Abstract
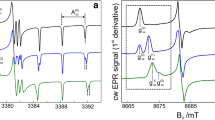
The effect of chloride concentration on Mn2+ (S = 5/2, I = 5/2) ions in frozen aqueous solutions is studied by high-field high-frequency electron paramagnetic resonance (HFEPR). The usually six sharp lines characteristic of Mn2+ ions, arising from the m s = −1/2 → 1/2 transition, is modified by the addition of Cl− anions and the six resonances become much broader and more complex. This new feature likely arises from the ligation of one Cl− anion to a hydrated Mn2+ ion forming a [Mn(H2O)5Cl]− complex. This complex increases linearly with Cl− concentration with an association constant of K a, apparent = 61 M−1. The structure of the putative chloride complex was studied using density functional theory calculations and the expected zero-field interaction of such a manganese center was calculated using the superposition model. The predicted values were similar to those determined from the simulation of the spectrum of the m s = −5/3 → −3/2 transition of the chloride complex. This effect of Cl− anions occurs at biologically relevant concentration and can be used to probe the Mn2+ ions in cellular and protein environments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.S. Jakubovics, H.F. Jenkinson, Microbiology 147, 1709–1718 (2001)
B.J. Gaffney, C. Su, E.H. Oliw, Appl. Magn. Reson. 21, 413–424 (2001)
S. Un, P. Dorlet, G. Voyard, L.C. Tabares, N. Cortez, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 10123–10124 (2001)
D. Goldfarb, K.V. Narasimhulu, R. Carmieli, Magn. Reson. Chem. 43, S40–S50 (2005)
A. Angerhofer, E.W. Moomaw, I. Garcia-Rubio, A. Ozarowski, J. Krzystek, R.T. Weber, N.G. Richards, J. Phys. Chem. B. 111, 5043–5046 (2007)
L.C. Tabares, N. Cortez, I. Agalidis, S. Un, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 6039–6047 (2005)
K. Barnese, E.B. Gralla, D.E. Cabelli, J.S. Valentine, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 4604–4606 (2008)
M.J. Horsburgh, S.J. Wharton, M. Karavolos, S.J. Foster, Trends. Microbiol. 10, 496–501 (2002)
J. Gätjens, M. Sjodin, V.L. Pecoraro, S. Un, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 13825–13827 (2007)
M. Sjodin, J. Gatjens, L.C. Tabares, P. Thuery, V.L. Pecoraro, S. Un, Inorg. Chem. 47, 2897–2908 (2008)
A. Potapov, D. Goldfarb, Inorg. Chem. 47, 10491–10498 (2008)
S. Un, P. Dorlet, A.W. Rutherford, Appl. Magn. Reson. 21, 341–361 (2001)
O. Burghaus, M. Plato, M. Rohrer, K. Moebius, F. MacMillan, W. Lubitz, J. Phys. Chem. 97, 7639–7647 (1993)
S. Un, L.C. Tabares, N. Cortez, B.Y. Hiraoka, F. Yamakura, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 2720–2726 (2004)
E. Meirovitch, Z. Luz, A.J. Kalb, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 96, 7538 (1974)
O. Matumura, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 108, 108 (1959)
C. Duboc, T. Phoeung, S. Zein, J. Pecaut, M.N. Collomb, F. Neese, Inorg. Chem. 46, 4905–4916 (2007)
M. Heming, S. Remme, G. Lehmann, J. Magn. Reson. 69, 134–143 (1986)
F. Weigend, F. Furche, R. Ahlrichs, J. Chem. Phys. 119, 12753–12762 (2003)
M.J. Frisch, G.W.T.H.B. Schlegel, G.E. Scuseria, M.A. Robb, J.R.C.J.A. Montgomery, Jr., T. Vreven, K.N. Kudin, J.C.B.J.M. Millam, S.S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, V. Barone, B.M.M. Cossi, G. Scalmani, N. Rega G.A. Petersson, H.N.M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J.H.M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, M.K.X. Li, J.E. Knox, H.P. Hratchian, J.B. Cross, C. Adamo, J.J.R. Gomperts, R.E. Stratmann, O. Yazyev, A.J. Austin, R.C.C. Pomelli, J.W. Ochterski, P.Y. Ayala, K. Morokuma, G.A.V.P. Salvador, J.J. Dannenberg, V.G. Zakrzewski, S.D.A.D. Daniels, M.C. Strain, O. Farkas, D.K.M.A.D. Rabuck, K. Raghavachari, J.B. Foresman, J.V.O.Q. Cui, A.G. Baboul, S. Clifford, J. Cioslowski, B.B.S.G. Liu, A. Liashenko, P. Piskorz, I. Komaromi, R.L.M.D.J. Fox, T. Keith, M.A. Al-Laham, C.Y. Peng, A.N.M. Challacombe, P.M.W. Gill, B. Johnson, W.C.M.W. Wong, C. Gonzalez, J.A. Pople, Gaussian 03, Revision B.05 (2003)
D.J. Newman, W. Urban, Adv. Phys. 24, 793–844 (1975)
Acknowledgments
We thank A. W. Rutherford for support and encouragement, T. L. Lai for technical assistance and F. Leach for valuable help in preparing this manuscript. A.S. is grateful for financial support from the IRTELIS (international research training for excellence in life science) graduate program. This research was supported by the (EU COST) European Cooperation in Science and Technology) P15 action on “Advanced paramagnetic resonance methods in molecular biophysics”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Un, S., Sedoud, A. High-field EPR Study of the Effect of Chloride on Mn2+ Ions in Frozen Aqueous Solutions. Appl Magn Reson 37, 247–256 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-009-0062-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-009-0062-y