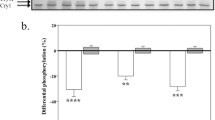
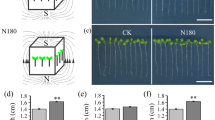
Abstract
To study magnetoreception of Arabidopsis thaliana, we analysed several developmental responses including cryptochrome-independent seed germination and the phytochrome- and cryptochrome-dependent hypocotyl elongation and photo-accumulation of anthocyanins and chlorophylls in weak static magnetic fields ranging from near null to 122 μT. A field of 50 μT accelerated seed germination by about 20 h relative to samples maintained in a near-null field. The double mutant, cry1cry2, lacking cryptochromes 1 and 2 displayed the same magnetic field–induced germination acceleration under blue light as the wild-type strain. Magnetic field–induced germination acceleration was masked in the presence of exogenous sucrose. Stimulus–response curves for hypocotyl elongation in a range between near-null to 122 μT indicated maxima near 9 and 60 μT for the wild-type strain as well as mutant cry1cry2. The photo-accumulation of anthocyanins and chlorophylls could be effectively modulated by magnetic fields in the presence of low-irradiance red and blue light, respectively. The findings indicate that Arabidopsis thaliana possesses light-independent mechanisms of magnetic field reception, which remain presently unidentified. Our results are in better agreement with predictions of the level crossing mechanism (LCM) of magnetoreception rather than those of the cryptochrome-associated radical-pair mechanism (RPM).













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRY:
-
Cryptochrome
- FAD:
-
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
- LCM:
-
Level crossing mechanism
- MF:
-
Magnetic field
- MS:
-
Murashige-Skoog growth medium
- RP:
-
Radical pair
- RPM:
-
Radical-pair mechanism
- PHOT:
-
Phototropin
- PHY:
-
Phytochrome
- SUT:
-
Sucrose transporter
- TRP:
-
Tryptophan
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Agliassa C, Maffei ME (2019) Reduction of geomagnetic field (GMF) to near null magnetic field (NNMF) affects some Arabidopsis thaliana clock genes amplitude in a light independent manner. J Plant Physiol 232:23–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2018.11.008
Agliassa C, Narayana R, Christie JM, Maffei ME (2018) Geomagnetic field impacts on cryptochrome and phytochrome signaling. J Photochem Photobiol B 185:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.05.027
Ahmad M (2016) Photocycle and signaling mechanisms of plant cryptochromes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 33:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2016.06.013
Ahmad M, Lin C, Cashmore AR (1995) Mutations throughout an Arabidopsis blue-light photoreceptor impair blue-light-responsive anthocyanin accumulation and inhibition of hypocotyl elongation. Plant J 8:653–658. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1995.08050653.x
Ahmad M, Grancher N, Heil M, Black RC, Giovani B, Galland P, Lardemer D (2002) Action spectrum for cryptochrome-dependent hypocotyl growth inhibition in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129:774–785. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010969
Ahmad M, Galland P, Ritz T, Wiltschko R, Wiltschko W (2007) Magnetic intensity affects cryptochrome-dependent responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 225:615–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0383-0
Belyavskaya NA (2004) Biological effects due to weak magnetic field on plants. Adv Space Res 34:1566–1574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2004.01.021
Bertea CM, Narayana R, Agliassa C, Rodgers CT, Maffei ME (2015) Geomagnetic field (Gmf) and plant evolution: investigating the effects of Gmf reversal on Arabidopsis thaliana development and gene expression. J Vis Exp 105:53286. https://doi.org/10.3791/2F53286
Binhi VN (2016) A primary physical mechanism of the biological effects of weak magnetic fields. Biophysics 61:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1134/S000635091601005X
Binhi VN (2019) Nonspecific magnetic biological effects: a model assuming the spin-orbit coupling. J Chem Phys 151:204101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5127972
Binhi V (2021) Random effects in magnetobiology and a way to summarize them. Bioelectromagnet 42:501–515. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.22359
Binhi VN, Prato FS (2017a) A physical mechanism of magnetoreception: extension and analysis. Bioelectromagnet 38:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.22011
Binhi VN, Prato FS (2017b) Biological effects of the hypomagnetic field: an analytical review of experiments and theories. PLoS ONE 12:e0179340. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179340
