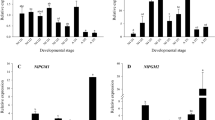
Abstract
Histidine is an essential amino acid assumed to be synthesized by an obligatory yeast-like symbiont (Entomomyces delphacidicola str. NLU) in Nilaparvata lugens, an important rice pest. The adenosine-triphosphate phosphoribosyltransferase (ATP-PRTase) facilities the committed first step of the histidine biosynthesis pathway. In the current study, a putative ATP-PRTase was cloned and verified to be of E. delphacidicola origin (EdePRTase). The expression of the gene was spatial and temporal universal with a profile that matched the distribution of the fungal symbiont. RNA interference aided the knockdown of the EdePRTase-suppressed EdePRTase expression by 32–48 %. Hemolymph histidine level was also reduced followed by significant reduction of adult body weight. However, other performance characters including nymph development, survival, and adult sex ratio were not adversely affected by the knockdown. Furthermore, forced histidine exposure (through injection or feeding) significantly inhibited the EdePRTase mRNA levels at higher concentrations, but significantly increased EdePRTase expression levels at lower concentrations (feeding only). The significance of these findings support that the EdePRTase is from symbiont E. delphacidicola, and its involvement in histidine biosynthesis of N. lugens was discussed. The results provide a better understanding of EdePRTase and the encoded functional ATP-PRTase enzyme regulation in N. lugens and insects in general.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aklujkar M (2011) Two ATP phosphoribosyltransferase isozymes of Geobacter sulfurreducens contribute to growth in the presence or absence of histidine and under nitrogen fixation conditions. Can J Microbiol 57(7):547–558. doi:10.1139/W11-047
Alifano P, Fani R, Lio P, Lazcano A, Bazzicalupo M, Carlomagno MS, Bruni CB (1996) Histidine biosynthetic pathway and genes: structure, regulation, and evolution. Microbiol Rev 60(1):44–69
Bikard D, Patel D, Le Mette C, Giorgi V, Camilleri C, Bennett MJ, Loudet O (2009) Divergent evolution of duplicate genes leads to genetic incompatibilities within A. thaliana. Science 323(5914):623–626. doi:10.1126/science.1165917
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55(4):611–622. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Chen J, Zhang D, Yao Q, Zhang J, Dong X, Tian H, Chen J, Zhang W (2010) Feeding-based RNA interference of a trehalose phosphate synthase gene in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Mol Biol 19(6):777–786. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2583.2010.01038.x
Chen YH, Bernal CC, Tan J, Horgan FG, Fitzgerald MA (2011) Planthopper “adaptation” to resistant rice varieties: changes in amino acid composition over time. J Insect Physiol 57(10):1375–1384. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2011.07.002
Cho Y, Sharma V, Sacchettini JC (2003) Crystal structure of ATP phosphoribosyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem 278(10):8333–8339. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212124200
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2011) ProtTest 3: fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 27(8):1164–1165. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr088
Dietrich FS, Mulligan J, Hennessy K, Yelton MA, Allen E, Araujo R, Aviles E, Berno A, Brennan T, Carpenter J, Chen E, Cherry JM, Chung E, Duncan M, Guzman E, Hartzell G, Hunicke-Smith S, Hyman RW, Kayser A, Komp C, Lashkari D, Lew H, Lin D, Mosedale D, Davis RW et al (1997) The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome V. Nature 387(6632 Suppl):78–81
Dong S, Pang K, Bai X, Yu X, Hao P (2011) Identification of two species of yeast-like symbiotes in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Curr Microbiol 62(4):1133–1138. doi:10.1007/s00284-010-9830-z
Fan H-W, Noda H, Xie H-Q, Suetsugu Y, Zhu Q-H, Zhang C-X (2015) Genomic analysis of an Ascomycete fungus from the rice planthopper reveals how it adapts to an endosymbiotic lifestyle. Genome Biol Evol 7(9):2623–2634. doi:10.1093/gbe/evv169
Fan H-W, Lu J-B, Ye Y-X, Yu X-P, Zhang C-X (2016) Characteristics of the draft genome of “Candidatus Arsenophonus nilaparvatae”, a facultative endosymbiont of Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Sci. doi:10.1111/1744-7917.12318
Fu Q, Zhang Z, Hu C, Lai F (2001a) The effects of high temperature on both yeast-like symbionts and amino acid requirements of Nilaparvata lugens. Kun Chong Xue Bao Acta Entomologica Sinica 44(4):534–540
Fu Q, Zhang Z, Hu C, Lai F, Sun Z (2001b) A chemically defined diet enables continuous rearing of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Appl Entomol Zool 36(1):111–116
