Abstract
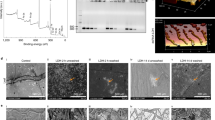
Globodera pallida, an obligate sedentary endoparasite, is a major economic pest that causes substantial potato yield losses. This research aimed to study the effects of gene silencing of three FMRFamide-like peptides (FLPs) genes to reduce G. pallida infestation on potato plants by using kaolinite nanoclay as a carrier to deliver dsRNAs via drenching. A dsRNA dosage of 2.0 mg/ml silenced flp-32c by 89.5%, flp-32p by 94.6%, and flp-2 by 94.3%. J2s incubated for 5 and 10 h showed no phenotypic changes. However, J2s of G. pallida efficiently uptake dsRNA of all targeted genes after 15 h of incubation. On the other hand, J2s that had been kept for 24 h had a rigid and straight appearance. Under fluorescence microscopy, all dsRNA-treated nematodes showed fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) signals in the mouth, nervous system, and digestive system. The untreated population of J2s did not show any FITC signals and was mobile as usual. The drenching of potato cultivar Kufri Jyoti with the dsRNA-kaolinite formulations induced deformation and premature death of J2s, compared with untreated J2s that entered J3 or J4 stages. This study validates that the nanocarrier-delivered RNAi system could be employed effectively to manage G. pallida infestations.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The manuscript contains all the data generated or analyzed during this study. Additional data is provided in supplementary files.
References
Atkinson LE, Stevenson M, McCoy CJ, Marks NJ, Fleming C, Zamanian M, Day TA, Kimber MJ, Maule AG, Mousley A (2013) flp-32 ligand/receptor silencing phenocopy faster plant pathogenic nematodes. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003169. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003169
Bachman P, Fischer J, Song Z, Urbanczyk-Wochniak E, Watson G (2020) Environmental fate and dissipation of applied dsRNA in soil, aquatic systems, and plants. Front Plant Sci 11:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00021
Bairwa A, Venkatasalam EP, Mhatre PH, Sharma S (2021) Introduction of potato cyst nematodes, life cycle and their management through biobased amendments. In: Kaushal M, Prasad R (eds) Microbial biotechnology in crop protection. Springer, Singapore, pp 79–95
Bairwa A, Venkatasalam EP, Mhatre PH, Bhatnagar A, Sharma AK, Dalamu, Dipta B, Subhash S, Sharma S (2022a) Biology and management of nematodes in potato. In: Chakrabarti SK, Sharma S, Shah MA (eds) Sustainable management of potato pests and diseases. Springer, Singapore, pp 281–307
Bairwa A, Venkatasalam EP, Subhash S, Dipta B (2022b) Management of potato cyst nematodes (Globodera spp.) using biotechnological approaches. In: Chakravarthy AK (ed) Genetic methods and tools for managing crop pests. Springer, Singapore, pp 343–360
Bakhetia M, Charlton W, Atkinson HJ, McPherson MJ (2005) RNA interference of dual oxidase in the plant nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-18-1099
Bawa AS, Anilakumar KR (2013) Genetically modified foods: safety, risks and public concerns: a review. J Food Sci Technol 50:1035–1046. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0899-1
Bernard GC, Egnin M, Bonsi C (2017) The impact of plant-parasitic nematodes on agriculture and methods of control. In: Shah MM, Mahamood M (eds) Nematology: concepts, diagnosis and control. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.68958
Bhagta S, Bhardwaj V, Kant A (2023) Exogenous dsRNA trigger RNAi in Venturia inaequalis resulting in down regulation of target genes and growth reduction. Mol Biol Rep 50:8421–8429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08736-3
Chen J, Hu L, Sun L, Lin B, Huang K, Zhuo K, Liao J (2018) A novel Meloidogyne graminicola effector, MgMO237, interacts with multiple host defence-related proteins to manipulate plant basal immunity and promote parasitism. Mol Plant Pathol 19:1942–1955. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12671
Cotton JA, Lilley CJ, Jones LM, Kikuchi T, Reid AJ, Thorpe P, Tsai IJ, Beasley H, Blok V, Cock PJA, Eves-van den Akker S, Holroyd N, Hunt M, Mantelin S, Naghra H, Pain A, Palomares-Rius JE, Zarowiecki M, Berriman M, Jones JT, Urwin PE (2014) The genome and life-stage specific transcriptomes of Globodera pallida elucidate key aspects of plant parasitism by a cyst nematode. Genome Biol 15:R43. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2014-15-3-r43
Dalzell JJ, McMaster S, Johnston MJ, Kerr R, Fleming CC, Maule AG (2009) Non-nematode-derived double-stranded RNAs induce profound phenotypic changes in Meloidogyne incognita and Globodera pallida infective juveniles. Int J Parasitol 39:1503–1516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.05.006
Dalzell JJ, McMaster S, Fleming CC, Maule AG (2010) Short interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing in Globodera pallida and Meloidogyne incognita infective stage juveniles. Int J Parasitol 40:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.07.003
Damalas CA, Koutroubas SD (2016) Farmers’ exposure to pesticides: toxicity types and ways of prevention. Toxics 4:1. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics4010001
