Abstract
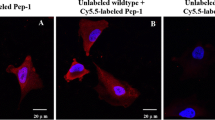
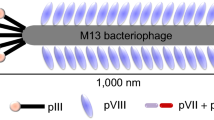
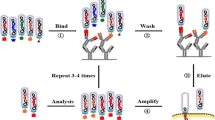
Discovery of the cancer-specific peptidic ligands have been emphasized for active targeting drug delivery system and non-invasive imaging. For the discovery of useful and applicable peptidic ligands, in vivo peptide-displayed phage screening has been performed in this study using a xenograft mouse model as a mimic microenvironment to tumor. To seek human lung cancer-specific peptides, M13 phage library displaying 2.9 × 109 random peptides was intravenously injected into mouse model bearing A549-derived xenograft tumor through the tail vein. Then the phages emerged from a course of four rounds of biopanning in the xenograft tumor tissue. Novel peptides were categorized into four groups according to a sequence-homology phylogenicity, and in vivo tumor-targeting capacity of these peptides was validated by whole body imaging with Cy5.5-labeled phages in various cancer types. The result revealed that novel peptides accumulated only in adenocarcinoma lung cancer cell-derived xenograft tissue. For further confirmation of the specific targeting ability, in vitro cell-binding assay and immunohistochemistry in vivo tumor tissue were performed with a selected peptide. The peptide was found to bind intensely to lung cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo, which was efficiently compromised with unlabeled phages in an in vitro competition assay. In conclusion, the peptides specifically targeting human lung cancer were discovered in this study, which is warranted to provide substantive feasibilities for drug delivery and imaging in terms of a novel targeted therapeutics and diagnostics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzazy HM, Highsmith WE Jr (2002) Phage display technology: clinical applications and recent innovations. Clin Biochem 35:425–445
Bartlett DW, Su H, Hildebrandt IJ, Weber WA, Davis ME (2007) Impact of tumor-specific targeting on the biodistribution and efficacy of siRNA nanoparticles measured by multimodality in vivo imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15549–15554. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707461104
Carrico ZM et al (2012) N-Terminal labeling of filamentous phage to create cancer marker imaging agents. ACS nano 6:6675–6680. doi:10.1021/nn301134z
Choi J et al (2012) Use of macrophages to deliver therapeutic and imaging contrast agents to tumors. Biomaterials 33:4195–4203. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.02.022
Collins LG, Haines C, Perkel R, Enck RE (2007) Lung cancer: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician 75:56–63
Conraux L et al (2013) Plasma peptide biomarker discovery for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry profiling. PloS One 8:e79733. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079733
Daniels TR, Delgado T, Rodriguez JA, Helguera G, Penichet ML (2006) The transferrin receptor part I: biology and targeting with cytotoxic antibodies for the treatment of cancer. Clin Immunol 121:144–158. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2006.06.010
de Bruin EC et al (2014) Reduced NF1 expression confers resistance to EGFR inhibition in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0741
Du B et al (2006) In vitro panning of a targeting peptide to hepatocarcinoma from a phage display peptide library. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342:956–962
Fei L, Yap LP, Conti PS, Shen WC, Zaro JL (2014) Tumor targeting of a cell penetrating peptide by fusing with a pH-sensitive histidine-glutamate co-oligopeptide. Biomaterials. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.01.047
Garanger E, Boturyn D, Dumy P (2007) Tumor targeting with RGD peptide ligands-design of new molecular conjugates for imaging and therapy of cancers. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 7:552–558
Ghosh D, Lee Y, Thomas S, Kohli AG, Yun DS, Belcher AM, Kelly KA (2012) M13-templated magnetic nanoparticles for targeted in vivo imaging of prostate cancer. Nat Nanotechnol 7:677–682. doi:10.1038/nnano.2012.146
Guckenberger M et al (2012) Is there a lower limit of pretreatment pulmonary function for safe and effective stereotactic body radiotherapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer? J Thorac 7:542–551. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e31824165d7
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107
Ko JH, Gu W, Lim I, Bang H, Ko EA, Zhou T (2014) Ion channel gene expression in lung adenocarcinoma: potential role in prognosis and diagnosis. PloS One 9:1. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086569
Larimer BM, Thomas WD, Smith GP, Deutscher SL (2014) Affinity maturation of an ERBB2-targeted SPECT imaging peptide by in vivo phage display. Mol Imaging Biol 16(4):449–458. doi:10.1007/s11307-014-0724-5
Liu C, Wen Z, Li Y, Peng L (2014) Application of ThinPrep bronchial brushing cytology in the early diagnosis of lung cancer: a retrospective study. PloS One 9:e90163. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090163
Molek P, Strukelj B, Bratkovic T (2011) Peptide phage display as a tool for drug discovery: targeting membrane receptors. Molecules 16:857–887. doi:10.3390/molecules16010857
Palma D, Lagerwaard F, Rodrigues G, Haasbeek C, Senan S (2012) Curative treatment of Stage I non-small-cell lung cancer in patients with severe COPD: stereotactic radiotherapy outcomes and systematic review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:1149–1156. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.03.005
Park HY, Kim J, Cho JH, Moon JY, Lee SJ, Yoon MY (2011) Phage display screen for peptides that bind Bcl-2 protein. J Biomol Screen 16:82–89. doi:10.1177/1087057110385816
Ploss M et al (2014) Selection of peptides binding to metallic borides by screening M13 phage display libraries. BMC Biotechnol 14:12. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-14-12
Qi Q, Lu N, Li C, Zhao J, Liu W, You Q, Guo Q (2014) Involvement of RECK in gambogic acid induced anti-invasive effect in A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Molecular Carcinog doi:10.1002/mc.22138
Schumacher TN, Tsomides TJ (2001) In vitro radiolabeling of peptides and proteins. Curr Protoc Protein Sci Chapter 3: Unit 3.3 doi:10.1002/0471140864.ps0303s00
Sidhu SS (2001) Engineering M13 for phage display. Biomol Eng 18:57–63
Smith GP (1985) Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science 228:1315–1317
Stefanick JF, Ashley JD, Kiziltepe T, Bilgicer B (2013) A systematic analysis of peptide linker length and liposomal polyethylene glycol coating on cellular uptake of peptide-targeted liposomes. ACS nano 7:2935–2947. doi:10.1021/nn305663e
Vincent RG et al (1977) The changing histopathology of lung cancer: a review of 1682 cases. Cancer 39:1647–1655
Wu X, Chen H, Wang X (2012) Can lung cancer stem cells be targeted for therapies? Cancer Treat Rev 38:580–588. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.02.013
Zhu W et al (2014) Expression of miR-29c, miR-93, and miR-429 as potential biomarkers for detection of early stage non-small lung cancer. PLoS One 9:e87780. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0087780
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (NRF-2012R1A2A2A01014671 and NRF-2013R1A1A2011346) and a Grant from the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI06C0868 and HI10C2014).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K.J., Lee, J.H., Chung, H.K. et al. Novel peptides functionally targeting in vivo human lung cancer discovered by in vivo peptide displayed phage screening. Amino Acids 47, 281–289 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1852-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1852-6