Binhi VN, Prato FS (2018) Rotations of macromolecules affect nonspecific biological responses to magnetic fields. Sci Rep 8:13495. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31847-y
Binhi V, Savin AV (2003) Effects of weak magnetic fields on biological systems: physical aspects. Physisc-Uspekhi 46:259–291. https://doi.org/10.1070/PU2003v046n03ABEH001283
Binhi VN, Alipov YD, Belyaev IY (2001) Effect of static magnetic field on E. coli cells and individual rotations of ion-protein complexes. Bioelectromagnetics 22:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-186X(200102)22:2%3C79::AID-BEM1009%3E3.0.CO;2-7
Bouly JP, Schleicher E, Dionisio-Sese M, Vandenbussche F, van der Straeten D, Bakrim N, Meier S, Batschauer A, Galland P, Bittl R, Ahmad M (2007) Cryptochrome blue-light photoreceptors are activated through interconversion of flavin redox states. J Biol Chem 282:9383–9391. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M609842200
Cakmak T, Dumlupinar R, Erdal S (2010) Acceleration of germination and early growth of wheat and bean seedlings grown under various magnetic fields and osmotic conditions. Bioelectromagnetics 31:120–129. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20537
Carbonell MV, Martinez E, Amaya JM (2000) Stimulation of germination in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by a static magnetic field. Electro Magnetobiol 19:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1081/JBC-100100303
Cashmore AR, Jarillo JA, Wu Y-J, Liu D (1999) Cryptochromes: blue light receptors for plants and animals. Science 284:760–765. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5415.760
Cellini A, Shankar MK, Wahlgren WY, Nimmrich A, Furrer A, James D, Wranik M, Aumonier S, Beale EV, Dworkowski F, Standfuss J, Weinert T, Westenhoff S (2022) Structural basis of the radical pair state in photolyases and cryptochromes. Chem Commun (camb) 58(31):4889–4892. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2cc00376g
Chaves I, Pokorny R, Byrdin M, Hoang N, Ritz T, Brettel K, Essen L-O, van der Horst GTJ, Batschauer A, Ahmad M (2011) The cryptochromes: blue light photoreceptors in plants and animals. Ann Rev Plant Biol 62:335–364. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103759
Das KP, Geul B, Choi S-B, Yoo S-D, Park Y-II (2011) Photosynthesis-dependent anthocyanin pigmentation in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 6:23–25. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.1.14082
de Wit M, Keuskamp DH, Bongers FJ, Hormitschek P, Gommers CMM, Reinen E, Martínez-Cerón Fankhauser C, Pierik RC (2016) Integration of phytochrome and cryptochrome signals determines plant growth during competition for light. Curr Biol 26:3320–3326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.10.031
Dhiman SK, Galland P (2018) Effects of weak static magnetic fields on the gene expression of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 231:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2018.08.016
Dwahi F, Al-Khayri JM (2009) Magnetic fields changes in photosynthetic pigments content in date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) seedlings. Open Agri J 3:1–5
Endler A, Meyer S, Schelbert S, Schneider T, Weschke W, Peters SW, Keller F, Baginsky S, Martinoia E, Schmidt UG (2006) Identification of a vacuolar sucrose transporter in barley and Arabidopsis mesophyll cells by a tonoplast proteomic approach. Plant Physiol 141:196–207. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.079533
Finch-Savage WE, Leubner-Metzger G (2006) Seed dormancy and the control of germination. New Phytol 171:501–523. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01787.x
Galland P, Pazur A (2005) Magnetic-field reception in plants. J Plant Res 118:371–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-005-0246-y
Hammad M, Albaqami M, Pooam M, Kernevez E, Witczak J, Ritz T, Martinoband C, Ahmad M (2020) Cryptochrome mediated magnetic sensitivity in Arabidopsis occurs independently of light-induced electron transfer to the flavin. Photochem Photobiol Sci 19:341–352. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9PP00469F
Harris S-R, Henbest KB, Maeda K, Pannell JR, Timmel CR, Hore PJ, Okamoto H (2009) Effect of magnetic fields on cryptochrome-dependent responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Roy Soc Interface 6:1193–1205. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2008.0519
Hasenstein KH, John S, Scherp P, Povinelli D, Mopper S (2013) Analysis of magnetic gradients to study gravitropism. Am J Bot 100:249–255. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1200304
Holden M (1965) Chlorophylls. Chemistry and biochemistry of plant pigments, 1st ed Academic Press: London, UK 461–488.
