Abstract
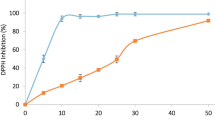
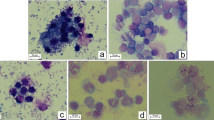
Cynanchum sarcomedium Meve & Liede is a member of Apocynaceae, seen in dry and rocky areas. The present study highlights the cytotoxic potential of C. sarcomedium mediated by apoptosis on cells of Allium cepa and human red blood cells (RBCs). Cytogenetic changes in A. cepa and in situ visualization of cell death were revealed through acetocarmine and Evans blue staining techniques. Quantitative estimation of cell death was carried out at 600 nm in a spectrophotometer. Membrane characteristics of RBC in response to the treatment were evaluated by May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Cell membrane damage is a major factor for assessing apoptosis which is observed in the present study (90.91 %). Cell shrinkage, cytoplasmic fragmentation, condensed chromatin and presence of apoptotic bodies were the common cytological changes in A. cepa associated with apoptosis. Blebs in RBC evidenced by SEM revealed the membrane damage potential of the plant. Results obtained hereby suggest that the plant is an effective source to be used in toxicological studies and anti-cancer therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achary VMM, Jena S, Panda KK, Panda BB (2008) Aluminium induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in root cells of Allium cepa L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 70(2):300–310
Baker CJ, Mock NM (1994) An improved method for monitoring cell death in cell suspension and leaf disc assays using Evan’s blue. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 39:7–12
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35(4):495–516
Golstein P, Kroemer G (2007) Cell death by necrosis: towards a molecular definition. Trends Biochem Sci 32(1):37–43
Hara-Nishimura I, Hatsugai N (2011) The role of vacuole in plant cell death. Cell Death Differ 18(8):1298–1304
Hatsugai N, Kuroyanagi M, Nishimura M, Hara-Nishimura I (2006) A cellular suicide strategy of plants: vacuole-mediated cell death. Apoptosis 11(6):905–911
Junqueira LC, Carneiro J (2004) Aparelho respiratório. Histologia Básica 8:285–300
Kirsch-Volders M, Elhajouji A, Cundari E, Van Hummelen P (1997) The in vitro micronucleus test: a multi-endpoint assay to detect simultaneously mitotic delay, apoptosis, chromosome breakage, chromosome loss and non-disjunction. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 392(1):19–30
Kumar SP, Soni K, Saraf MN (2006) In-vitro tocolytic activity of Sarcostemma brevistigma Wight. Indian J Pharm Sci 68:190–194
Kumar SP, Soni K, Jadhav SR, Doshi NS, Saraf MN (2007) Mechanism of spasmolytic activity of a fraction of Sarcostemma brevistigma Wight. Indian J Exp Biol 45:419–424
Kumari TKS, Muthukumarasamy S, Mohan VR (2012) GC-MS analysis of ethanol extract of Sarcostemma secamone (L.) Bennet (Asclepiadaceae). Sci Res Rep 2:187–191
Lim G, Wortis M, Mukhopadhyay R (2002) Stomatocyte-discocyte-echinocyte sequence of the human red blood cell: evidence for the bilayer-couple hypothesis from membrane mechanics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:16766–16769
Maiworm AI, Presta GA, Santos-Filho SD, Paoli SD, Giani TS, Fonseca AS, Bernardo-Filho M (2008) Osmotic and morphological effects on red blood cell membrane: action of an aqueous extract of Lantana camara. Rev Bras Farm 18(1):42–46
Meve U, Liede-Schumann S (2012) Taxonomic dissolution of Sarcostemma (Apocynaceae: Asclepiadoideae). Kew Bull 67(4):751–758
Nostro A, Germano MP, Dángelo V, Cannatelli MA (2000) Extraction methods and bioautography for evaluation of medicinal plant antimicrobial activity. Lett Appl Microbiol 30:379–384
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT, Liu B, Bao JK (2012) Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: a review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif 45(6):487–498
Panda KK, Achary VMM, Krishnaveni R, Padhi BK, Sarangi SN, Sahu SN, Panda BB (2011) In vitro biosynthesis and genotoxicity bioassay of silver nanoparticles using plants. Toxicol In Vitro 25(5):1097–1105
Prashar A, Locke IC, Evans CS (2004) Cytotoxicity of lavender oil and its major components to human skin cells. Cell Prolif 37(3):221–229
Prashar A, Locke IC, Evans CS (2006) Cytotoxicity of clove (Syzygium aromaticum) oil and its major components to human skin cells. Cell Prolif 39(4):241–248
Suwalsky M, Vargas P, Avello M, Villena F, Sotomayor CP (2008) Human erythrocytes are affected in vitro by flavonoids of Aristotelia chilensis (Maqui) leaves. Int J Pharm 363(1):85–90
Taraphdar AK (2001) Natural products as inducers of apoptosis: implication for cancer therapy and prevention. Curr Sci 80(11):1387–1396
Zavodnik IB, Lapshina EA, Zavodnik LB, Bartosz G, Soszynski M, Bryszewska M (2001) Hypochlorous acid damages erythrocyte membrane proteins and alters lipid bilayer structure and fluidity. Free Radic Biol Med 30:363–369
Acknowledgments
The first author gratefully acknowledges INSPIRE-DST, Government of India (C/2003/1FD/2014-15), for the award of fellowship. It is grateful to acknowledge Anjali Prashar, Hypha Discovery Ltd, UK, for providing supporting literature.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Jan Raoul De Mey
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhagyanathan, N.K., Thoppil, J.E. Pre-apoptotic activity of aqueous extracts of Cynanchum sarcomedium Meve & Liede on cells of Allium cepa and human erythrocytes. Protoplasma 253, 1433–1438 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0898-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0898-y