Abstract
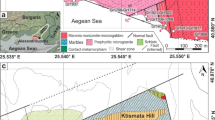
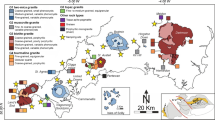
Carbonate-replacement Pb–Zn–Ag ± Au deposits in the Kamariza area, Lavrion district, Attica, Greece, are genetically related to the emplacement of Miocene andesitic dikes within a rapidly extending continental back-arc basin, which formed during exhumation of the Attic-Cycladic Crystalline Belt. Replacement veins as well as chimneys and mantos of massive sulfides are the major orebody types with mantos grading into chimneys and veins. Ore minerals are similar among the various types of orebodies in the Kamariza area and consist of sulfides and sulfarsenides (pyrite, arsenopyrite, chalcopyrite, galena, sphalerite, gersdorffite, marcasite), native metals (Au and Bi), Sn-bearing phases (petrukite), sulfosalts and sulfbismuthites of Ag, Bi, Cu, Pb, As, Sb (tetrahedrite-group minerals, bournonite, boulangerite, stephanite, pyrargyrite, semseyite, enargite, bismuthinite, lillianite homologues, Cu-matildite, aikinite, Ag-aikinite, mummeite, emplectite, wittichenite). The elemental association of Bi, Au, and Ag is common. The assemblages gersdorffite-bismuthinite-native gold and native gold-native bismuth are evidence for a contribution of magmatic components to the hydrothermal system. A fluctuation in the sulfidation states of the ore fluid during the evolution of the Kamariza system is evident from the deposition of early arsenopyrite, as well as of enargite-luzonite and both low-Fe and Fe-rich sphalerite in the same samples. Microthermometry of fluid inclusion assemblages show that carbonate replacement mineralization was deposited from a warm to hot (100°C to 400°C), low to moderately saline (1.8 to 17.3 wt% NaCl equiv) fluid. Eutectic temperatures of fluid inclusions as low as −55°C suggest the presence of CaCl2 in addition to NaCl, in the ore fluid. The Kamariza deposit occurs distal to the Plaka granodiorite intrusion and the associated porphyry-Mo mineralization, but is likely to be genetically related to a granitoid buried at depth.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriessen PAM, Banga G, Hebeda EH (1987) Isotopic age studies in the basal units on Naxos, Sikinos and Ios, Greek Cyclades. Geol en Mijnbouw 66:3–14
Altherr R, Kreuzer H, Wendt I, Lenz H, Wagner G, Keller J, Harre W, Hohndorf A (1982) A late Oligocene/Early Miocene high temperature belt in the Attic-Cycladic crystalline complex (SE Pelagonian, Greece). Geol Jb 23:97–164
Altherr R, Siebel W (2002) I-type plutonism in a continental back-arc setting: Miocene granitoids and monzonites from the central Aegean Sea, Greece. Contrib Mineral Petrol 143:397–415
Arikas K, Pape M, Serelis K, Tsagalidis A (2001) Petrological–mineralogical study of the metabasites (prasinites) of the Lavreotiki and the geotectonic environment of their formation. Bull Geol Soc Greece 34:901–910
Avigad D, Garfunkel Z (1991) Uplift and exhumation of high-pressure metamorphic terrains: the example of the Cycladic blueschist belt (Aegean Sea). Tectonophysics 188:357–372
Bakker RJ (2003) Package FLUIDS 1. Computer programs for analysis of fluid inclusion data and for modelling bulk fluid properties. Chem Geol 194:3–23
Baltatzis E (1981) Contact metamorphism of the calc-silicate hornfels from Plaka area, Laurium, Greece. N Jb Miner Mh 11:481–488
Baltatzis E (1996) Blueschist to greenschist transition and the P–T path of prasinites from Lavrion area, Greece. Mineral Mag 60:551–561
Bassi E, Soukis K, Lekkas S (2004) The presence of Vari-Kirou Pira Unit at Panion Hill (SE Attica, Greece). Bull Geol Soc Greece 36:1608–1617