Holdsworth MJ, Bentsink L, Soppe WJJ (2008) Molecular networks regulating Arabidopsis seed maturation, after ripening, dormancy and germination. New Phytol 179:33–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02437.x
Islam M, Maffei ME, Vigani G (2020) The geomagnetic field is a contributing factor for an efficient iron uptake in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 11:325. https://doi.org/10.3389/2Ffpls.2020.00325
Jedynak P, Mysliwa-Kurdziel B, Turek E, Malec P (2013) Photoinduction of seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana is modulated by phototropins. Acta Biol Cracov Ser Bot 55:67–72. https://doi.org/10.2478/abcsb-2013-0008 (https://www.google.de/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwimsca0z-zxAhUBvaQKHQGBCWYQFjAAegQIAhAD&url=https%3A%2F%2Fzfibr.wbbib.uj.edu.pl%2Fprzemyslaw-malec&usg=AOvVaw3KwGEMhLqp79wKCVI6bumm)
Kircher S, Schopfer P (2012) Photosynthetic sucrose acts as cotyledon-derived long-distance signal to control root growth during early seedling development in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:11217–11221. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1203746109
Kubasek WL, Shirley BW, McKillop A, Goodman HM, Briggs W, Ausubel FM (1992) Regulation of flavonoid biosynthetic genes in germinating Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 4:1229–1236. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.4.10.1229
Kuznetsov OA, Schwuchow J, Sack FD, Hasenstein KH (1999) Curvature induced by amyloplast magnetophoresis in protonemata of the moss Ceratodon purpureus. Plant Physiol 119:645–650. https://doi.org/10.1104/2Fpp.119.2.645
Lee AA, Lau JCS, Hogben HJ, Biskup T, Kattrig DR, Hore PJ (2014) Alternative pairs for cryptochrome-based magnetoreception. J R Soc Interface 11:1063. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2013.1063
Li J, Li G, Wang H, Deng XW (2011) Phytochrome Signaling Mechanisms. The Arabidopsis Book 9:e0148. https://doi.org/10.1199/2Ftab.0148e0148
Li Y, Li L-L, Fan R-C, Peng C-C, Sun H-L, Zhu S-Y, Wang X-F, Zhang L-Y, Zhang D-P (2012) Arabidopsis sucrose transporter SUT4 interacts with cytochrome b5–2 to regulate seed germination in response to sucrose and glucose. Mol Plant 5:1029–1041. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sss001
Liedvogel M, Mouritsen H (2010) Cryptochromes — a potential magnetoreceptor: what do we know and what do we want to know? J R Soc Interface 7(Suppl 2):S147–S162. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2009.0411.focus
Liu H, Liu B, Zhao C, Pepper M, Lin C (2011) The action mechanisms of plant cryptochromes. Trends Plant Sci 16:684–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2011.09.002
Lohmann KJ, Willows AO (1987) Lunar-modulated geomagnetic orientation by a marine mollusk. Science 235:331–334. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3798115
MacKinney G (1941) Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. J Biol Chem 140:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)51320-X
Maffei M (2014) Magnetic field effects on plant growth, development, and evolution. Plant Sci 5:445–460. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00445
Neff MM, Chory J (1998) Genetic interactions between phytochrome A, phytochrome B, and cryptochrome 1 during Arabidopsis development. Plant Physiol 118:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1104/2Fpp.118.1.27
Occipinti A, De Santis A, Maffei ME (2014) Magnetoreception: an unavoidable step for plant evolution? Trends Plant Sci 19:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.10.007
Palmer JD (1963) Organismic spatial response in very weak spatial magnetic fields. Nature 198:1061–1062
Paponov I, Fliegmann J, Narayana R, Maffei M (2021) Differential root and shoot magnetoresponses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci Rep 11:9195. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88695-6
