Abstract
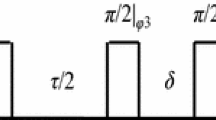
Performing a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiment in an unstable magnetic field causes fluctuations in the NMR frequency, leading to a loss of reproducibility and an effective shortening of the free induction decay after data averaging. Reference deconvolution allows the compensation of field fluctuations via simultaneous measurement of an internal or external reference signal. The technique was applied to compensate the effect of field fluctuations in a resistive electromagnet used for fast field cycling NMR. An external sample was chosen as the reference.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In our case, the complex signal is recorded and digitized in two-channel quadrature detection and the magnitude is taken in signal post-processing.
Our circuit behaves similar to a low-pass filter with a cut-off frequency of 5 kHz. This corresponds to a time-constant of 200 μs.
Note that this will be incorrect when using a reference and a sample with different gyromagnetic ratios, i.e., using different spin species. See [6] for an appropriate modification of the algorithm.
References
R.M. Hawk, R.R. Sharp, J.W. Tolan, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 45(1), 96 (1974). doi:10.1063/1.1686457
V. Soghomonian, M. Sabo, A. Powell, P. Murphy, R. Rosanske, T.A. Cross, H.J. Schneider-Muntau, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71(7), 2882 (2000). doi:10.1063/1.1150707
K. Kazimierczuk, W. Koźmiński, J. Magn. Reson. 174(2), 287 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2005.02.018
E. Sigmund, V. Mitrović, E. Calder, G. Thomas, H. Bachman, W. Halperin, P. Kuhns, A. Reyes, J. Magn. Reson. 159(2), 190 (2002) doi:10.1016/S1090-7807(02)00012-5
E.S. Meyer, I.F. Silvera, B.L. Brandt, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 60(9), 2964 (1989). doi:10.1063/1.1140636
P. van Bentum, J. Maan, J. van Os, A. Kentgens, Chem. Phys. Lett. 376(3–4), 338 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0009-2614(03)01014-5
P. Galvosas, F. Stallmach, G. Seiffert, J. Kärger, U. Kaess, G. Majer, J. Magn. Reson. 151(2), 260 (2001). doi:10.1006/jmre.2001.2381.
G.A. Morris, H. Barjat, T.J. Home, Prog. Nucl Magn Reson Spectr 31(2–3), 197 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0079-6565(97)00011-3
G.A. Morris, J. Magn. Reson. (1969) 80(3), 547 (1988). doi:10.1016/0022-2364(88)90253-3
M. Goez, R. Heun, J. Magn. Reson. 136(1), 69 (1999). doi:10.1006/jmre.1998.1617
Z. Gan, H. Kwak, M. Bird, T. Cross, P. Gor'kov, W. Brey, K. Shetty, J. Magn. Reson. 191(1), 135 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2007.12.008
T. Iijima, K. Takegoshi, K. Hashi, T. Fujito, T. Shimizu, J. Magn. Reson. 184(2), 258 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2006.10.010
T. Iijima, K. Takegoshi, J. Magn. Reson. 191(1), 128 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2007.12.009
F. Noack, Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectr. 18(3), 171 (1986). doi:10.1016/0079-6565(86)80004-8
R. Kimmich, E. Anoardo, Progr. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectr. 44(34), 257 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.pnmrs.2004.03.002
O. Lips, A. Privalov, S. Dvinskikh, F. Fujara, J. Magn. Reson. 149(1), 22 (2001). doi:10.1006/jmre.2000.2279
B. Kresse, A. Privalov, F. Fujara, Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 40(4), 134 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.ssnmr.2011.10.002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reutter, S., Privalov, A. Compensation of Magnetic Field Instabilities in Field Cycling NMR by Reference Deconvolution. Appl Magn Reson 44, 55–63 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-012-0396-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-012-0396-8