Baumgartl U, Burow J (2002) Laurion. Der Aufschluss 53:246–372
Beaty DW, Cunningham CG, Rye RO, Steven TA, Gonzalez-Urien E (1986) Geology and geochemistry of the Deer Trail Pb–Zn–Ag–Au–Cu manto deposits, Marysvale district, West-Central Utah. Econ Geol 81:1932–1952
Bodnar RJ (2003) Introduction to fluid inclusions. In: Samson I, Anderson A, Marshall D (eds) Fluid inclusions: analysis and interpretation. Mineral. Assoc. Canada, Short Course 32:1–8
Bonsall TA, Spry PG, Voudouris P, Seymour KSt, Tombros S, Melfos V (2007) Fluid inclusion and stable isotope characteristics of carbonate replacement Pb–Zn–Ag deposits in the Lavrion district, Greece. In: Andrew CJ et al (eds) Digging deeper. 9th SGA meeting, Dublin, pp 283–286
Borg G, Daliran F (2004) Hypogene and supergene formation of sulphides and non-sulphides at the Angouran high-grade zinc deposit, NW-Iran. In: Abstract volume of Geoscience Africa 2004. University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, 69–70
Breskovska V, Tarkian M (1994) Compositional variation in Bi-bearing fahlores. N Jb Miner Mh 5:230–240
Bröcker M, Bieling D, Hacker B, Gans P (2004) High-Si phengite records the time of greenschist facies overprinting: implications for models suggesting mega-detachments in the Aegean Sea. J Metamorph Geol 22:427–442
Bröcker M, Keasling A (2006) Ion probe U–Pb zircon ages from the high-pressure/low-temperature mélange of Syros, Greece: age diversity and the importance of pre-Eocene subduction. J Metammorph Geol 24:615–631
Choi SG, Youm SJ (2000) Compositional variation of arsenopyrite and fluid evolution at the Ulsan deposit, southeastern Korea: a low-sulfidation porphyry system. Can Mineral 38:567–583
Ciobanu CL, Cook NJ, Pring A (2005a) Bismuth tellurides as gold scavengers. In: Chen et al. (eds) Mineral deposit research: Meeting the global challenge. Springer, pp 1383–1386
Ciobanu CL, Cook NJ, Capraru N, Gheorghe D, Cristea P (2005b) Mineral assemblages from the vein salband at Sacarimb, Golden Quadrilateral, Romania: I. Sulphides and sulphosalts. In: Cook NJ, Bonev IK (eds) Geochem mineral petrol, vol 43, pp 47–55
Ciobanu CL, Cook NJ, Pring A, Brugger J, Netting A, Danushevskiy L (2006) LA-ICP-MS evidence for the role of Bi-minerals in controlling gold distribution in ores. 12th IAGOD symp Moscow, CD-ROM
Conophagos C (1980) The Lavrion and the ancient Greek techniques for silver production. Publishing of Greece S.A., Athens, Greece, 458 p
Cook NJ (1997) Bismuth and bismuth-antimony sulfosalts from Neogene vein mineralisation, Baia Borsa area, Maramures, Romania. Mineral Mag 61:387–409
Cook NJ (1998) Bismuth sulfosalts from hydrothermal vein deposits of Neogene age, NW Romania. Mitt Österr Miner Ges 143:19–39
Crawford ML (1981) Phase equilibria in aqueous fluid inclusions. In: Hollister LS, Crawford ML (eds) Short course in fluid inclusions: applications to petrology, pp 75–100
Douglas N, Mavrogenes J, Hack A, England R (2000) The liquid bismuth collector model: an alternative gold deposition mechanism. Austral Geol Conv Abstr 59:135
Dürr S, Altherr R, Keller J, Okrusch M, Seidel E (1978) The median Aegean crystalline belt: stratigraphy, structure, metamorphism, magmatism. In: Cloos H, Roeder D, Schmid H (eds) Alps, Appenines, Hellenides. Union Commission on Geodynamics, pp 455–477
Economou M Skounakis S, Papathanassiou K (1981) Magnetite deposits of skarn type from the Plaka area of Laurium, Greece. Chem Erde 40:241–252