Pazur A, Schimek C, Galland P (2007) Magnetoreception in microorganisms and fungi. Centr Eur J Biol 2:597–659. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-007-0032-z
Pedmale UV, Huang S-S, Zander M, Cole BJ, Hetzel J, Ljung K, Reis PAB, Sridevi P, Nito K, Nery JR, Ecker JR, Chory J (2016) Cryptochromes interact directly with PIFs to control plant growth in limiting blue light. Cell 164:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.018
Philips JB, Jorge RE, Mulheim R (2010) Light-dependent magnetic compass orientation in amphibians and insects: candidate receptors and candidate molecular mechanisms. J R Soc Interface 7:S241–S256. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2009.0459.focus
Pittman UJ (1963a) Effects of magnetism on seedling growth of cereal plants. Biomedical Sci Inst 1:117–122
Pittman UJ (1963b) Magnetism and plant growth. I. Effects on germination and early growth of cereal seeds. Can J Plant Sci 43:513–551
Pooam M, Arthaut L-D, Burdick D, Link J, Martino CF, Ahmad M (2019) Magnetic sensitivity mediated by the Arabidopsis blue-light receptor cryptochrome occurs during flavin reoxidation in the dark. Planta 249:319–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-3002-y
Reed JW, Nagatani A, Elich TD, Fagan M, Chory J (1994) Phytochrome A and phytochrome B have overlapping but distinct functions in Arabidopsis development. Plant Physiol 104:1139–1149. https://doi.org/10.1104/2Fpp.104.4.1139
Reinders A, Sivitz AB, Starker CG, Gantt JS, Ward JM (2008) Functional analysis of LjSUT4, a vacuolar sucrose transporter from Lotus japonicus. Plant Mol Biol 68:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9370-0
Ritz T (2011) Quantum effects in biology: bird navigation. Proc Chem 3:262–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2011.08.034
Ritz T, Adem S, Schulten K (2000) A model for photoreceptor-based magnetic-field reception in birds. Biophys J 78:707–718. 10.16/2FS0006–3495(00)76629-X
Rodgers CT, Hore PJ (2009) Chemical magnetic-field reception in birds: The radical pair mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:353–360. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0711968106
Sellaro R, Crepy M, Trupkin SA, Karayekov E, Buchovsky AS, Rossi C, Casal JJ (2010) Cryptochrome as a sensor of the blue/green ratio of natural radiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 154:401–409. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.160820
Shabrangi A, Hassanpour H, Majd A, Sheidai M (2015) Induction of genetic variation by electromagnetic fields in Zea mays L. and Brassica napus L. Caryologia 68:272–279. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2015.1109920
Shinomura T, Nagatani A, Hanzawa H, Kubota M, Watanabe M, Furuya M (1996) Action spectra for phytochrome A- and B-specific photoinduction of seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8129–8133. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.15.8129
Solov’yov IA, Schulten K (2009) Magnetic-field reception through cryptochrome may involve superoxide. Biophys J 96:4804–4813. https://doi.org/10.1016/2Fj.bpj.2009.03.048
Su L, Hou P, Song M, Zheng X, Guo L, Xiao Y, Yan L, Li W, Yang J (2015) Synergistic and antagonistic action of phytochrome (Phy) A and PhyB during seedling de-etiolation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci 16:12199–12212. https://doi.org/10.3390/2Fijms160612199
Taia W, Al-Zahrani H, Kotbi A (2007) The effect of static magnetic forces on water contents and photosynthetic pigments in sweet basil Ocimum basilicum L. (Laminaceae). Saudi J Bio Sci 14:103–107
Teng S, Keurentjes J, Bentsink L, Koornneef M, Smeekens S (2005) Sucrose-specific induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis requires the MYB75/PAP1 gene. Plant Physiol 139:1840–1852. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.066688
