Abstract
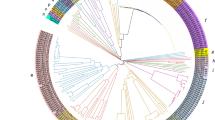
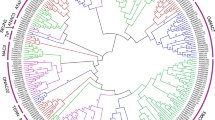
The myeloblastosis (MYB) gene family, involved in regulating many important physiological and biochemical processes, is one of the largest transcript factor superfamilies in plants. Since the identification of genome sequencing of Panax notoginseng has been completed, there was little known about the whole genome of its specific MYB gene family and the response to abiotic stresses, in consideration of the excessive application of nitrogen fertilizers in P. notoginseng. In this study, 123 PnMYB genes (MYB genes of P. notoginseng) have been identified and divided into 3 subfamilies by the phylogenetic analysis. These PnMYB genes were unevenly located on 12 chromosomes. Meanwhile, the gene structure and protein conserved domain were established by MEME Suite. The analysis of collinear relationships reflected that there were 121 homologous genes between P. notoginseng and Arabidopsis and 30 between P. notoginseng and rice. Moreover, cis-acting elements of PnMYB gene promoters were predicted which indicated that PnMYBs are involved in biotic, abiotic stress, and hormone induction. The expressions of PnMYB transcription factors in its roots, flowers, and leaves were detected by qRT-PCR and they had tissue-specific expressions and related to the growth of different tissues. Under nitrogen stress, MYB transcription factors had great feedback. Ten R2R3-MYB subfamily genes were significantly induced and indicated the possible function of protecting P. notoginseng from excess nitrogen. With further knowledge on identification of PnMYB gene related to tissue selectivity and abiotic stresses, this study laid the foundation for the functional development of PnMYB gene family and improved the cultivation of P. notoginseng.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 June 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-022-01782-x
References
Afrin S, Zhu J, Cao H, Huang J, Xiu H, Luo T, Luo Z (2015) Molecular cloning and expression profile of an abiotic stress and hormone responsive MYB transcription factor gene from Panax ginseng. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 47(4):267–277. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmv012
Ambawat S, Sharma P, Yadav NR, Yadav RC (2013) MYB transcription factor genes as regulators for plant responses: an overview. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 19(3):307–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-013-0179-1
Balkos KD, Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2010) Optimization of ammonium acquisition and metabolism by potassium in rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. IR-72). Plant Cell Environ 33:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02046.x
Baumann K, Perez-Rodriguez M, Bradley D, Venail J, Bailey P, Jin H, Koes R, Roberts K, Martin C (2007) Control of cell and petal morphogenesis by R2R3 MYB transcription factors. Development 134(9):1691–1701. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02836
Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2002) NH4+ toxicity in higher plants: a critical review. J Plant Physiol 159(6):567–584. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-0774
Cao ZH, Zhang SZ, Wang RK, Zhang RF, and Hao YJ (2013) Genome wide analysis of the apple MYB transcription factor family allows the identification of MdoMYB121 gene confering abiotic stress tolerance in plants. PLoS ONE 8(7):e69955. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069955
Chen W, Kui L, Zhang GH, Zhu SS, Zhang J, Wang X, Yang M, Huang HC, Liu YX, Wang Y, Li YH, Zeng LP, Wang E, He XH, Dong Y, Yang SC (2017) Whole-genome sequencing and analysis of the Chinese herbal plant Panax notoginseng. Molecular Plant 10(6):899–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2017.02.010
Du H, Zhang L, Liu L, Tang XF, Yang WJ, Wu YM, Huang YB, Tang YX (2009) Biochemical and molecular characterization of plant MYB transcription factor family. Biochemistry (Moscow) 74(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297909010015
Du YT, Zhao MJ, Wang CT, Gao Y, Wang YX, Liu YW, Chen M, Chen J, Zhou YB, Xu ZS, Ma YZ (2018) Identification and characterization of GmMYB118 responses to drought and salt stress. BMC Plant Biol 18(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1551-7
Du H, Yang SS, Liang Z, Feng BR, Liu L, Huang YB, and Tang YX (2012) Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 12(1):106. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2229/12/106
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15(10):573–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2010.06.005
Espley RV, Hellens RP, Putterill J, Stevenson DE, Kutty-Amma S, Allan AC (2007) Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J 49(3):414–427. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02964.x
Fang G, Yang J, Sun T, Wang X, Li Y (2021) Synergism between potassium and nitrate enhances the alleviation of ammonium toxicity in rice seedling root. PLoS ONE 16(9):e0248796. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.08.434377
Hajiebrahimi A, Owji H, Hemmati S, Cloutier S (2017) Genome-wide identification, functional prediction, and evolutionary analysis of the R2R3-MYB superfamily in Brassica napus. Genome 60(10):797–814. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2017-0059
