Abstract.
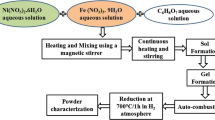
Thermally stable macroporous CaSiO3, Fe3+- and Ni2+-doped (0.5 to 5 mol%) ceramics have been prepared by solution combustion process by mixing respective metal nitrates (oxidizers), fumed silica. Diformol hydrazine is used as a fuel. The combustion products were identified by their X-ray diffraction and thermal gravimetry/differential thermal analysis. Single phases of β-CaSiO3 and α-CaSiO3 were observed at 950 and 1200 °C, respectively. The phase transition temperatures of combustion-derived CaSiO3 were found to be lower compared to those obtained via solid-state reaction method. It is interesting to note that with an increase in the calcination temperature the samples become more porous with an increase in the pore diameter from 0.2 to 8 µm. The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectrum of Fe3+ ions in CaSiO3 exhibits a weak signal at g = 4.20 ± 0.1 followed by an intense signal at g = 2.0 ± 0.1. The signal at g = 4.20 is ascribed to isolated Fe3+ ions at rhombic site. The signal at g = 2.0 is due to Fe3+ coupled together with dipolar interaction. In Ni2+-doped CaSiO3 ceramics the EPR spectrum exhibits a symmetric absorption at g = 2.23 ± 0.1. This deviation from the free electron g-value is ascribed to octahedrally coordinated Ni2+ ions with moderately high spin–orbit coupling. The number of spins participating in resonance and the paramagnetic susceptibilities have been evaluated from EPR data as a function of Fe3+ as well as Ni2+ content. The effect of alkali ions (Li, Na and K) on the EPR spectra of these ceramics has also been studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kresge, C.T., Leonowicz, M.E., Roth, W.J., Vartuli, J.C., Beck, J.S.: Nature 359, 710 (1992)
Yang, P., Zhao, D., Margolese, D.I., Bates, B.F., Stucky, G.D.: Nature 396, 152 (1998)
Zhao, D., Feng, F., Quo, Q., Melosh, N., Fredrickson, G.H., Chmelka, B.F., Stucky, G.D.: Science 279, 548 (1999)
Corbin, S.F., Apte, P.S.: J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 693–701 (1999)
Chandrappa, G.T., Steunou, N., Livage J.: Nature, 416, 702 (2002)
Shevchenko, Ya.V.: Introduction to Engineering Ceramics. Nauka, Moscow (1993)
Shevchenko, Ya.V., Barinov, S.M.: Engineering Ceramics. Nauka, Moscow (1993)
Boccaccini, A.R., Petitmermel, M., Wintermantel, E.: J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76, 75 (1997)
Kingsley, J.J., Patil, K.C.: Mater. Lett. 6, 427 (1988)
Ainsworth, C., Jones, R.: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 77, 621 (1995)
Chandrappa, G.T., Chandran, R.G., Patil, K.C.: Int. J. Self-Propag. High Temp. Synthes. 4, 183 (1995)
Yun, Y.H., Yun, S.D., Park, H.R., Lee, Y.K., Youn, Y.N.: J. Mater. Synth. Process. 10, 205 (2002)
Lin, K., Chang, J., Zeng, Y., Qian, W.: Mater. Lett. 58, 2109 (2004)
Yoshizawa, J., Matushita, H., Iwamoto, K., Katsui, A.: J. Adv. Sci. 13, 52 (2001)
Kanzaki, M., Stebbins, J.F., Xue, X.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 18, 463 (1991)
Klug, H., Alexander L.: X-Ray Diffraction Procedures, p. 491. Wiley, New York (1962)
Fan, X., Wang, M., Hong, X., Qian, G.: J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, 3479 (1997)
Ming, T.J., Lin, R.Y., Ko, Y.H.: Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 70, 1167 (1991)
Brumauer, S., Emmete, P.H., Teller, E.: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 66, 309 (1938)
Abragam, A., Bleaney, B.: Electron Paramagnetic Resonance of Transition Ions. Clarendon, Oxford (1970)
Pilbrow, J.R.: Transition Ion Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. Clarendon, Oxford (1990)
Mabbs, F.E., Collison, D.: Electron Paramagnetic Resonance of d Transition-Metal Compounds. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1992)
Weil, J.A., Bolton, J.R., Wertz, J.E.: Electron Paramagnetic Resonance: Elementary Theory and Practical Applications. Wiley, New York (1994)
Poole, C.P. Jr., Farach, H.A. (eds.): Handbook of Electron Spin Resonance. American Institute of Physics, New York (1994)
Poole, C.P. Jr., Farach, H.A. (eds.): Handbook of Electron Spin Resonance, vol. 2. AIP Press, New York (1999)
Stevens, K.W.H.: Magnetic Ions in Crystals. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1997)
Rudowicz, C.: Magn. Reson. Rev. 13, 1 (1987)
Rudowicz, C.: Magn. Reson. Rev. 13, 335 (1988)
Rudowicz, C.: J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, L417 (2000)
Rudowicz, C., Misra S.K.: Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 36, 11 (2001)
Bleaney, B., Stevens, K.W.H.: Rep. Prog. Phys. 16, 108 (1953)
Gibson, J.F., in: Norman, R.O.C. (ed.) Electron Spin Resonance, vol. 3, pp. 90–133. Specialist Periodical Reports. Chemical Society, London (1976)
Rudowicz, C., Bramely, R.: J. Chem. Phys. 83, 5192 (1985)
Rudowicz, C.: J. Chem. Phys. 84, 5045 (1986)
Rudowicz, C.: Mol. Phys. 74, 1159 (1991)
Gaite, J.M., Michoulier, J.: Crystallographie 93, 341 (1970)
Castner, T., Newell, G.S. Jr., Holton, W.C., Slichter, C.P.: J. Chem. Phys. 32, 668 (1960)
Burzo, E., Chipara, M., Ungur, D., Ardelean, I.: Phys. Status Solidi 124, K117 (1984)
Kishore, N., Bansal, T.K., Kamal, R., Mendiratta, R.G.: Phys. Chem. Glasses 25, 52 (1984)
Yang, H., Prewitt, C.T.: Am. Mineral. 84, 929 (1999)
Yeom, T.H., Rudowicz, C., Choh, S.H., McGavin, D.G.: Phys. Status Solidi B 198, 839 (1996)
Pilbrow, J.R., Lowrey, M.R.: Rep. Prog. Phys. 43, 434 (1980)
Rudowicz, C., Qin, J.: J. Lumin. 110, 39 (2004)
Rao, B.G., Rao, K.J.: Chem. Phys. 102, 121 (1986)
Ashcroft, N.W., Mermin, N.D.: Solid State Physics, p. 656. Harcourt Brace College Publishers, New York (1976)
Sreedhar, B., Sumalatha, C., Kojima, K.: J. Mater. Sci. 31, 1445 (1996)
Lever, A.B.P.: Inorganic Electronic Spectroscopy. Elsevier, Ansterdam (1968)
Figgis, B.N.: Introduction to Ligand Fields. Wiley Eastern, New Delhi (1976)
Wong, J., Angell, C.A.: Glass Structure by Spectroscopy. Marcel Dekker, New York (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Authors' address: R. P. Sreekanth Chakradhar, Glass Technology Laboratory, Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute, Kolkata 700032, India
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakradhar, R., Nagabhushana, B., Chandrappa, G. et al. EPR Study of Fe3+- and Ni2+-Doped Macroporous CaSiO3 Ceramics. Appl Magn Reson 33, 137–152 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-008-0060-5
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-008-0060-5