Einaudi MT, Hedenquist JW, Inan EE (2003) Sulfidation state of hydrothermal fluids: the porphyry-epithermal transition and beyond. In: Simmons SF, Graham IJ (eds) Volcanic, geothermal and ore-forming fluids: rulers and witnesses of processes within the Earth. Soc Econ Geol Spec Publ, vol 10, pp 285–313
Foord EE, Shawe DR (1989) The Pb–Bi–Ag–Cu–(Hg) chemistry of galena and some associated sulfosalts: a review and some new data from Colorado, California and Pennsylvania. Can Mineral 27:363–382
Foord EE, Shawe DR, Conklin NM (1988) Coexisting galena, PbSss and sulfosalts: evidence for multiple episodes of mineralization in the Round Mountain and Manhattan gold districts, Nevada. Can Mineral 27:355–376
Forster MA, Lister GS (2005) Several-distinct tectono-metamorphic slices in the Cycladic eclogite-blueschist belt, Greece. Contrib Mineral Petrol 150:523–545
Gautier P, Brun JP (1994) Crustal-scale geometry and kinematics of late-orogenic extension in the cetral Aegean (Cyclades and Evvia Island). Tectonophysics 238:399–424
Gelaude P, Van Kalmthout P (1996) Laurion—the minerals in the ancient slags. Christian Rewitzer Pages, 194 p
Gilg, HA (1993) Geochronology (K–Ar), fluid inclusion and stable isotope (C, O, H) studies of skarn, porphyry copper, and carbonate-hosted Pb–Zn (Ag–Au) replacement deposits in the Kassandra mining district (Eastern Chalkidiki, Greece). PhD thesis, ETH Zurich, p 152
Gilg, HA (1996) Fluid inclusion and isotope constraints on the genesis of high-temperature carbonate-hosted Pb–Zn–Ag deposits. In: Sangster DF (ed) Carbonate-hosted lead–zinc deposits. Soc Econ Geol Spec Publ vol 4, pp 501–514
Gilg HA, Boni M, Balassone G, Allen CR, Banks D, Moore F (2006) Marble-hosted sulfide ores in the Angouran Zn–(Pb–Ag) deposit, NW Iran: interaction of sedimentary brines with a metamorphic core complex. Mineral Deposita 41:1–16
Goldstein R (2003) Petrographic analysis of fluid inclusions. In: Samson IM, Anderson AJ, Marshall DD (eds) Fluid inclusions: analysis and interpretation. Mineralogical Association of Canada, Short Course, vol 32, pp 9–53
Goldstein RH, Reynolds TJ (1994) Systematics of fluid inclusions in diagenetic minerals. SEPM Short Course 31, p 199
Haas JL (1976) Physical properties of the coexisting phases and thermochemical properties of the H2O component in boiling NaCl solution (Preliminary steam tables for NaCl solution). US Geol Surv Bull 1421-A, pp 73
Heinrich CA, Eadington PJ (1986) Thermodynamic predictions of the hydrothermal chemistry of arsenic, and their significance for the paragenetic sequence of some cassiterite–arsenopyrite-base metal sulfide deposits. Econ Geol 81:511–529
Horner J, Neubauer F, Paar WH, Hansmann W, Koeppel V, Robl K (1997) Structure, mineralogy, and Pb isotopic composition of the As–Au–Ag deposit Rotgülden, Eastern Alps (Austria): significance for formation of epigenetic ore deposits within metamorphic domes. Mineral Deposita 32:555–568
Johnson NE, Craig JR, Rimstidt JD (1986) Compositional trends in tetrahedrite. Can Mineral 24:385–397
Jolivet L, Rimmelé G, Oberhänsli R, Goffé B, Candan O (2004a) Correlation of syn-orogenic tectonic and metamorphic events in the Cyclades, the Lycian nappes and the Menderes massif. Geodynamic implications. Bull Soc Géol Fr 175:217–238
Jolivet L, Famin V, Mehl C, Parra T, Aubourg C, Hebert R, Philippot P (2004b) Strain localization during crustal-scale boudinage to form extensional metamorphic domes in the Aegean Sea. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 380:185–210
Kalogeropoulos S, Mitropoulos P (1983) Fluid inclusion characteristics of fluorite from Laurium (Greece). Ann Geol Pays Hellen 31:130–135
Karup-Møller S, Macovicky E (1992) Mummeite—a new member of the pavonite homologous series from Alaska Mine, Colorado. N Jb Miner Mh 12:555–576
