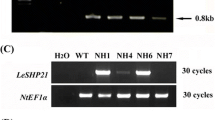
Abstract
Chloroplast is one of the most sensitive organelles to heat stress in plants. In chloroplasts, various proteases affect photosynthesis by degrading proteins under stress conditions. Tomato Lutescent2 (SlL2), a chloroplast zinc metalloprotease, was previously reported to alter chloroplast development and delay fruit ripening. However, its enzyme activity and roles in plant response to abiotic stress are still unclear. Here, we confirmed that the SlL2 protein which localized on thylakoid membrane was an ATP-independent hydrolase, and SlL2 gene responded to heat stress. Phenotype analysis showed that SlL2 plays a negative role in the heat-response mechanism. Under heat stress, the transgenic plants overexpressing SlL2 (OE) grew worse than the wild type (WT), as reflected by their decreased membrane stability, osmotic-regulating substance, and antioxidative enzyme activities, as well as increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation. By contrast, l2 mutant line showed the opposite phenotype and corresponding physiological indices under heat stress. In addition, overexpression of SlL2 decreased the photosynthetic activities, especially photosystem II. Moreover, SlL2 was found to interact with chloroplast-located chaperone protein SlCDJ1, decreasing its content under heat stress. These results indicate that SlL2 reduces the thermotolerance of tomato by reducing the content of SlCDJ1.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asada K (2006) Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions. Plant Physiol 141:391–396. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.082040
Ashraf M (2021) Thermotolerance in plants: potential physio-biochemical and molecular markers for crop improvement. Environ Exp Bot 186:104454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104454
Barry CS, Aldridge GM, Herzog G, Ma Q, McQuinn RP, Hirschberg J, Giovannoni JJ (2012) Altered chloroplast development and delayed fruit ripening caused by mutations in a zinc metalloprotease at the lutescent2 locus of tomato. Plant Physiol 159:1086–1098. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.197483
Chen Gu, Bi Yu, Rong Li, Ning, (2004) EGY1 encodes a membrane-associated and ATP-independent metalloprotease that is required for chloroplast development. Plant J 41:364–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02308.x
Chen KM, Holmstrom M, Raksajit W, Suorsa M, Piippo M, Aro EM (2010) Small chloroplast-targeted DnaJ proteins are involved in optimization of photosynthetic reactions in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 10:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-43
Chen J, Burke JJ, Xin Z (2018) Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis revealed essential roles of FtsH11 protease in regulation of the adaptive responses of photosynthetic systems to high temperature. BMC Plant Biol 18:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1228-2
Chen Q, Xu X, Xu D, Zhang H, Zhang C, Li G (2019) WRKY18 and WRKY53 coordinate with histone acetyltransferase1 to regulate rapid responses to sugar. Plant Physiol 180:2212–2226. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00511
Craig EA, Huang P, Aron R, Andrew A (2006) The diverse roles of J-proteins, the obligate Hsp70 co-chaperone. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 156:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10254-005-0001-0
Feng HL, Ma NN, Meng X, Zhang S, Wang JR, Chai S, Meng QW (2013) A novel tomato MYC-type ICE1-like transcription factor, SlICE1a, confers cold, osmotic and salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol Biochem 73:309–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.09.014
Fragkostefanakis S, Roth S, Schleiff E, Scharf KD (2015) Prospects of engineering thermotolerance in crops through modulation of heat stress transcription factor and heat shock protein networks. Plant Cell Environ 38:1881–1895. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12396
Guo D, Gao X, Li H, Zhang T, Chen G, Huang P, An L, Li N (2008) EGY1 plays a role in regulation of endodermal plastid size and number that are involved in ethylene-dependent gravitropism of light-grown Arabidopsis hypocotyls. Plant Mol Biol 66:345–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9273-5
Hennessy F, Nicoll WS, Zimmermann R, Cheetham ME, Blatch GL (2005) Not all J domains are created equal: Implications for the specificity of Hsp40–Hsp70 interactions. Protein Sci 14:1697–1709. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.051406805
Kampinga HH, Craig EA (2010) The HSP70 chaperone machinery: J proteins as drivers of functional specificity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:579–592. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2941
Kato Y, Kouso T, Sakamoto W (2012) Variegated tobacco leaves generated by chloroplast FtsH suppression: implication of FtsH function in the maintenance of thylakoid membranes. Plant Cell Physiol 53:391–404. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcr189
Kong F, Deng Y, Wang G, Wang J, Liang X, Meng Q (2014a) LeCDJ1, a chloroplast DnaJ protein, facilitates heat tolerance in transgenic tomatoes. J Integr Plant Biol 56:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12119
Kong F, Deng Y, Zhou B, Wang G, Wang Y, Meng Q (2014b) A chloroplast-targeted DnaJ protein contributes to maintenance of photosystem II under chilling stress. J Exp Bot 65:143–158. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert357
Kotak S, Larkindale J, Lee U, von Koskull-Doring P, Vierling E, Scharf KD (2007) Complexity of the heat stress response in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:310–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.011
