acids and taurine in the rat brain in vivo. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003543
Herranz AS, Solís JM, Herreras O, Menéndez N, Ambrosio E, Orensanz LM, Martín del Río R (1990) The epileptogenic action of the taurine analogue guanidinoethane sulfonate may be caused by a blockade of GABA receptors. J Neurosci Res 26:98–104
Hiramatsu M, Edamatsu R, Kabuto H, Higashihara Y, Mori A (1989) Increased seizure susceptibility induced by guanidinoethane sulfonate in El mice and its relation to glutamatergic neurons. Neurochem Res 14:85–89
Huxtable RJ (1982) Guanidinoethane sulfonate and the disposition of dietary taurine in the rat. J Nutr 112:2293–2300
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev 72:101–163
Huxtable RJ, Laird HE, Lippincott SE (1979) The transport of taurine in the heart and the rapid depletion of tissue taurine content by guanidinoethyl sulfonate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 211:465–471
Kelleher 3rd RJ, Govindarajan A, Jung HY, Kang H, Tonegawa S (2004) Translational control by MAPK signalling in long-term synaptic plasticity and memory. Cell 116:467–479
Kim HY, Kim HV, Yoon JH, Kang BR, Cho SM, Lee S, Kim JY, Kim JW, Cho Y, Woo J, Kim YS (2014) Taurine in drinking water recovers learning and memory in the adult APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 4:7467
Lehmann A, Hamberger A (1984) A possible interrelationship between extracellular taurine and phosphoethanolamine in the hippocampus. J Neurochem 42:1286–1290
Lehmann A, Hagberg H, Huxtable RJ, Sandberg M (1987) Reduction of brain taurine: effects on neurotoxic and metabolic actions of kainate. Neurochem Int 10:265–274
Liljequist R, Winblad B (1993) Guanidinoethanesulphonic acid facilitates retention of spatial memory in old rats. Pharmacol Toxicol 73:186–188
Liu QR, Lopez-Corcuera B, Nelson H, Mandiyan S, Nelson N (1992) Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding the transporter of taurine and beta-alanine in mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:12145–12149
Manabe T, Wyllie DJ, Perkel DJ, Nicoll RA (1993) Modulation of synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation: effects on paired pulse facilitation and EPSC variance in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 70:1451–1459
Marnela KM, Kontro P (1984) Free amino acids and the uptake and binding of taurine in the central nervous system of rats treated with guanidinoethanesulphonate. Neuroscience 12:323–328
Mellor JR, Gunthorpe MJ, Randall AD (2000) The taurine uptake inhibitor guanidinoethyl sulphonate is an agonist at gamma-aminobutyric acid (A) receptors in cultured murine cerebellar granule cells. Neurosci Lett 286:25–28
Menéndez N, Solís JM, Herreras O, Sánchez-Herranz A, Martín del Río R (1990) Role of endogenous taurine on the glutamate analogue-induced neurotoxicity in the rat hippocampus in vivo. J Neurochem 55:714–717
Metzner L, Dorn M, Markwardt F, Brandsch M (2009) The orally active antihyperglycemic drug β-guanidinopropionic acid is transported by the human proton-coupled amino acid transporter hPAT1. Mol Pharm 6:1006–1011
Mori M, Gahwiler BH, Gerber U (2002) Beta-alanine and taurine as endogenous agonists at glycine receptors in rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol 539:191–200
Mozaffari MS, Tan BH, Lucia MA, Schaffer SW (1986) Effect of drug-induced taurine depletion on cardiac contractility and metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol 35:985–989
Neves G, Cooke SF, Bliss TVP (2008) Synaptic plasticity, memory and the hippocampus: a neural network approach to causality. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:65–75
Park E, Park SY, Dobkin C, Schuller-Levis G (2014) Development of a novel cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase knockout mouse: dietary taurine reduces neonatal mortality. J Amino Acids. doi:10.1155/2014/346809
Pasantes-Morales H, Schousboe A (1988) Volume regulation in astrocytes: a role for taurine as osmoeffector. J Neurosci Res 20:505–509
Pasantes-Morales H, Tuz K (2006) Volume changes in neurons: hyperexcitability and neuronal death. Contrib Nephrol 152:221–240