Katerinopoulos A, Zissimopoulou E (1994) Minerals of the Lavrion mines. The Greek Association of Mineral and Fossil Collectors, Athens, Greece, p 304
Katzir Y, Avigad D, Matthews A, Garfunkel Z, Evans BW (2000) Origin, HP/LT metamorphism and cooling of ophiolitic mélanges in southern Evia (NW Cyclades), Greece. J Metamorph Geol 18:699–718
Kissin SA, Owens DR (1989) The relatives of stannite in the light of new data. Can Mineral 27:673–688
Klünder MH, Karup-Møller S, Macovicky E (2003) Exploratory studies on substitutions in the tetrahedrite–tennantite solid solution series Part II. The solubility of bismuth in tetrahedrite–tennantite containing iron and zinc. N Jb Miner Mh 4:153–175
Knoll O (1988) Ore mineralogy and fluid inclusion studies on Pb–Zn-ores from Lavrion/Greece. Thesis, University of Hamburg, p 72
Kretchmar U, Scott SD (1976) Phase relations involving arsenopyrite in the system Fe–As–S and their application. Can Mineral 14:364–386
Lang JR, Baker T (2001) Intrusion-related gold-systems: the present level of understanding. Mineral Deposita 36:477–489
Leleu M, Morikis A, Picot P (1973) Sur des mineralisations de type skarn au Laurium (Grece). Mineral Deposita 8:259–263
Liati A, Skarpelis N, Pe-Piper G (2007) Deciphering the time of igneous activity in the Lavrion ore province, Attica, Greece: Manifestation of Late Miocene and Triassic magmatism. Goldschmidt Conf Abst A578
Lister GS, Banga G, Feenstra A (1984) Metamorphic core complexes of Cordilleran type in the Cyclades, Aegean Sea, Greece. G eology 12:221–225
Lueth VW, Megaw PKM, Pingatore NE, Goodell PC (2000) Systematic variation in galena solid solution at Santa Eulalia, Chihuahua, Mexico. Econ Geol 95:1673–1687
Makovicky E, Karup-Møller S (1977) Chemistry and crystallography of the lillianite homologous series. N Jb Miner Abh 131:56–82
Malakhov AA (1968) Bismuth and antimony galenas as indicators of some conditions of ore formation. Geochim Int 5:1055–1068
Marinos G (1971) On the radio-dating of rocks in Greece. Ann Geol Pays Hell 23:1–10
Marinos G, Makris J (1975) Geological and geophysical considerations of new mining possibilities in Laurium, Greece. Ann Geol Pays Hellen 27:1–10
Marinos G, Petrascheck WE (1956) Laurium. Geological and geophysical research. Institute for Geology and Subsurface Research, IV (1)
Matthews A, Schliestedt M (1984) Evolution of the blueschist and greenschist facies rocks of Sifnos, Cyclades, Greece. Contrib Mineral Petrol 88:150–163
McCoy DT, Newberry RJ, Layer PW, DiMarchi JJ, Bakke A, Masterman JS, Minehahe DL (1997) Plutonic-related gold deposits of interior Alaska. Econ Geol Mon 9:191–241
Megaw PKM, Ruiz J, Titley SR (1988) High-temperature, carbonate-hosted Ag–Pb–Zn(Cu) deposits in northern Mexico. Econ Geol 83:1856–1885
Megaw PKM, Barton MD, Islas-Falce J (1996) Carbonate-hosted lead–zinc (Ag–Cu–Au) deposits of northern Chihuahua, Mexico. In: Sangster DF (ed) Carbonate-hosted lead–zinc deposits. Soc Econ Geol Spec Publ, vol 4, pp 277–289
Meinert DL (2000) Gold in skarns related to epizonal intrusions. Rev Econ Geol 13:347–375
Mitsaki VD (1972) Geochemical investigation of hydrothermal-pneumatolitic fluorites from Greece. Thesis, University of Athens, Greece, p 87
Mladenova V, Kerestedjian T, Dimitrova D (2001) Ag–Cu–Pb–Bi mineralization from the Svishti Plaz gold deposit, Central Balkan Mountain, Bulgaria. Geoch Mineral Petrol 38:55–66
Morris HT (1968) The Main Tintic mining district, Utah. In: Ridge JD (ed) Ore deposits of the United States, 1933–1967. Am Inst Min Eng 2, pp 1043–1073.