Das PR, Sherif SM (2020) Application of exogenous dsRNAs induced RNAi in agriculture: challenges and triumphs. Front Plant Sci 11:946. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00946
Dubrovina AS, Kiselev KV (2019) Exogenous RNAs for gene regulation and plant resistance. Int J Mol Sci 20:2282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092282
Fenwick DW (1940) Methods for the recovery and counting of cysts of Heterodera schachtii from soil. J Helminthol 18:155–172. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X00031485
Fire A, Xu SQ, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC (1998) Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 391:806–811. https://doi.org/10.1038/35888
Fletcher SJ, Reeves PT, Hoang BT, Mitter N (2020) A perspective on RNAi-based biopesticides. Front Plant Sci 11:51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00051
Gartner U, Hein I, Brown LH, Chen X, Mantelin S, Sharma SK, Dandurand LM, Kuhl JC, Jones JT, Bryan GJ, Blok VC (2021) Resisting potato cyst nematodes with resistance. Front Plant Sci 12:661194. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.661194
Hockland S, Niere B, Grenier E, Blok V, Phillips M, den Nijs L, Anthoine G, Pickup J, Viaene N (2012) An evaluation of the implications of virulence in non-European populations of Globodera pallida and G. rostochiensis for potato cultivation in Europe. Nematology 14:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1163/138855411X587112
Huang L, Lieberman J (2013) Production of highly potent recombinant siRNAs in Escherichia coli. Nat Protoc 8:2325–2336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.149
Kimber MJ, Fleming CC, Bjourson AJ, Halton DW, Maule AG (2001) FMRFamide-related peptides in potato cyst nematodes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 116:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-6851(01)00323-1
Kimber MJ, McKinney S, McMaster S, Day TA, Fleming CC, Maule AG (2007) flp gene disruption in a parasitic nematode reveals motor dysfunction and unusual neuronal sensitivity to RNA interference. FASEB J 21:1233–1243. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-7343com
Konakalla NC, Kaldis A, Berbati M, Masarapu H, Voloudakis AE (2016) Exogenous application of double-stranded RNA molecules from TMV p126 and CP genes confers resistance against TMV in tobacco. Planta 244:961–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2567-6
Kort J, Ross H, Rumpenhorst HJ, Stone AR (1977) An international scheme for identifying and classifying pathotypes of potato cyst-nematodes Globodera rostochiensis and G. pallida. Nematologica 23:333–389. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529277X00057
Kumar A, Siddappa S, Bhardwaj V, Dalamu Singh B, Sharma N, Dipta B, Kumar V, Goutam U, Sood S (2023) Generation of asynaptic mutants in potato by disrupting StDMC1 gene using RNA interference approach. Life 13:174. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010174
Laudani F, Strano CP, Edwards MG, Malacrino A, Campolo O, Abd El Halim HM, Gatehouse AMR, Palmeri V (2017) RNAi-mediated gene silencing in Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Oliver) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Open Life Sci 12:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2017-0025
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
McBeth CW, Taylor AL, Smith AL (1941) Note on staining nematodes in root tissues. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 8:3–6
Mitter N, Worrall EA, Robinson KE, Li P, Jain RG, Taochy C, Fletcher SJ, Carroll BJ, Lu GQ, Xu ZP (2017) Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses. Nat Plants 3:16207. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2016.207
Molesini B, Pennisi F, Cressoni C, Vitulo N, Dusi V, Speghini A, Pandolfini T (2022) Nanovector-mediated exogenous delivery of dsRNA induces silencing of target genes in very young tomato flower buds. Nanoscale Adv 4:4542–4553. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2na00478j
Niu J, Jian H, Xu J, Chen C, Guo Q, Liu Q, Guo Y (2012) RNAi silencing of the Meloidogyne incognita Rpn7 gene reduces nematode parasitic success. Eur J Plant Pathol 134:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-012-9971-y
Niu J, Chen R, Wang JJ (2024) RNA interference in insects: the link between antiviral defense and pest control. Insect Sci 31:2–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7917.13208
Peymen K, Watteyne J, Frooninckx L, Schoofs L, Beets I (2014) The FMRFamide-like peptide family in nematodes. Front Endocrinol 5:90. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2014.00090
Prasad KSK (2006) Potato cyst nematodes and their management in the Nilgiris (India). CPRI Technical Bulletin No. 77. Central Potato Research Institute, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh
Qiu Y, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Zhou H, Deng YQ, Li XF, Miao M, Zhang Q, Zhong B, Hu Y, Zhang FC, Wu L, Qin CF, Zhou X (2017) Human virus-derived small RNAs can confer antiviral immunity in mammals. Immunity 46:992–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2017.05.006