Pasantes-Morales H, Quesada O, Cárabez A, Huxtable RJ (1983) Effect of taurine transport antagonist guanidinoethane sulfonate and β-alanine on the morphology of rat retina. J Neurosci Res 9:135–144
Pasantes-Morales H, Arzate ME, Quesada O, Huxtable RJ (1987) Higher susceptibility of taurine-deficient rats to seizures induced by 4-aminopyridine. Neuropharmacology 26:1721–1725
Paxinos G, Watson C (1997) The rat brain in steriotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Rodríguez-Navarro JA, Gonzalo-Gobernado R, Herranz AS, González-Vigueras JM, Solís JM (2009) High potassium induces taurine release by osmosensitive and osmoresistant mechanisms in the rat hippocampus in vivo. J Neurosci Res 87:208–217
Schmieden V, Kuhse J, Betz H (1992) Agonist pharmacology of neonatal and adult glycine receptor α subunits: identification of amino acid residues involved in taurine activation. EMBO J 11:2025–2032
Schousboe A, Sánchez-Olea R, Morán J, Pasantes-Morales H (1991) Hyposmolarity-induced taurine release in cerebellar granule cells is associated with diffusion and not with high-affinity transport. J Neurosci Res 30:661–665
Sergeeva OA, Chepkova AN, Haas HL (2002) Guanidinoethyl sulphonate is a glycine receptor antagonist in striatum. Br J Pharmacol 137:855–860
Sergeeva OA, Chepkova AN, Doreulee N, Eriksson KS, Poelchen W, Mönnighoff Heller-Stilb B, Warskulat U, Häussinger D, Haas HL (2003) Taurine-induced long-lasting enhancement of synaptic transmission in mice: role of transporters. J Physiol 550(3):911–919
Solís JM, Herranz AS, Herreras O, Lerma J, Martín del Río R (1988) Does taurine act as an osmoregulatory substance in the rat brain? Neurosci Lett 91:53–58
Sturman J (1973) Taurine pool sizes in the rat: effects of vitamin B-6 deficiency and high taurine diet. J Nutr 103:1566–1580
Suárez LM, Solís JM (2006) Taurine potentiates presynaptic NMDA receptors in hippocampal Schaffer collateral axons. Eur J Neurosci 24:405–418
Suárez LM, Bustamante J, Orensanz LM, Martin del Río R, Solís JM (2014) Cooperation of taurine uptake and dopamine D1 receptor activation facilitates the induction of protein synthesis-dependent late LTP. Neuropharmacology 79:101–111
Suárez LM, Muñoz MD, Martín del Río R, Solís JM (2016) Taurine content in different brain structures during ageing: effect on hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-015-2155-2
Sved DW, Godsey JL, Ledyard SL, Mahoney AP, Stetson PL, Ho S, Myers NR, Resnis P, Renwick AG (2007) Absorption, tissue distribution, metabolism and elimination of taurine given orally to rats. Amino Acids 32:459–466
Vohra PS, Hui X (2000) Improvement of impaired memory in mice by taurine. Neural Plast 7:245–259
Warskulat U, Heller-Stilb B, Oermann E, Zilles K, Haas H, Lang F, Häussinger D (2007) Phenotype of the taurine transporter knockout mouse. Methods Enzymol 428:439–458
Zhou Y, Holmseth S, Guo C, Hassel B, Höfner G, Huitfeldt HS, Wanner KT, Danbolt NC (2012) Deletion of the γ-aminobutyric acid transporter 2 (GAT2 and SLC6A13) gene in mice leads to changes in liver and brain taurine contents. J Biol Chem 287:35733–35746
Zhu WJ, Vicini S (1997) Neurosteroid prolongs GABAA channel deactivation by altering kinetics of desensitized states. J Neurosci 17:4022–4031
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from “Instituto de Salud Carlos III” (PIU081067) to JMS. We thank Amparo Latorre and José Barbado for technical assistance. This article was revised by Proof-Reading-Service.com.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The care and use of animals was carried out following the European Communities Council Directive (86/609/ECC). Protocols were approved by “Comité Ético de Bienestar Animal” at Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal (animal facilities ES280790000092).
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: E. I. Closs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suárez, L.M., Muñoz, MD., González, J.C. et al. The taurine transporter substrate guanidinoethyl sulfonate mimics the action of taurine on long-term synaptic potentiation. Amino Acids 48, 2647–2656 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2298-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2298-9