Timmel CR, Henbest KB (2004) A study of spin chemistry in weak magnetic fields. Phil Trans R Soc London A 362:2573–2589. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2004.1459
Tognetti JA, Pontis HG, Martinez-Noel MA (2013) Sucrose signaling in plants. A world yet to be explored. Plant Signal Behav 8:e23316-1–23316-10. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.23316
Turker M, Temirici C, Battal P, Erez ME (2007) The effects of artificial and static magnetic field on plant growth, chlorophyll and phytohormone levels in maize and sunflower plants. Phyton Ann Rei Bot Horn 46:271–284. Field reversal
Vashisth A, Nagarajan S (2008) Exposure of seeds to static magnetic field enhances germination and early growth characteristics in chickpea (Cicer arietum L.). Bioelectromagnetics 29:571–578. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20426
Vashisth A, Nagarajan S (2010) Effect on germination and early growth characteristics in sunflower (Helianthus annuus) seeds exposed to static magnetic fields. J Plant Physiol 167:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2009.08.011
Volpe P (2003) Interaction of zero-frequency and oscillating magnetic fields with biostructure and biosystems. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2:637–648. https://doi.org/10.1039/b212636b
Wang K, Mattern E, Ritz T (2006) On the use of magnets to disrupt the physiological compass of birds. Physical Biol 3:220–231. https://doi.org/10.1088/1478-3975/3/3/007
Weise A, Barker L, Kühn C, Lalonde S, Buschmann H, Frommer WB, Ward JM (2000) A new subfamily of sucrose transporters, SUT4, with low affinity/high capacity localized in enucleate sieve elements of plants. Plant Cell 12:1345–1355. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.8.1345
Wiltschko R, Wiltschko W (1995) Magnetic orientation in animals. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Wiltschko W, Wiltschko R (2005) Magnetic orientation and magnetoreception in birds and other animals. J Comp Physiol A 191:675–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-005-0627-7
Wiltschko R, Wiltschko W (2012) Magnetic-field reception. Adv Exp Med Biol 739:126–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-1704-0_8
Xu C, Yin X, Lu Y, Wu C, Zhang Y, Song T (2012) A near-null magnetic field affects cryptochrome-related hypocotyls growth and flowering in Arabidopsis. Adv Space Res 49:834–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2011.12.004 (https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/link_gateway/2012AdSpR..49..834X)
Xu C, Lu Y, Chen C, Hang Y (2014) Blue light-dependent phosphorylations of cryptochromes are affected by magnetic fields in Arabidopsis. Adv Space Res 53:1118–1124. https://doi.org/10.1016/2Fj.asr.2014.01.033
Xu C, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Wei S (2017) Gibberellins are involved in effect of near-null magnetic field on Arabidopsis flowering. Bioelectromagnet 38:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.22004
Xu C, Zhang Y, Yu Y, Li Y, Wei S (2018) Suppression of Arabidopsis flowering by near-null magnetic field is mediated by auxin. Bioelectromag 39:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.22086
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Vladimir N. Binhi for many helpful suggestions. The authors are grateful for the excellent technical assistance of M. Göttig and S. Völk and the continued support of our electronic and mechanical machine shops.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from DLR (German Space Agency/BMWi 50WB1025 and 50WB1325) to PG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dhiman, S.K., Wu, F. & Galland, P. Effects of weak static magnetic fields on the development of seedlings of Arabidopsis thaliana. Protoplasma 260, 767–786 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-022-01811-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-022-01811-9