Neubauer F (2005) Structural control of mineralization in metamorphic core complexes. In: Mao J, Bierlein FP (eds) Mineral deposit research: meeting the global challenge. Springer, Berlin, pp 561–564
Oakes CS, Bodnar RJ, Simonson JM (1990) The system NaCl–CaCl2–H2O: I. The ice liquidus at 1 atm total pressure. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:603–610
Okamoto H, Massalski TB (1983) Au–Bi (gold–bismuth). Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, vol I. ASM Intl, pp 238–240
Okrusch M, Bröcker M (1990) Eclogites associated with high-grade blueschists in the Cyclades archipelago, Greece: a review. Eur J Miner 2:451–478
Papanikolaou DJ (1979) Unités tectoniques et phases de déformation dans l’ile de Samos, Mer Egée, Grèce. Bull Soc Géol Fr 7:745–762
Papanikolaou DJ (1987) Tectonic evolution of the Cycladic blueschist belt (Aegean Sea, Greece). In: Helgeson HC (ed) Chemical Transport in Metasomatic Processes, NATO ASI series, 218, pp 429–450
Papanikolaou DJ, Syskakis D (1991) Geometry of acid intrusives in Plaka, Laurium and relation between magmatism and deformation. Bull Geol Soc Greece 25:355–368
Papastavrou S, Theophilopoulos D, Tzanikian Z, Vergos S, Zagouroglou K, Karantasis S, Mavridou-Kanaki F (1987) Results on the research of massive sulfide ores in Lavrion area. Int Report, I.G.M.E. Athens, p 124
Pe-Piper G, Piper DJ (2002) The igneous rocks of Greece. The anatomy of an orogen, Beit region. Geol Erde 30, 573 p
Photiades A, Carras N (2001) Stratigraphy and geological structure of the Lavrion area (Attica, Greece). Bull Geol Soc Greece 34:103–109
Photiades A, Saccani E (2006) Geochemistry and tectono-magmatic significance of HP/LT metaophiolites of the Attic-Cycladic zone in the Lavrion area (Attica, Greece). Ofioliti 31:89–102
Pirajno F, Chen Y (2005) Hydrothermal ore systems associated with the extensional collapse of collision orogens. In: Mao J, Bierlein FP (eds) Mineral deposit research: meeting the global challenge. Springer, pp 1045–1048
Pirajno F, Chen Y, Xiao W (2006) Hydrothermal ore systems associated with the collapse of orogens—key examples from eastern, central and northwestern China, 12th IAGOD symp Moscow, CD-ROM.