Gao Q, Jin K, Ying SH, Zhang Y, Xiao G, Shang Y, Duan Z, Hu X, Xie XQ, Zhou G, Peng G, Luo Z, Huang W, Wang B, Fang W, Wang S, Zhong Y, Ma LJ, St Leger RJ, Zhao GP, Pei Y, Feng MG, Xia Y, Wang C (2011) Genome sequencing and comparative transcriptomics of the model entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and M. acridum. PLoS Genet 7(1):e1001264. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001264
Harding MM (2004) The architecture of metal coordination groups in proteins. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60(Pt 5):849–859. doi:10.1107/S0907444904004081
Hu J, Xia Y (2015) F -ATP synthase alpha subunit: a potential target for RNAi-mediated pest management of Locusta migratoria manilensis. Pest Manag Sci. doi:10.1002/ps.4185
Huvenne H, Smagghe G (2010) Mechanisms of dsRNA uptake in insects and potential of RNAi for pest control: a review. J Insect Physiol 56(3):227–235. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2009.10.004
Ingle RA (2011) Histidine biosynthesis. Arabidopsis Book 9:e0141. doi:10.1199/tab.0141
Koslowsky S, Riegler H, Bergmuller E, Zrenner R (2008) Higher biomass accumulation by increasing phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase activity in Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Biotechnol J 6(3):281–294. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2007.00314.x
Kulis-Horn RK, Persicke M, Kalinowski J (2014) Histidine biosynthesis, its regulation and biotechnological application in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microb Biotechnol 7(1):5–25. doi:10.1111/1751-7915.12055
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Li J, Chen Q, Lin Y, Jiang T, Wu G, Hua H (2011) RNA interference in Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae) based on dsRNA ingestion. Pest Manag Sci 67(7):852–859. doi:10.1002/ps.2124
Li H, Guan R, Guo H, Miao X (2015) New insights into an RNAi approach for plant defence against piercing-sucking and stem-borer insect pests. Plant Cell Environ 38(11):2277–2285. doi:10.1111/pce.12546
Liu S, Ding Z, Zhang C, Yang B, Liu Z (2010) Gene knockdown by intro-thoracic injection of double-stranded RNA in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 40(9):666–671. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.06.007
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(−Delta Delta C) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lohkamp B, McDermott G, Campbell SA, Coggins JR, Lapthorn AJ (2004) The structure of Escherichia coli ATP-phosphoribosyltransferase: identification of substrate binding sites and mode of AMP inhibition. J Mol Biol 336(1):131–144. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.12.020
Meyering-Vos M, Müller A (2007) RNA interference suggests sulfakinins as satiety effectors in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. J Insect Physiol 53(8):840–848. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2007.04.003
Morton DP, Parsons SM (1977) Inhibition of ATP phosphoribosyltransferase by AMP and ADP in the absence and presence of histidine. Arch Biochem Biophys 181(2):643–648
Palli SR (2014) RNA interference in Colorado potato beetle: steps toward development of dsRNA as a commercial insecticide. Curr Opin Insect Sci 6:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.cois.2014.09.011
Pang K, Dong SZ, Hou Y, Bian YL, Yang K, Yu XP (2012) Cultivation, identification and quantification of one species of yeast-like symbiotes, Candida, in the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Sci 19(4):477–484. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7917.2011.01486.x
Pedreno S, Pisco JP, Larrouy-Maumus G, Kelly G, de Carvalho LP (2012) Mechanism of feedback allosteric inhibition of ATP phosphoribosyltransferase. Biochemistry 51(40):8027–8038. doi:10.1021/bi300808b
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45. doi:10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Piszkiewicz D, Tilley BE, Rand-Meir T, Parsons SM (1979) Amino acid sequence of ATP phosphoribosyltransferase of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76(4):1589–1592
Polgar L (2005) The catalytic triad of serine peptidases. Cell Mol Life Sci 62(19–20):2161–2172. doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5160-x
Rajani MS, Aniruddha Raychaudhuri MMT, Duff SMG (2013) Histidine biosynthesis pathway: a test case for engineering plant metabolism and growth. Plant Physiol 5:51–62
Rebek J (1990) On the structure of histidine and its role in enzyme active sites. Struct Chem 1:129–131
Shakesby AJ, Wallace IS, Isaacs HV, Pritchard J, Roberts DM, Douglas AE (2009) A water-specific aquaporin involved in aphid osmoregulation. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39(1):1–10. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2008.08.008
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML Version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30(9):1312–1313. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