He Y, Li W, Lv J, Jia Y, Wang M, Xia G (2012) Ectopic expression of a wheat MYB transcription factor gene, TaMYB73, improves salinity stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Experimental 63(3):1511–1522. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err389
He Q, Jones DC, Li W, Xie F, Ma J, Sun R, Wang Q, Zhu S, Zhang B (2016) Genome-wide identification of R2R3-MYB genes and expression analyses during abiotic stress in Gossypium raimondii. Scientific Reports 6(1):22980. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22980
Huang W, Sun W, Lv H, Xiao G, Zeng S, Wang Y (2013) Isolation and molecular characterization of thirteen R2R3-MYB transcription factors from epimedium sagittatum. Int J Mol Sci 14(1):594–610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14010594
Jin H, Martin C (1999) Multifunctionality and diversity within the plant MYB-gene family. Plant Mol Biol 41(5):577–585. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006319732410
Lea US, Slimestad R, Smedvig P, Lillo C (2007) Nitrogen deficiency enhances expression of specific MYB and bHLH transcription factors and accumulation of end products in the flavonoid pathway. Planta 225:1245–1253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0414-x
Li Q, Li BH, Kronzucker HJ, Shi WM (2010) Root growth inhibition by NH4+ in Arabidopsis is mediated by the root tip and is linked to NH4+ efflux and GMPase activity. Plant Cell Environ 33(9):1529–1542. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02162.x
Li BH, Li Q, Su YH, Chen H, Xiong LM, Mi GH, Kronzucker HJ, Shi WM (2011) Shoot-supplied ammonium targets the root auxin influx carrier AUX1 and inhibits lateral root emergence in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 34(6):933–946. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02295.x
Li X, Guo C, Ahmad S, Wang Q, Yu J, Liu C, Guo Y (2019) Systematic analysis of MYB family genes in potato and their multiple roles in development and stress responses. Biomolecules 9(8):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080317
Li Y, Liang J, Zeng X, Guo H, Luo Y, Kear P, Zhang S, Zhu G (2021) Genome-wide analysis of MYB gene family in potato provides insights into tissue-specific regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Hortic Plant J 7(2):129–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpj.2020.12.001
Li J, Liu H, Yang C, Wang J, Yan G, Si P, Bai Q, Lu Z, Zhou W, Xu L (2020) Genome-wide identification of MYB genes and expression analysis under different biotic and abiotic stresses in Helianthus annuus L. Industrial Crops and Products 143:111924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111924
Lin-Wang, K., Bolitho, K., Grafton, K., Kortstee, A., Karunairetnam, S., McGhie, T. K., Espley, R. V., Hellens, R. P., Allan, A. C. (2010) An R2R3 MYB transcription factor associated with regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Rosaceae. BMC Plant Biology 10(1):50. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-50
Liu Y, Zeng Y, Li Y, Liu Z, Lin-Wang K, Espley RV, Allan AC, Zhang J (2020) Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the MYB-related transcription factor superfamily in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Int J Biol Macromol 164:2450–2464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.062
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London
Miyake K, Ito T, Senda M, Ishikawa R, Harada T, Niizeki M et al (2003) Isolation of a subfamily of genes for R2R3-MYB transcription factors showing up-regulated expression under nitrogen nutrient-limited conditions. Plant Mol Biol 53:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLAN.0000009296.91149.34
Peng L, Wang Y, Sun X, Wang X, Zhao C, Wang C, Xiang L, Chen J, Lai Z, Liu S (2019) Expression and functional analysis of AmMYB2 related to betalain metabolism of Amaranthus tricolor. Acta Horticulturae Sinica 46:473–485. https://doi.org/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0572
Saedler H, Paz-Ares J, Wienand U (1987) Molecular analysis of the regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Zea mays. Organization and Function of the Eucaryotic Genome 1987/88/1987/3:4. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-46611-3_5
Seo PJ, Lee SB, Suh MC, Park MJ, Park CM (2011) The MYB96 transcription factor regulates cuticular wax biosynthesis under drought conditions in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23(3):1138–1152. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.083485
Song X, Yang Q, Liu Y, Li J, Chang X, Xian L, Zhang J (2021) Genome-wide identification of Pistacia R2R3-MYB gene family and function characterization of PcMYB113 during autumn leaf coloration in Pistacia chinensis. Int J Biol Macromol 192:16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.092
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Huep G, Barsch A, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B (2007) Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J 50:660–677. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03078.x
Tabatabaei SJ, Yusefi M, Hajiloo J (2008) Effects of shading and NO3:NH4 ratio on the yield, quality and N metabolism in strawberry. Sci Hortic 116(3):264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2007.12.008
Wang T, Guo R, Zhou G, Zhou X, Kou Z, Sui F, Li C, Tang L, Wang Z (2016) Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen: A review. J Ethnopharmacol 188:234–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.005
