Abstract
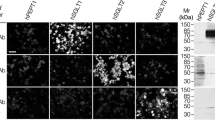
d-Aspartate (d-Asp) is an endogenous substance in mammals. Degradation of d-Asp is carried out only by d-aspartate oxidase (DDO). We measured DDO activity in porcine tissues, and produced an anti-porcine DDO antibody to examine the cellular localization of DDO. All the tissues examined showed DDO activities, whereas the substrate d-Asp was not detected in kidney cortex, liver, heart, and gastric mucosa. In the kidney, intensive immunohistochemical staining for DDO was found in the epithelial cells of the proximal tubules. In the liver, the epithelial cells of interlobular bile ducts, liver sinusoid-lining cells with cytoplasmic processes, and the smooth muscle cells of arterioles were strongly stained for DDO. In the heart, cardiomyocytes and the smooth muscle cells of arterioles showed DDO-immunoreactivity. In the gastric mucosa, only the chief cells were DDO-positive. These newly identified DDO-positive cells seem to actively degrade d-Asp to prevent an excess of d-Asp from exerting harmful effects on the respective functions of porcine tissues.



Similar content being viewed by others

Abbreviations
- DDO:
-
d-Aspartate oxidase
- d-Asp:
-
d-Aspartate
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- DAB:
-
3,3′-Diaminobenzidine
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate
References
Boni R, Santillo R, Macchia G, Spinelli P, Ferrandino G, D’Aniello A (2006) d-Aspartate and reproductive activity in sheep. Theriogenology 65:1265–1278
D’Aniello A (2007) d-Aspartic acid: an endogenous amino acid with an important neuroendocrine role. Brain Res Rev 53:215–234
D’Aniello A, D’Onofrio G, Pischetola M, D’Aniello G, Vetere A, Petrucelli L, Fisher GH (1993) Biological role of d-amino acid oxidase and d-aspartate oxidase. Effects of d-amino acids. J Biol Chem 268:26941–26949
D’Aniello A, Di Fiore MM, Fisher GH, Milone A, Seleni A, D’Aniello S, Perna AF, Ingrosso D (2000a) Occurrence of d-aspartic acid and N-methyl-d-aspartic acid in rat neuroendocrine tissues and their role in the modulation of luteinizing hormone and growth hormone release. FASEB J 14:699–714
D’Aniello G, Tolino A, D’Aniello A, Errico F, Fisher GH, Di Fiore MM (2000b) The role of d-aspartic acid and N-methyl-d-aspartic acid in the regulation of prolactin release. Endocrinology 141:3862–3870
De Marco C (1966) d-Aspartate oxidase of the pig kidney. II. Inhibition by malic and tartaric acid. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper 42:1455–1457
Errico F, Pirro MT, Affuso A, Spinelli P, De Felice M, D’Aniello A, Di Lauro R (2006) A physiological mechanism to regulate d-aspartic acid and NMDA levels in mammals revealed by d-aspartate oxidase deficient mice. Gene 374:50–57
Errico F, Nistico R, Palma G, Federici M, Affuso A, Brilli E, Topo E, Centonze D, Bernardi G, Bozzi Y, D’Aniello A, Di Lauro R, Mercuri NB, Usiello A (2008a) Increased levels of d-aspartate in the hippocampus enhance LTP but do not facilitate cognitive flexibility. Mol Cell Neurosci 37:236–246
Errico F, Rossi S, Napolitano F, Catuogno V, Topo E, Fisone G, D’Aniello A, Centonze D, Usiello A (2008b) d-Aspartate prevents corticostriatal long-term depression and attenuates schizophrenia-like symptoms induced by amphetamine and MK-801. J Neurosci 28:10404–10414
Hamase K (2007) Sensitive two-dimensional determination of small amounts of d-amino acids in mammals and the study on their functions. Chem Pharm Bull 55:503–510
Hashimoto A, Oka T (1997) Free d-aspartate and d-serine in the mammalian brain and periphery. Prog Neurobiol 52:325–353
Homma H (2007) Biochemistry of d-aspartate in mammalian cells. Amino Acids 32:3–11
Horiike K, Arai R, Tojo H, Yamano T, Nozaki M, Maeda T (1985) Histochemical staining of cells containing flavoenzyme d-amino acid oxidase based on its enzymatic activity: application of a coupled peroxidation method. Acta Histochem Cytochem 18:539–550
Hosoya K, Sugawara M, Asaba H, Terasaki T (1999) Blood-brain barrier produces significant efflux of l-aspartic acid but not d-aspartic acid: in vivo evidence using the brain efflux index method. J Neurochem 73:1206–1211
Huang AS, Beigneux A, Weil ZM, Kim PM, Molliver ME, Blackshaw S, Nelson RJ, Young SG, Snyder SH (2006) d-Aspartate regulates melanocortin formation and function: behavioral alterations in d-aspartate oxidase-deficient mice. J Neurosci 26:2814–2819