Pósfai M, Buseck PR (1998) Relationships between microstructure and composition in enargite and luzonite. Amer Mineral 83:373–382
Potter RW, Clynne MA, Brown DL (1978) Freezing point depression of aqueous sodium chloride solutions. Econ Geol 73:284–285
Putz H, Paar WH, Topa D, Horner J, Lüders V (2003) Structurally controlled gold and sulfosalt mineralization: the Altenberg example, Salzburg Province, Austria. Mineral Petrol 78:111–138
Ren Y, Liu L, Zhang H (2005) Gold deposits rich in bismuth minerals: An important type of gold deposits. In: Chen et al. (eds) Mineral deposit research: Meeting the global challenge. Springer Verlag, 581–583
Ring U, Laws S, Bernet M (1999) Structural analysis of a complex nappe sequence and late-orogenic basins from the Aegean Island of Samos, Greece. J Struct Geol 21:1575–1601
Ring U, Layer PW, Reischmann T (2001) Miocene high-pressure metamorphism in the Cyclades and Crete, Aegean Sea, Greece: evidence for large-magnitude displacement on the Cretan detachment. Geology 29:395–398
Ring U, Glodny J, Will T, Thomson S (2007) An Oligocene extrusion wedge of blueschist-facies nappes on Evia, Aegean Sea, Greece: implications for the early exhumation of high-pressure rocks. J Geol Soc London 164:637–652
Roedder E (1984) Fluid Inclusions. Rev Mineral 12:646
Scott SD (1983) Chemical behaviour of sphalerite and arsenopyrite in hydrothermal and metamorphic environments. Mineral Mag 47:427–435
Sharp TG, Buseck PR (1993) The distribution of Ag and Sb in galena: inclusions versus solid solution. Am Mineral 78:85–95
Shepherd T, Rankin A, Alderton D (1985) A practical guide to fluid inclusion studies. Blackie and Son, Glasgow, p 239
Skarpelis N (2002) Geodynamics and evolution of the Miocene mineralization in the Cycladic-Pelagonian belt, Hellenides. Bull Geol Soc Greece 34:2191–2206
Skarpelis N (2007) The Lavrion deposit (SE Attika, Greece): geology, mineralogy and minor elements chemistry. N Jb Miner Abh 183:227–249
Skarpelis N, Tsikouras B, Pe-Piper G (2008) The Miocene igneous rocks in the Basal unit of Lavrion (SE Attica, Greece): petrology and geodynamic implications. Geol Mag 145:1–15
Smith DMJr (1996) Sedimentary basins and the origin of intrusion-related carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb-Ag deposits. In: Sangster DF (ed) Carbonate-hosted lead–zinc deposits. Soc Econ Geol Spec Publ 4, pp 255–263
Solomos C, Voudouris P, Katerinopoulos A (2004) Mineralogical studies of a bismuth–gold–antimony mineralization in Kamariza Lavrion. Bull Geol Soc Greece 36:387–396
Sourirajan S, Kennedy GC (1962) The system H2O–NaCl at elevated temperatures and pressures. Am J Sci 260:115–141
Springer G (1969) Naturally occuring compositions in the solid-solution series Bi2S3–Sb2S3. Mineral Mag 37:294–296
Spry PG, Tombros SF, Seymour KSt, Williams-Jones A, Zouzias DP (2006) Geology, mineralogy and geochemistry of granite-hosted gold telluride mineralization at Panormos Bay, Tinos Island, Greece. GSA, Abstracts with Programs, 38, p 55
Tarkian M, Breskovska V (1995) Mineralogy and fluid inclusion study of the Zidarovo copper polymetallic deposit, eastern Bulgaria. N Jb Miner Abh 168:283–298
Thompson JFH, Newberry RJ (2000) Gold deposits related to reduced granitic intrusions. Rev Econ Geol 13:377–397
Thompson TB, Beaty DW (1990) Geology and the origin of ore deposits in the Leadville district, Colorado. Part II. Oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, sulfur, and lead isotope data and the development of a genetic model, In: Thompson TB, Beaty DW (eds) Carbonate-hosted sulfide deposits of the Central Colorado mineral belt. Econ Geol Monog 8, pp 156–179
Titley SR (1993) Characteristics of high temperature carbonate-hosted massive sulfide ores in the United States, Mexico and Peru. In: Kirkham RV, Sinclair WD, Thorpe RI, Duke JM (eds) Mineral deposit modeling. Geol Assoc Can Spec Pap 40, pp 585–614
Titley SR (1996) Characteristics of high temperature carbonate-hosted replacement ores and some comparisons with Missisippi Valley-type ores. In: Sangster DF (ed) Carbonate-hosted lead–zinc deposits. Soc Econ Geol Spec Publ 4, pp 244–254