Wang S, Shi M, Zhang Y, Xie X, Sun P, Fang C, Zhao J (2021a) FvMYB24, a strawberry R2R3-MYB transcription factor, improved salt stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 569:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.06.085
Wang X, Zheng Y, Chen B, Zhi C, Qiao L, Liu C, Pan Y, Cheng Z (2021b) Genome-wide identification of small heat shock protein (HSP20) homologs in three cucurbit species and the expression profiles of CsHSP20s under several abiotic stresses. Int J Biol Macromol 190:827–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.222
Wessler SR, Carrington JC (2005) Genome studies and molecular genetics: the consequences of gene and genome duplication in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8(2):119–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2005.01.015
Xia P, Guo H, Zhao H, Jiao J, Deyholos MK, Yan X, Liu Y, Liang Z (2016) Optimal fertilizer application for panax notoginseng and effect of soil water on root rot disease and saponin contents. J Ginseng Res 40(1):38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2015.04.003
Xiao Y, Zhou L, Lei X, Cao H, Wang Y, Dou Y, Tang W, Xia W (2017) Genome-wide identification of WRKY genes and their expression profiles under different abiotic stresses in Elaeis guineensis. PLoS ONE 12(12):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189224
Yang X, Guo T, Li J, Chen Z, Guo B, An X (2021a) Genome-wide analysis of the MYB-related transcription factor family and associated responses to abiotic stressors in Populus. Int J Biol Macromol 191:359–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.042
Yang ZJ, Liu GZ, Zhang GH, Yan J, Dong Y, Lu YC, Fan W, Hao B, Lin Y, Li Y, Li XJ, Tang QY, Xiang GS, He SM, Chen JW, Chen W, Xu ZP, Mao ZC, Duan SC, Jin SX, Yang SC (2021b) The chromosome-scale high-quality genome assembly of Panax notoginseng provides insight into dencichine biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnol Journal 19(5):869–871. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13558
Yanhui C, Xiaoyuan Y, Kun H, Meihua L, Jigang L, Zhaofeng G, Zhiqiang L, Yunfei Z, Xiaoxiao W, Xiaoming Q, Yunping S, Li Z, Xiaohui D, Jingchu L, Xing-Wang D, Zhangliang C, Hongya G, Li-Jia Q (2006) The MYB transcription factor superfamily of Arabidopsis: expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice MYB family. Plant Mol Biol 60(1):107–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-2910-y
Zhang D, Li W, Xia E-H, Zhang Q-J, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Tong Y, Zhao Y, Niu Y-C, Xu J-H, Gao LZ (2017) The medicinal herb Panax notoginseng genome provides insights into ginsenoside biosynthesis and genome evolution. Molecular Plant 10(6):903–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2017.02.011
Zhang B, Xia P, Yu H, Li W, Chai W, Liang Z (2021) Based on the whole genome clarified the evolution and expression process of fatty acid desaturase genes in three soybeans. Int J Biol Macromol 182:1966–1980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.161
Zhang C, Ma R, Xu J, Yan J, Guo L, Song J, Feng R, Yu M (2018) Genome-wide identification and classification of MYB superfamily genes in peach. PLoS ONE 13(6):e0199192. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199192
Zheng X, He K, Kleist T, Chen F, Luan S (2015) Anion channel SLAH3 functions in nitrate-dependent alleviation of ammonium toxicity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 38:474–486. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12389
Zhou C, Chen Y, Wu Z, Lu W, Han J, Wu P, Chen Y, Li M, Jiang H, Wu G (2015) Genome-wide analysis of the MYB gene family in physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.). Gene 572(1):63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.06.072
Zhou L, Yarra R, Jin L, Cao H (2020) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MYB gene family in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) under abiotic stress conditions. Environ Exp Bot 180:104245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104245
Zhuang K, Shi D, Hu Z, Xu F, Chen Y, Shen Z (2019) Subcellular accumulation and source of O2− and H2O2 in submerged plant Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle under NH4+-N stress condition. Aquat Toxicol 207:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.11.011
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Zhejiang Province Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project (CN) (LGN21C020003), Development and application of intelligent information platform of Chinese herbal medicine P. notoginseng industry (202102AA100052), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81703641).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.X. conceived and designed this study. X.C. conducted analysis. Z.L., W.C., and K.Y. contributed the analytical methods. Y.M. and P.X. wrote the manuscript. P.X. edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The correct assigned Author affiliations is modified in the original published proof.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Mao, Y., Chai, W. et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MYB gene family under nitrogen stress in Panax notoginseng. Protoplasma 260, 189–205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-022-01770-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-022-01770-1