Rosso MN, Dubrana MP, Cimbolini N, Jaubert S, Abad P (2005) Application of RNA interference to root-knot nematode genes encoding esophageal gland proteins. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:615–620. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-18-0615
Routhu GK, Borah M, Siddappa S, Nath PD (2022) Exogenous application of coat protein-specific dsRNA inhibits cognate cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) of ghost pepper. J Plant Dis Prot 129:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-021-00558-4
Statistical Analysis System (2011) Base SAS® 9.3 Procedures guide: statistical procedures. Cary, NC
Sharma N, Siddappa S, Malhotra N, Thakur K, Salaria N, Sood S, Bhardwaj V (2022) Advances in potato functional genomics: implications for crop improvement. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 148:447–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02221-0
Silva AT, Nguyen A, Ye C, Verchot J, Moon JH (2010) Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for effective siRNA delivery to tobacco BY-2 protoplasts. BMC Plant Biol 10:291. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-291
Sundaresha S, Bairwa A, Tomar M, Kumar R, Venkatasalam EP, Sagar V, Bhardwaj V, Sharma S (2022a) In vitro method for synthesis of large-scale dsRNA molecule as a novel plant protection strategy. In: Mysore KS, Senthil-Kumar M (eds) Plant gene silencing: methods and protocols. Methods in molecular biology. Springer, pp 211–226
Sundaresha S, Sharma S, Bairwa A, Tomar M, Kumar R, Bhardwaj V, Jeevalatha A, Bakade R, Salaria N, Thakur K, Singh BP, Chakrabarti SK (2022b) Spraying of dsRNA molecules derived from Phytophthora infestans, along with nanoclay carriers as a proof of concept for developing novel protection strategy for potato late blight. Pest Manag Sci 78:3183–3192. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6949
Tan JACH, Jones MGK, Fosu-Nyarko J (2013) Gene silencing in root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) significantly reduces reproduction in a plant host. Exp Parasitol 133:166–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2012.11.011
Turner SJ, Rowe JA (2006) Cyst nematodes. In: Perry RN, Moens M (eds) Plant nematology. CABI International, Wallingford, Oxon, pp 91–122
Urwin PE, Lilley CJ, Atkinson HJ (2002) Ingestion of double-stranded RNA by preparasitic juvenile cyst nematodes leads to RNA interference. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:747–752. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.8.747
Wang X, Ji S, Bi S, Tang Y, Zhang G, Yan S, Wan F, Lu Z, Liu W (2023) A promising approach to an environmentally friendly pest management solution: nanocarrier delivered dsRNA towards controlling the destructive invasive pest Tuta absoluta. Environ Sci Nano 10:1003. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2en01076c
Wen TY, Wu XQ, Hu LJ, Qiu YJ, Rui L, Zhang Y, Ding XL, Ye JR (2021) A novel pine wood nematode effector, BxSCD1, suppresses plant immunity and interacts with an ethylene-forming enzyme in pine. Mol Plant Pathol 22:1399–1412. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.13121
Xu X, Jiao Y, Shen L, Li Y, Mei Y, Yang W, Li C, Cao Y, Chen F, Li B, Yang J (2023) Nanoparticle-dsRNA treatment of pollen and root systems of diseased plants effectively reduces the rate of tobacco mosaic virus in contemporary seeds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 15:29052–29063. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c02798
Zhang Y, Long M, Huang P, Yang H, Chang S, Hu Y, Tang A, Mao L (2016) Emerging integrated nanoclay-facilitated drug delivery system for papillary thyroid cancer therapy. Sci Rep 6:33335. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33335
Zhang YH, Ma ZZ, Zhou H, Chao ZJ, Yan S, Shen J (2022) Nanocarrier-delivered dsRNA suppresses wing development of green peach aphids. Insect Sci 29:669–682. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7917.12953
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge ICAR-CPRI, Shimla for conducting the laboratory and glass house experiments.
Funding
We acknowledge the financial help received from DST-SERB, New Delhi (Project code: ECR/2017/000402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AB, SuS, and EPV conceptualized and designed the study. SS and BrS contributed reagents and materials. AB, SuS, and BD performed experiments. BS, KCN, and PHM analyzed the data. AB and BD did literature research and drafted the manuscript. BD and NS revised the manuscript. The submitted version of the manuscript has been approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence this research paper.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Alla Yemets
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bairwa, A., Dipta, B., Siddappa, S. et al. Kaolinite nanoclay-shielded dsRNA drenching for management of Globodera pallida: An environmentally friendly pest management approach. Protoplasma (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-024-01950-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-024-01950-1