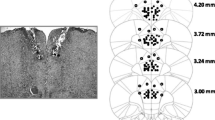
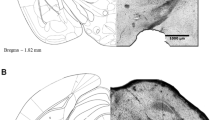
Summary.
Evidence from several laboratories indicates that the anxiogenic effects of cholecystokinin (CCK) are mediated by CCKB receptors. However, it has been reported that CCKA receptors have been found in brain and CCKA antagonists have anxiolytic properties. The aim of this work was to study whether CCKA receptors are also involved in the modulation of anxiety. Anxiogenic effects were observed in the elevated plus maze in rats when pure CCKB receptor agonists (CCK-4 and CCK-8 non-sulfated) or CCK-8S, a CCKB/CCKA agonist, were injected into the lateral ventricle. In contrast, CCK-33, a CCKA agonist or CCK-(1–21) and CCK-(26–29) were ineffective. Furthermore, the anxiogenic effects of CCK-8S were prevented by blocking CCKB but not CCKA receptors. Finally, CCK-33 injected into the postero-medial nucleus accumbens failed to affect the anxiety level of the rats. These results indicate that CCKA receptors are not involved in anxiety, as measured by the paradigms used in this work.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received August 6, 2001 Accepted September 1, 2001 Published online July 31, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernandez-Gómez, A., Aguilar-Roblero, R. & Pérez de la Mora, M. Role of cholecystokinin-A and cholecystokinin-B receptors in anxiety. Amino Acids 23, 283–290 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-001-0139-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-001-0139-x