Abstract
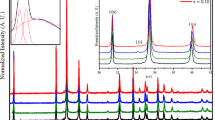
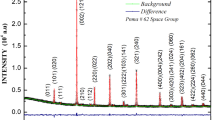
The results of studying the magnetic and magnetoresonance properties of the diluted magnetic semiconductor Hg0.5Cd0.4Cr0.1Se are presented. Microanalysis of the samples shows that the introduction of cadmium and chromium elements into the host HgSe matrix leads to the formation in the crystal of the four-component compound HgCdCrSe with the high chromium content [Cr (18.96 %)] and the three-component compound HgCdSe. The measured temperature dependence of the crystal magnetization illustrates the transition to ferromagnetic ordering at the Curie temperature T C = 126 K. It is noted that the measured magnetization value points out the indicates the presence of both Cr3+ and Cr2+ ions in the compound HgCdCrSe, which is responsible for the magnetic and magnetoresonance properties of the sample under test. The electron paramagnetic resonance studies are carried out on the an X-band spectrometer in the temperature range 77 K < T < 300 K. The angular dependences of electron paramagnetic resonance spectra are shown in the paramagnetic and ferromagnetic temperature ranges. As follows from the analysis of experimental data, the aforementioned transition is accompanied by the evolution of the electron paramagnetic resonance spectrum at changing the temperature and the orientation of the sample relative to the static magnetic field in the ferromagnetic temperature range. In the assumption of the g-tensor axial symmetry the components of the latter are determined and the different law of their temperature changing is revealed in the ferromagnetic ordering state of the sample.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Pogoreliy, S. Ryabchenko, O. Tolstolitkin, Ukr. J. Phys. 6, 37 (2010)
G. Bastard, C. Rigaux, Y. Guldner, A. Mycielski, J.K. Furdyna, D.P. Mullin, Phys. Rev. B. 24, 1961 (1981)
J. Furdyna, Appl. Phys. 53, 7637 (1982)
X. Cui, J. Medvedeva, B. Delley, A. Freeman, N. Newman, C. Stampfl, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 256404 (2005)
T. Dietl, Nature Mater. 2, 646 (2003)
I. Žutić, J. Fabian, S. Das Sarma, Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 323 (2004)
N. Samarth, Nature Mater. 6, 403 (2007)
S. Kuroda, N. Nishizawa, K. Takita, M. Mitome, Y. Bando, K. Osuch, T. Dietl, Nature Mater. 6, 440 (2007)
S. Picozzi, Nature Mater. 3, 349 (2004)
K. Lamonova, I. Ivanchenko, S. Orel, S. Paranchich, V. Tkach, E. Zhitlukhina, N. Popenko, Yu. Pashkevich, J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 21, 045603 (2009). doi:10.1088/0953-8984/21/4/045603
B. Bekirov, I. Ivanchenko, N. Popenko, V. Tkach, Funct. Mater. 19, 319 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bekirov, B., Ivanchenko, I., Popenko, N. et al. Magnetic and Magnetoresonance Properties of the Solid Solution Hg0.5Cd0.4Cr0.1Se. Appl Magn Reson 45, 75–82 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-013-0503-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-013-0503-5