Imai K, Fukushima T, Santa T, Homma H, Hamase K, Sakai K, Kato M (1996) Analytical chemistry and biochemistry of d-amino acids. Biomed Chromatogr 10:303–312
Ishio S, Yamada H, Hayashi M, Yatsushiro S, Noumi T, Yamaguchi A, Moriyama Y (1998) d-Aspartate modulates melatonin synthesis in rat pinealocytes. Neurosci Lett 249:143–146
Negri A, Massey V, Williams CH Jr (1987) d-Aspartate oxidase from beef kidney. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem 262:10026–10034
Negri A, Massey V, Williams CH Jr, Schopfer LM (1988) The kinetic mechanism of beef kidney d-Aspartate oxidase. J Biol Chem 263:13557–13563
Pampillo M, del Carmen Diaz M, Duvilanski BH, Rettori V, Seilicovich A, Lasaga M (2001) Differential effects of glutamate agonists and d-aspartate on oxytocin release from hypothalamus and posterior pituitary of male rats. Endocrine 15:309–315
Pampillo M, Scimonelli T, Bottino MC, Duvilanski BH, Rettori V, Seilicovich A, Lasaga M (2002) The effect of d-aspartate on luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone, α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, GABA and dopamine release. Neuroreport 13:2341–2344
Parola M, Marra F, Pinzani M (2008) Myofibroblast-like cells and liver fibrogenesis: emerging concepts in a rapidly moving scenario. Mol Aspects Med 29:58–66
Rinaldi A (1971) Partial purification and some properties of beef kidney d-aspartate oxidase. Enzymologia 40:314–321
Schell MJ, Cooper OB, Snyder SH (1997) d-Aspartate localizations imply neuronal and neuroendocrine roles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2013–2018
Still JL, Buell MV, Knox WE, Green DE (1949) Studies on the cyclophorase system. VII. d-Aspartic oxidase. J Biol Chem 179:831–837
Takigawa Y, Homma H, Lee JA, Fukushima T, Santa T, Iwatsubo T, Imai K (1998) d-Aspartate uptake into cultured rat pinealocytes and the concomitant effect on l-aspartate levels and melatonin secretion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 248:641–647
Tanaka H, Yamamoto A, Ishida T, Horiike K (2007) Simultaneous measurement of d-serine dehydratase and d-amino acid oxidase activities by the detection of 2-oxo-acid formation with reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 362:83–88
Van Rossen E, Borght SV, van Grunsven LA, Reynaert H, Bruggeman V, Blomhoff R, Roskams T, Geerts A (2009) Vinculin and cellular retinol-binding protein-1 are markers for quiescent and activated hepatic stellate cells in formalin-fixed paraffin embedded human liver. Histochem Cell Biol 131:313–325
Wang H, Wolosker H, Pevsner J, Snyder SH, Selkoe DJ (2000) Regulation of rat magnocellular neurosecretory system by d-aspartate: evidence for biological role(s) of a naturally occurring free d-amino acid in mammals. J Endocrinol 167:247–252
Yamamoto A, Tanaka H, Ishida T, Horiike K (2007) Functional and structural characterization of d-aspartate oxidase from porcine kidney: non-Michaelis kinetics due to substrate activation. J Biochem 141:363–376
Zaar K (1996) Light and electron microscopic localization of d-aspartate oxidase in peroxisomes of bovine kidney and liver: an immunocytochemical study. J Histochem Cytochem 44:1013–1019
Zaar K, Köst H-P, Schad A, Völkl A, Baumgart E, Fahimi HD (2002) Cellular and subcellular distribution of d-aspartate oxidase in human and rat brain. J Comp Neurol 450:272–282
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Takefumi Yamamoto, Central Research Laboratory of our University, for technical advice regarding immunohistochemistry. The present study was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Sciences and Technology of Japan, Grant-in-aid for Cooperation of Innovative Technology and Advanced Research in City Area Program in the Southern Area of Lake Biwa, 2007–2009, and Grants-in-aid (Heisei era 19 and 20) from Shiga University of Medical Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, A., Tanaka, H., Ishida, T. et al. Immunohistochemical localization of d-aspartate oxidase in porcine peripheral tissues. Amino Acids 41, 529–536 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0785-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0785-y