Summary.
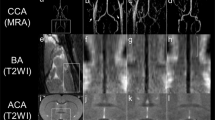
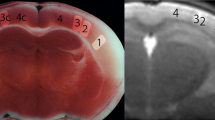
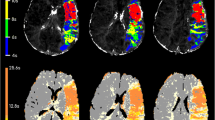
The combined use of perfusion imaging (PI) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is opening a new window into the processes that occur during the first hours of ischemia. DWI detects changes in molecular diffusion associated with cytotoxic edema. PI characterizes the degree of regional hypoperfusion. Regions showing mismatches between DWI and PI, i.e. hypoperfused areas with normal diffusion behavior are considered potentially salvageable. We present results of 11 patients with an occlusion of the middle cerebral artery stem and spontaneous stroke evolution. Whereas the infarct was clearly visible on initial DWI and PI, surrounding tissue at risk of infarction was marked in all patients by an increased blood volume and transit time, but only in a subgroup (n = 3) where alteration were more pronounced this tissue at risk was progressively infarcted. These human DWI and PI data show alterations in the area of tissue at risk which correlates with infarct progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received June 29, 2001 Accepted August 6, 2001 Published online August 20, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flacke, S., Urbach, H., Block, W. et al. Perfusion and molecular diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain: In vivo assessment of tissue alteration in cerebral ischemia. Amino Acids 23, 309–316 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-001-0143-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-001-0143-1