Abstract
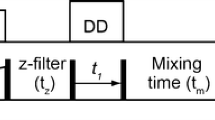
Domain sizes in complex polymer materials on the 2- to 400-nm scale can be probed by 1H spin diffusion NMR with 13C detection, which may be competitive with microscopy. In glassy systems, two-dimensional 1H–13C heteronuclear correlation (HetCor) NMR with 1H spin diffusion is the method of choice. Limits to its applicability have been overcome here by improved data analysis. Single-spectrum referencing eliminates the need for asymptotic equilibration and expands the range of accessible domain sizes to long periods of ~ 400 nm and makes time-consuming measurements with series of mixing times unnecessary. Systematic 1H peak overlap correction in two-domain systems after local equilibration within 3 ms greatly expands the applicability of quantitative long-period determination from HetCor NMR with 1H spin diffusion. It usually works even if the 1H spectra of the two components are fully overlapped, as long as their fractional intensity contributions to at least one 1H peak are distinctly different. This is documented for microphase-separated diblock copolymers of polystyrene and PMMA (alkyl slices) and of polystyrene and poly(4-vinyl pyridine), a polystyrene analogue. Based on extensive spin diffusion simulations utilizing coarse graining to reduce simulation times, convenient graphs are presented that enable conversion of a measured equilibration percentage to a tight range of minimum and maximum long period, as a robust, model-independent result.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The NMR data generated in the course of the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The materials used in this study are available from Polymer Source, Inc. (Dorval, QC, Canada).
References
R.A. Assink, H-1 spin diffusion between polyurethane microphases. Macromolecules 11, 1233 (1978)
P. Caravatti, P. Neuenschwander, R.R. Ernst, Characterization of heterogeneous polymer blends by two-dimensional proton spin diffusion spectroscopy. Macromolecules 18, 119–122 (1985)
J.R. Havens, D.L. VanderHart, Morpholgy of poly (ethylene terephthalate) fibers as studied by multiple-pulse NMR. Macromolecules 18, 1663–1676 (1985)
J. Clauss, K. Schmidt-Rohr, H.W. Spiess, Determination of domain sizes in polymers. Acta Polymer 44, 1–17 (1993)
S. Kaplan, Compatibility of TPD/polycarbonate blends by carbon-13-proton HETCOR in the solid state. Macromolecules 26, 1060–1064 (1993)
J.L. White, P.A. Mirau, Heteronuclear correlation in solid polymers: identification of hydrogen bond donors and acceptors in miscible polymer blends. Macromolecules 27, 1648–1650 (1994)
F. Mellinger, M. Wilhelm, H.W. Spiess, Calibration of 1H NMR spin diffusion coefficients for mobile polymers through transverse relaxation measurements. Macromolecules 32, 4686–4691 (1999)
X. Jia, J. Wolak, X. Wang, J.L. White, Independent calibration of H-1 spin-diffusion coefficients in amorphous polymers by intramolecular polarization transfer. Macromolecules 36, 712–718 (2003)
A. Buda, D.E. Demco, M. Bertmer, B. Blümich, V.M. Litivinov, J.P. Penning, Complex morphology of melt-spun nylon-6 fibers investigated by 1H double-quantum-filtered NMR spin-diffusion. Chem. Phys. Chem. 5, 876–883 (2004)
M.A. Voda, D.E. Demco, A. Voda, T. Schauber, M. Adler, T. Dabisch, A. Adams, M. Baias, B. Blümich, Morphology of thermoplastic polyurethanes by 1H spin diffusion. Macromolecules 39, 4802–4810 (2006)
C. Hedesiu, R. Kleppinger, D.E. Demco, A. Buda, B. Blümich, K. Remerie, V.M. Litvinov, The effect of temperature and annealing on the phase composition, molecular mobility and the thickness of domains in high-density polyethylene. Polymer 48, 763–777 (2007)
K. Schäler, M. Roos, P. Micke, Y. Golitsyn, A. Seidlitz, T. Thurn-Albrecht, H. Schneider, G. Hempel, K. Saalwächter, Basic principles of static proton low-resolution spin diffusion NMR in nanophase-separated materials with mobility contrast, Solid State. NMR 72, 50–63 (2015)