Tombros S, Seymour K, Spry PG (2004) Description and conditions of formation of new unnamed Ag–Cu and Ag–Cu–Au sulfotellurides in epithermal polymetallic Ag–Au–Te mineralization, Tinos Island, Hellas. N Jb Miner Abh 179:295–310
Tombros SF, St Seymour K, Zouzias D, Mastrakas N, Spry PG, Williams-Jones AE (2007) The evolution of a W, Au–Ag–Te and Au–Ag hydrothermal system, Tinos Island, Cyclades, Greece. In: Andrews CJ et al. (eds) Mineral Exploration and Research: Digging Deeper. Millpress, Rotterdam, pp 641–644
Törmänen TO, Koski R (2005) Gold enrichment and the Bi–Au association in pyrrhotite-rich massive sulfide deposits, Escanaba Trough, southern Gorda ridge. Econ Geol 100:1135–1150
Trotet F, Vidal O, Jolivet L (2001) Exhumation of Syros and Sifnos metamorphic rocks (Cyclades, Greece). New constraints on the P–T paths. Eur J Mineral 13:901–920
Tsikouras V, Pe-Piper G, Skarpelis N (2006) Petrology of the Miocene igneous rocks of Lavrion area (SE Attica, Greece). Abstract Volume of the Conference “International magmatism of the Central Aegean and adjacent areas: Petrology, tectonics, geodynamics, mineral resources and environment, Milos
Tsokas GN, Stampolidis A, Angelopoulos AD, Kilias S (1998) Analysis of potential field anomalies in Lavrion mining area, Greece. Geophysics 63:1965–1970
Vanko DA, Bodnar RJ, Sterner SM (1988) Synthetic fluid inclusions. VIII. Vapour-saturated halite solubility in part of the system NaCl–CaCl2–H2O, with application to fluid inclusions from oceanic hydrothermal systems. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2451–2456
Vavelidis M (1997) Au-bearing quartz veins and placer gold on Sifnos Island, Aegean Sea, Greece. In: Papunen H (ed) Mineral deposits: research and exploration—Where do They Meet? Balkema, pp 335–338
Vavelidis M, Michailidis K (1990) Gold composition in the Fe–Pb–Cu–(Ag–Zn) hydrothermal quartz veins of Kallianou area, Southern Evia (Greece). Bull Geol Soc Greece 32:87–96
Voudouris P (2005) Gold and silver mineralogy of the Lavrion deposit Attika/Greece. In: Mao J, Bierlein FP (eds) Mineral deposit research: meeting the global challenge. Springer, pp 1089–1092
Voudouris P, Economou-Eliopoulos M (2003) Mineralogy and chemistry of Cu-rich ores from the Kamariza carbonate-hosted deposit (Lavrion), Greece. In: Eliopoulos et al. (eds) Mineral Exploration and Sustainable Development. Millpress, Rotterdam, pp 499–502
Voudouris P, Spry PG (2007) The mineralogy and genesis of precious metal telluride deposits of Greece. GSA Abstracts with Programs, 39, p 625
Voudouris P, Melfos V, Spry PG, Bonsall T, Tarkian M, Economou-Eliopoulos M (2007) Mineralogical and fluid inclusion constraints on the evolution of the Plaka intrusion-related ore system, Lavrion, Greece. Mineral Petrol, DOI 10.1007/s00710-007-0218-0
Walcott CR, White SH (1998) Constraints on the kinematics of post-orogenic extension imposed by stretching lineations in the Aegean region. Tectonophysics 298:155–175
Zeffren S, Avigad D, Heimann A, Gvirtzman Z (2005) Age resetting of hanging wall rocks above a low-angle detachment fault: Tinos Island (Aegean Sea). Tectonophysics 400:1–25
Acknowledgements
A. Tsolakos is especially thanked for his assistance with underground sampling in the Lavrion area. The assistance of S. Heidrich and E. Michailidis with electron microprobe analyses is greatly appreciated. V. Maneta is thanked for drafting figures. This project was, in part, financially supported by a Hugh E. McKinstry grant to T. Bonsall from the Society of Economic Geologists. This manuscript was improved considerably by the reviews of P. Garofalo and N. White which are greatefully acknowledged. We thank Associate Editor P. Garofalo for the editorial handling of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: P. Garofalo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voudouris, P., Melfos, V., Spry, P.G. et al. Carbonate-replacement Pb–Zn–Ag ± Au mineralization in the Kamariza area, Lavrion, Greece: Mineralogy and thermochemical conditions of formation. Miner Petrol 94, 85–106 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-008-0007-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-008-0007-4