Li B, Li Q, Xiong L, Kronzucker HJ, Kramer U, Shi W (2012) Arabidopsis plastid AMOS1/EGY1 integrates abscisic acid signaling to regulate global gene expression response to ammonium stress. Plant Physiol 160:2040–2051. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.206508
Li B, Gao K, Ren H, Tang W (2018) Molecular mechanisms governing plant responses to high temperatures. J Integr Plant Biol 60:757–779. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12701
Li T, Lei W, He R, Tang X, Han J, Zou L, Yin Y, Lin H, Zhang D (2020) Brassinosteroids regulate root meristem development by mediating BIN2-UPB1 module in Arabidopsis. Plos Genet 16:e1008883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008883
Liu ZM, Yue MM, Yang DY, Zhu SB, Ma NN, Meng QW (2017) Over-expression of SlJA2 decreased heat tolerance of transgenic tobacco plants via salicylic acid pathway. Plant Cell Rep 36:529–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2100-9
Ma L, Xue N, Fu X, Zhang H, Li G (2017) Arabidopsis thaliana far-red elongated hypocotyls3 (FHY3) and far-red-impaired response1 (FAR1) modulate starch synthesis in response to light and sugar. New Phytol 213:1682–1696. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14300
Mathur S, Agrawal D, Jajoo A (2014) Photosynthesis: response to high temperature stress. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 137:116–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.01.010
Murata N, Takahashi S, Nishiyama Y, Allakhverdiev SI (2007) Photoinhibition of photosystem II under environmental stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 1767:414–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.11.019
Nijabat A, Bolton A, Mahmood-ur-Rehman M, Shah AI, Hussain R, Naveed NH, Ali A, Simon P (2020) Cell membrane stability and relative cell injury in response to heat stress during early and late seedling stages of diverse carrot (Daucus carota L.) germplasm. Hortscience 55:1446–1452. https://doi.org/10.21273/Hortsci15058-20
Nilsson Cederholm S, Backman HG, Pesaresi P, Leister D, Glaser E (2009) Deletion of an organellar peptidasome PreP affects early development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 71:497–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9534-6
Nishimura K, Kato Y, Sakamoto W (2016) Chloroplast proteases: updates on proteolysis within and across suborganellar compartments. Plant Physiol 171:2280–2293. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00330
Rivero RM, Mestre TC, Mittler R, Rubio F, Garcia-Sanchez F, Martinez V (2014) The combined effect of salinity and heat reveals a specific physiological, biochemical and molecular response in tomato plants. Plant Cell Environ 37:1059–1073. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12199
Schiermeier Q (2018) Droughts, heatwaves and floods: how to tell when climate change is to blame. Nature 560:20–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-018-05849-9
Takahashi S, Badger MR (2011) Photoprotection in plants: a new light on photosystem II damage. Trends Plant Sci 16:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2010.10.001
Wang G, Kong F, Zhang S, Meng X, Wang Y, Meng Q (2015) A tomato chloroplast-targeted DnaJ protein protects Rubisco activity under heat stress. J Exp Bot 66:3027–3040. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv102
Wang G, Cai G, Xu N, Zhang L, Sun X, Guan J, Meng Q (2019) Novel DnaJ protein facilitates thermotolerance of transgenic tomatoes. Int J Mol Sci 20:367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020367
Yamamoto Y (2016) Quality control of photosystem II: the mechanisms for avoidance and tolerance of light and heat stresses are closely linked to membrane fluidity of the thylakoids. Front Plant Sci 7:1136. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01136
Yu FW, Zhu XF, Li GJ, Kronzucker HJ, Shi WM (2016) The chloroplast protease AMOS1/EGY1 affects phosphate homeostasis under phosphate stress. Plant Physiol 172:1200–1208. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00786
Yue R, Wang X, Chen J, Ma X, Zhang H, Mao C, Wu P (2010) A rice stromal processing peptidase regulates chloroplast and root development. Plant Cell Physiol 51:475–485. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcq012
Zhang L, Yu Z, Xu Y, Yu M, Ren Y, Zhang S, Yang G, Huang J, Yan K, Zheng C, Wu C (2021) Regulation of the stability and ABA import activity of NRT1.2/NPF4.6 by CEPR2-mediated phosphorylation in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 14:633–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.01.009
Zhou W, Zhou T, Li MX, Zhao CL, Jia N, Wang XX, Sun YZ, Li GL, Xu M, Zhou RG, Li B (2012) The Arabidopsis J-protein AtDjB1 facilitates thermotolerance by protecting cells against heat-induced oxidative damage. New Phytol 194:364–378. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04070.x
Zhuang K, Kong F, Zhang S, Meng C, Yang M, Liu Z, Wang Y, Ma N, Meng Q (2019) Whirly1 enhances tolerance to chilling stress in tomato via protection of photosystem II and regulation of starch degradation. New Phytol 221:1998–2012. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15532
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31900208 and 31870239) and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2021QC149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lü, J., Yang, M., Meng, Q. et al. Chloroplast metalloproteinase SlL2 reduces the thermotolerance of tomato by decreasing the content of SlCDJ1. Protoplasma 260, 1193–1205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-023-01840-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-023-01840-y