Stepansky A, Leustek T (2006) Histidine biosynthesis in plants. Amino Acids 30(2):127–142. doi:10.1007/s00726-005-0247-0
Tang Q-Y, Zhang C-X (2013) Data processing system (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci 20(2):254–260. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7917.2012.01519.x
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3(7):1–12. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Wan PJ, Yang L, Wang WX, Fan JM, Fu Q, Li GQ (2014) Constructing the major biosynthesis pathways for amino acids in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae), based on the transcriptome data. Insect Mol Biol 23(2):152–164. doi:10.1111/imb.12069
Wan P-J, Fu K-Y, Lü F-G, Guo W-C, Li G-Q (2015a) Knockdown of a putative alanine aminotransferase gene affects amino acid content and flight capacity in the Colorado potato beetle Leptinotarsa decemlineata. Amino Acids 47(7):1445–1454. doi:10.1007/s00726-015-1978-1
Wan P-J, Yang L, Yuan S-Y, Tang Y-H, Fu Q, Li G-Q (2015b) RNA interference-aided knockdown of a putative saccharopine dehydrogenase leads to abnormal ecdysis in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Bull Entomol Res 105(4):390–398. doi:10.1017/S0007485315000231
Wan P-J, Yuan S-Y, Tang Y-H, Li K-L, Yang L, Fu Q, Li G-Q (2015c) Pathways of amino acid degradation in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) with special reference to lysine-ketoglutarate reductase/saccharopine dehydrogenase (LKR/SDH). PLoS One 10(5):e0127789. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0127789
Wang ZM, Luecke H, Yao NH, Quiocho FA (1997) A low energy short hydrogen bond in very high resolution structures of protein receptor-phosphate complexes. Nat Struct Biol 4(10):840
Wilkinson TL, Ishikawa H (2001) On the functional significance of symbiotic microorganisms in the Homoptera: a comparative study of Acyrthosiphon pisum and Nilaparvata lugens. Physiol Entomol 26(1):86–93. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3032.2001.00214.x
Xue J, Zhou X, Zhang C-X, Yu L-L, Fan H-W, Wang Z, Xu H-J, Xi Y, Zhu Z-R, Zhou W-W, Pan P-L, Li B-L, Colbourne J, Noda H, Suetsugu Y, Kobayashi T, Zheng Y, Liu S, Zhang R, Liu Y, Luo Y-D, Fang D-M, Chen Y, Zhan D-L, Lv X-D, Cai Y, Wang Z-B, Huang H-J, Cheng R-L, Zhang X-C (2014) Genomes of the rice pest brown planthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation. Genome Biol 15(12):521
Yu R, Xu X, Liang Y, Tian H, Pan Z, Jin S, Wang N, Zhang W (2014) The insect ecdysone receptor is a good potential target for RNAi-based pest control. Int J Biol Sci 10(10):1171–1180. doi:10.7150/ijbs.9598
Yuan M, Lu Y, Zhu X, Wan H, Shakeel M, Zhan S, Jin BR, Li J (2014) Selection and evaluation of potential reference genes for gene expression analysis in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) using reverse-transcription quantitative PCR. PLoS One 9(1):e86503. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086503
Zha W, Peng X, Chen R, Du B, Zhu L, He G (2011) Knockdown of midgut genes by dsRNA-transgenic plant-mediated RNA interference in the hemipteran insect Nilaparvata lugens. PLoS One 6(5):e20504. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020504
Zhang Y, Morar M, Ealick SE (2008) Structural biology of the purine biosynthetic pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(23):3699–3724. doi:10.1007/s00018-008-8295-8
Zhang Y, Shang X, Deng A, Chai X, Lai S, Zhang G, Wen T (2012) Genetic and biochemical characterization of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATP phosphoribosyltransferase and its three mutants resistant to feedback inhibition by histidine. Biochimie 94(3):829–838. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2011.11.015
Zhang Y-X, Ge L-Q, Jiang Y-P, Lu X-L, Li X, Stanley D, Song Q-S, Wu J-C (2015) RNAi knockdown of acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene eliminates jinggangmycin-enhanced reproduction and population growth in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Sci Rep 5:15360. doi:10.1038/srep15360
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grants of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371939), the National Rice Industrial Technology System (CARS-1-18) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP) of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All animal work was conducted according to relevant national and international guidelines.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Handling Editor: J. González López.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, PJ., Tang, YH., Yuan, SY. et al. ATP phosphoribosyltransferase from symbiont Entomomyces delphacidicola invovled in histidine biosynthesis of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Amino Acids 48, 2605–2617 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2287-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2287-z