M. Goldman, L. Shen, Spin-spin relaxation in LaF3. Phys. Rev. 144, 321 (1966)
S. Spiegel, K. Schmidt-Rohr, C. Boeffel, H.W. Spiess, 1H spin diffusion coefficient of highly mobile polymers. Polymer 34, 4566–4569 (1993)
P. Caravatti, L. Braunschweiler, R.R. Ernst, Heteronuclear correlation spectroscopy in rotating solids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 100, 305–310 (1983)
X. Jia, X. Wang, A.E. Tonelli, J.L. White, Two-dimensional spin-diffusion NMR reveals differential mixing in biodegradable polymer blends. Macromolecules 38, 2775–2780 (2005)
J.-D. Mao, K. Schmidt-Rohr, Absence of mobile carbohydrate domains in dry humic substances proven by NMR, and implications for organic-contaminant sorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 1751–1756 (2005)
P. Duan, M.S. Lamm, F. Yang, W. Xu, D. Skomski, Y. Su, K. Schmidt-Rohr, Quantifying molecular mixing and heterogeneity in pharmaceutical dispersions at sub-100 nm resolution by spin diffusion NMR. Mol. Pharm. 17, 3567–3580 (2020)
J. Peng, D.H. Kim, W. Knoll, Y. Xuan, B. Li, Y. Han, Morphologies in solvent-annealed thin films of symmetric diblock copolymer. J. Chem. Phys. 125, 064702 (2006)
X. Zhang, K.D. Harris, N.L.Y. Wu, J.N. Murphy, J.M. Buriak, Fast assembly of ordered block copolymer nanostructures through microwave annealing. ACS Nano 4, 7021–7029 (2010)
F. Ferrarese Lupi, T.J. Giammaria, M. Ceresoli, G. Seguini, K. Sparnacci, D. Antonioli, V. Gianotti, M. Laus, M. Perego, Rapid thermal processing of self-assembling block copolymer thin films. Nanotechnol. 24, 315601 (2013)
M. Ceresoli, F.G. Volpe, G. Seguini, D. Antonioli, V. Gianotti, K. Sparnacci, M. Laus, M. Perego, Scaling of correlation length in lamellae forming PS-b-PMMA thin films upon high temperature rapid thermal treatments. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 8618–8624 (2015)
S. Yuan, P. Duan, D.L. Berthier, G. Léon, H. Sommer, J.-Y. de Saint-Laumer, K. Schmidt-Rohr, Multinuclear solid-state NMR of complex nitrogen-rich polymeric microcapsules: weight fractions, spectral editing, component mixing, and persistent radicals. Solid State NMR 106, 101650 (2020)
A.E. Bennett, C.M. Rienstra, M. Auger, K.V. Lakshmi, R.G. Griffin, Heteronuclear decoupling in rotating solids. J. Chem. Phys. 103, 6951–6958 (1995)
W.T. Dixon, Spinning-sideband-free and spinning-sideband-only NMR spectra of spinning samples. J. Chem. Phys. 77, 1800–1809 (1982)
Q. Chen, K. Schmidt-Rohr, Measurement of the local 1H spin diffusion coefficient in homogeneous polymers. Solid State NMR 29, 142–152 (2006)
D.L. VanderHart, G.B. McFadden, Some perspectives on the interpretation of proton NMR spin diffusion data in terms of polymer morphologies. Solid State NMR 7, 45–66 (1996)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. H. Sommer and dsm-firmenich for generous support of this work. The solid-state NMR spectrometer utilized in this work was funded by the NSF MRI program (Award No. 1726346).
Funding
Generous, sustained funding of this work was provided by dsm-firmenich.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KSR planned the experiments and analysis methods. SY prepared samples by careful annealing. SY, ZS, and KSR performed the NMR experiments, processed the data, and prepared the figures. ZS performed spin-diffusion simulations to produce best-fit curves and long-period graphs. KSR wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Prepared for the special issue in honor of Prof. Bernhard Blümich on the occasion of his 70th birthday.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Yuan, S. & Schmidt-Rohr, K. Quantification of Large Long Periods in Rigid Polymer Systems by 1H Spin Diffusion in HetCor NMR with Heavy Peak Overlap. Appl Magn Reson 54, 1135–1163 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-023-01570-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-023-01570-7