Abstract
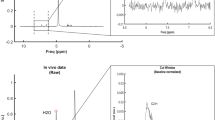
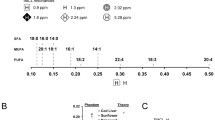
Intramyocellular lipids (IMCL) play an important role in muscle metabolism. 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy is the method of choice for non-invasive assessment of IMCL. However, IMCL quantitation is hampered by the larger overlapping resonances of extramyocellular lipids (EMCL). A phantom that mimics EMCL and IMCL, i.e., the 0.2-ppm resonance splitting, would be useful for testing acquisition strategies and post-processing algorithms. Here, we propose a phantom that consists of a cylindrical bottle filled with dairy cream and sunflower oil. Similar to EMCL, the oil (CH2) n protons resonate at 1.5 ppm; similar to IMCL, the spherical shape of droplets in cream results in (CH2) n protons resonating at 1.3 ppm. The relative amount of IMCL versus EMCL can be easily controlled in a systematic and exact fashion by displacing the voxel of interest across the cream–oil interface. This phantom is of simple construction and made of inexpensive and readily available materials, and should be of value in testing both acquisition and spectral analysis strategies in the context of ICML/ECML studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Krssak, K. Falk Petersen, A. Dresner, L. DiPietro, S.M. Vogel, D.L. Rothman, M. Roden, G.I.M. Shulman, Intramyocellular lipid concentrations are correlated with insulin sensitivity in humans: a 1H NMR spectroscopy study. Diabetologia 42, 113–116 (1999)
C. Boesch, J. Machann, P. Vermathen, F. Schick, Role of proton MR for the study of muscle lipid metabolism. NMR Biomed. 19, 968–988 (2006)
J. Decombaz, B. Schmitt, M. Ith, B. Decarli, P. Diem, R. Kreis, H. Hoppeler, C. Boesch, Postexercise fat intake repletes intramyocellular lipids but no faster in trained than in sedentary subjects. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 281, R760–R769 (2001)
F. Brouns, G.J. van der Vusse, Utilization of lipids during exercise in human subjects: metabolic and dietary constraints. Br. J. Nutr. 79, 117–128 (1998)
M. van der Graaf, C.J. Tack, J.H. de Haan, D.W. Klomp, A. Heerschap, Magnetic resonance spectroscopy shows an inverse correlation between intramyocellular lipid content in human calf muscle and local glycogen synthesis rate. NMR Biomed. 23, 133–141 (2010)
L.S. Szczepaniak, E.E. Babcock, F. Schick, R.L. Dobbins, A. Garg, D.K. Burns, J.D. McGarry, D.T. Stein, Measurement of intracellular triglyceride stores by H spectroscopy: validation in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. 276, E977–E989 (1999)
F. Schick, B. Eismann, W.I. Jung, H. Bongers, M. Bunse, O. Lutz, Comparison of localized proton NMR signals of skeletal muscle and fat tissue in vivo: two lipid compartments in muscle tissue. Magn. Reson. Med. 29, 158–167 (1993)
C. Boesch, J. Slotboom, H. Hoppeler, R. Kreis, In vivo determination of intra-myocellular lipids in human muscle by means of localized 1H-MR-spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 37, 484–493 (1997)
S.C. Chu, Y. Xu, J.A. Balschi, C.S. Springer Jr, Bulk magnetic susceptibility shifts in NMR studies of compartmentalized samples: use of paramagnetic reagents. Magn. Reson. Med. 13, 239–262 (1990)
J. Weis, L. Johansson, F. Courivaud, F.A. Karlsson, H. Ahlstrom, Quantification of intramyocellular lipids in obese subjects using spectroscopic imaging with high spatial resolution. Magn. Reson. Med. 57, 22–28 (2007)
B.R. Newcomer, J.C. Lawrence, S. Buchthal, J.A. den Hollander, High-resolution chemical shift imaging for the assessment of intramuscular lipids. Magn. Reson. Med. 57, 848–858 (2007)
S. Lipnick, G. Verma, S. Ramadan, J. Furuyama, M.A. Thomas, Echo planar correlated spectroscopic imaging: implementation and pilot evaluation in human calf in vivo. Magn. Reson. Med. 64, 947–956 (2010)
S. Ramadan, E.M. Ratai, L.L. Wald, C.E. Mountford, In vivo 1D and 2D correlation MR spectroscopy of the soleus muscle at 7T. J. Magn. Reson. 204, 91–98 (2010)
J. Ren, A.D. Sherry, C.R. Malloy, 1H MRS of intramyocellular lipids in soleus muscle at 7 T: spectral simplification by using long echo times without water suppression. Magn. Reson. Med. 64, 662–671 (2010)
M.H. Cui, J.H. Hwang, V. Tomuta, Z. Dong, D.T. Stein, Cross contamination of intramyocellular lipid signals through loss of bulk magnetic susceptibility effect differences in human muscle using (1)H-MRSI at 4 T. J. Appl. Physiol. 103, 1290–1298 (2007)
L.S. Szczepaniak, R.L. Dobbins, D.T. Stein, J.D. McGarry, Bulk magnetic susceptibility effects on the assessment of intra- and extramyocellular lipids in vivo. Magn. Reson. Med. 47, 607–610 (2002)
Z. Ababneh, M. Haque, S.E. Maier, R.V. Mulkern, Dairy cream as a phantom material for biexponential diffusion decay. MAGMA 17, 95–100 (2004)
C. Jones, A. MacKay, B. Rutt, Bi-exponential T2 decay in dairy cream phantoms. Magn. Reson. Imaging 16, 83–85 (1998)
R.V. Mulkern, Y.P. Hung, Z. Ababneh, S.E. Maier, A.B. Packard, M.C. Uluer, D.F. Kacher, G. Gambarota, S. Voss, On the strong field dependence and nonlinear response to gadolinium contrast agent of proton transverse relaxation rates in dairy cream. Magn. Reson. Imag. 23, 757–764 (2005)
F. Jiru, A. Skoch, U. Klose, W. Grodd, M. Hajek, Error images for spectroscopic imaging by LCModel using Cramer–Rao bounds. MAGMA 19, 1–14 (2006)
L.A. Stables, R.P. Kennan, A.W. Anderson, J.C. Gore, Density matrix simulations of the effects of J coupling in spin echo and fast spin echo imaging. J. Magn. Reson. 140, 305–314 (1999)
G. Gambarota, M. van der Graaf, D. Klomp, R.V. Mulkern, A. Heerschap, Echo-time independent signal modulations using PRESS sequences: a new approach to spectral editing of strongly coupled AB spin systems. J. Magn. Reson. 177, 299–306 (2005)
J. Slotboom, C. Boesch, R. Kreis, Versatile frequency domain fitting using time domain models and prior knowledge. Magn. Reson. Med. 39, 899–911 (1998)
P. Vermathen, R. Kreis, C. Boesch, Distribution of intramyocellular lipids in human calf muscles as determined by MR spectroscopic imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 51, 253–262 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gambarota, G., Janiczek, R.L., Mulkern, R.V. et al. An NMR Phantom Mimicking Intramyocellular (IMCL) and Extramyocellular Lipids (EMCL). Appl Magn Reson 43, 451–457 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-012-0355-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-012-0355-4