Summary.
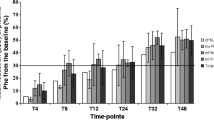
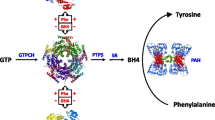
We describe six children with tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) deficiency. All patients carry two mutant alleles in the PAH gene. Cofactor deficiency was excluded. The effect of BH4 administration was studied by correlating different oral BH4 doses with plasma phenylalanine levels under defined protein intake. Our results indicate that oral BH4 supplementation may be used as long-term treatment for individuals with BH4-responsive PAH deficiency, either without or in combination with a less restrictive diet. Previous in vitro studies have demonstrated that BH4 inhibits PAH tetramers but activates PAH dimers. This may indicate, that BH4-responsiveness results from BH4 induced stabilization of mutant PAH dimers. In addition, interindividual differences in the cellular folding apparatus may determine the tertiary structure and the amount of mutant PAH dimers and hence may account for divergent BH4-responsiveness reported for the same PAH genotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis MD, Parniak MA, Kaufman K, Kempner E (1996) Structurefunction relationships of phenylalanine hydroxylase revealed by radiation target analysis. Arch Biochem Biophys 325: 235–241
Davis MD, Parniak MA, Kaufman S, Kempner E (1997) The role of phenylalanine in structure-function relationships of phenylalanine hydroxylase revealed by radiation target analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 491–495
Erlandsen H, Stevens RC (1999) The structural basis of phenylketonuria. Mol Genet Metab 68: 103–125
Erlandsen H, Stevens RC (2001) A structural hypothesis for BH4 responsiveness in patients with mild forms of hyperphenylalaninaemia and phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 24: 213–230
Gregersen N, Bross P, Andresen BS, Pedersen CB, Corydon TJ, Bolund L (2001) The role of chaperone-assisted folding and quality control in inborn errors of metabolism: protein folding disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis 24: 189–212
Guldberg P, Rey F, Zschocke J, Romano V, Francois B, Michiels L, Ullrich K, Hoffmann G, Burgard P, Schmidt H, Meli C, Riva E, Dianzani I, Ponzone A, Rey J, Güttler F (1998) A European multicenter study of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency: classification of 105 mutations and a general system for genotypebased prediction of metabolic phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 63: 71–79
Kayaalp E, Treacy E, Waters PJ, Byck S, Nowacki P, Scriver CR (1997) Human phenylalanine hydroxylase mutations and hyperphenylalaninemia phenotypes: a metanalysis of genotypephenotype correlations. Am J Hum Genet 61: 1309–1317
Kure S, Hou DC, Ohura T, Iwamoto H, Suzuki S, Sugiyama N, Sakamoto O, Fujii K, Matsubara Y, Narisawa K (1999) Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. J Pediatr 135: 375–378
Lindner M, Haas D, Zschocke J, Burgard P (2001) Tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness in phenylketonuria differs between patients with the same genotype. Mol Genet Metab 73: 104–106
Phillips RS, Kaufman S (1984) Ligand effects on the phosphorylation state of hepatic phenylalanine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem 259: 2474–2479
Scriver CR, Waters PJ, Sarkissian C, Ryan S, Prevost L, Cote D, Novak J, Teebi S, Nowacki PM (2000) PAHdb: a locus-specific knowledgebase. Hum Mutat 15: 99–104
Spaapen LJM, Bakker JA, Velter C, Loots W, Rubio-Gonzalbo ME, Forget PP, Dorland L, De Koning TJ, Polle-The BT, Ploos van Amstel HK, Bekhof J, Blau N, Duran M (2001) Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency in Dutch neonates. J Inherit Metab Dis 24: 352–358
Trefz FK, Aulela-Scholz C, Blau N (2001) Successful treatment of phenylketonuria with tetrahydrobiopterin. Eur J Pediatr 160: 315 Xia, T, Gray DW, Shiman R (1994) Regulation of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase. III. Control of catalysis by (6R)- tetrahydrobiopterin and phenylalanine. J Biol Chem 269: 24657– 24665
Zschocke J, Hoffmann GF (1999) Phenylketonuria mutations in Germany. Hum Genet 104: 390–398
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Acknowledgements We express our gratitude to Dr. J. Zschocke for the genetic analysis of the PAH mutants, to Dr. N. Blau (Switzerland) for pterin analysis and to Dr. V. Wagner (Univ. Lübeck, Germany) for additional data on patient EM. Furthermore, we thank the technical staff of our laboratories for their accurate work throughout the project.
Authors' address: Dr. Zoltan Lukacs, Metabolic Laboratory, Department of Pediatrics, University of Hamburg, Martinistr. 52, D-20246 Hamburg, Germany, Fax: +49-40-42803 6717, E-mail: Lukacs@uke.uni-hamburg.de
List of abbreviations: BH4, Tetrahydrobiopterin; DGGE, Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis; DHPR, Dihydropteridine reductase; HPA, Hyperphenylalaninemia; MHP, Mild hyperphenylalaninemia; PAH, Phenylalanine hydroxylase; Phe, Phenylalanine; PKU, Phenylketonuria; Tyr, Tyrosine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinfeld, R., Kohlschütter, A., Ullrich, K. et al. A hypothesis on the biochemical mechanism of BH4-responsiveness in phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Amino Acids 25, 63–68 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-002-0354-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-002-0354-0