Abstract
Copper is a micronutrient required for living organisms, but is potentially toxic in excess. EDDS enhances the phytoextraction of many metals, but the underlying mechanism is fully unclear. Exposure of 200 μM Cu2+ for 3 days resulted in rice seedling growth inhibition, accompanied by a decrease in plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity, and an increase in relative electrolyte leakage ratios, indicating that maintaining of membrane structure integrity is crucial in acclimation of plants to heavy metal stress. In addition, the chlorophyll and carotenoid content was markedly decreased and the level of the mRNA of Cytochrome P450 gene, OsHMA9, the sulfate transporter gene, and the metallothionein-like protein gene was observed to increase in response to Cu stress. Cu treatment also induced a global epigenetic response which is associated with cell nucleus condensation. These physiological, genetic, and epigenetic responses of rice seedlings to excess copper were modified by the addition of EDDS, suggesting that the supply of EDDS in medium containing a high concentration of Cu ions could enhance plant tolerance potential to excess Cu toxicity through alleviating Cu-induced poisonous effects at various levels.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cu:
-
Copper
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- EDDS:
-
Ethylenediamine-N,N′-disuccinic acid
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- H3K4me2:
-
Histone H3 di-methyl Lys4
References
Alkorta I, Hernández-Allica J, Becerril J, Amezaga I, Albizu I, Onaindia M, Garbisu C (2004) Chelate-enhanced phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy metals. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 3:55–70
Backor M, Dzubaj A (2004) Short-term and chronic effects of copper, zinc and mercury on the chlorophyll content of four lichen photobionts and related alga. J Hattori Bot Lab 95:271–284
Bačkor M, Váczi P (2002) Copper tolerance in the lichen photobiont Trebouxia erici (Chlorophyta). Environ Exp Bot 48:11–20
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34
Berthiaume M, Boufaied N, Moisan A, Gaudreau L (2006) High levels of oxidative stress globally inhibit gene transcription and histone acetylation. DNA Cell Biol 25:124–134
Bode K, Schroder K, Hume D, Ravasi T, Heeg K, Sweet M, Dalpke A (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors decrease toll-like receptor-mediated activation of proinflammatory gene expression by impairing transcription factor recruitment. Immunology 122:596–606
Cestone B, Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J, Sgherri C, Navari-Izzo F (2012a) The influence of EDDS on the metabolic and transcriptional responses induced by copper in hydroponically grown Brassica carinata seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 55:43–51
Cestone B, Vogel-Mikuš K, Quartacci MF, Rascio N, Pongrac P, Pelicon P, Vavpetič P, Grlj N, Jeromel L, Kump P (2012b) Use of micro-PIXE to determine spatial distributions of copper in Brassica carinata plants exposed to CuSO (4) or CuEDDS. Sci Total Environ 427:339–346
Chen CT, Chen L-M, Lin CC, Kao CH (2001) Regulation of proline accumulation in detached rice leaves exposed to excess copper. Plant Sci 160:283–290
Chinnusamy V, Zhu J-K (2009) Epigenetic regulation of stress responses in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:133–139
Evangelou MW, Bauer U, Ebel M, Schaeffer A (2007) The influence of EDDS and EDTA on the uptake of heavy metals of Cd and Cu from soil with tobacco Nicotiana tabacum. Chemosphere 68:345–353
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Noutoshi Y, Takahashi F, Narusaka Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses: a current view from the points of convergence in the stress signaling networks. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:436–442
Hu Y, Zhang L, Zhao L, Li J, He S, Zhou K, Yang F, Huang M, Jiang L, Li L (2011) Trichostatin A selectively suppresses the cold-induced transcription of the ZmDREB1 gene in maize. PloS ONE 6:e22132
Jaenisch R, Bird A (2003) Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet 33:245–254
Janicka-Russak M, Kabała K, Burzyński M, Kłobus G (2008) Response of plasma membrane H-ATPase to heavy metal stress in Cucumis sativus roots. J Exper Bot 59:3721–3728
Janicka-Russak M, Kabała K, Burzyński M (2012) Different effect of cadmium and copper on H + -ATPase activity in plasma membrane vesicles from Cucumis sativus roots. J Exp Bot 63:4133–4142
Janicka-Russak M, Kabała K, Wdowikowska A, Kłobus G (2013) Modification of plasma membrane proton pumps in cucumber roots as an adaptation mechanism to salt stress. J Plant Physiol 170:915–922
Kłobus G, Buczek J (1995) The role of plasma membrane oxidoreductase activity in proton transport. J Plant Physiol 146:103–107
Lan H-X, Wang Z-F, Wang Q-H, Wang M-M, Bao Y-M, Huang J, Zhang H-S (2013) Characterization of a vacuolar zinc transporter OZT1 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Biol Rep 40:1201–1210
Lee S, Kim Y-Y, Lee Y, An G (2007) Rice P1B-type heavy-metal ATPase, OsHMA9, is a metal efflux protein. Plant Physiol 145:831–842
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592
Martins N, Gonçalves S, Romano A (2013) Aluminum inhibits root growth and induces hydrogen peroxide accumulation in Plantago algarbiensis and P. almogravensis seedlings. Protoplasma 250:1295–1302
Nomura T, Hasezawa S (2011) Regulation of gemma formation in the copper moss Scopelophila cataractae by environmental copper concentrations. J Plant Res 124:631–638
Oakley RV, Wang Y-S, Ramakrishna W, Harding SA, Tsai C-J (2007) Differential expansion and expression of α-and β-tubulin gene families in Populus. Plant Physiol 145:961–973
Påhlsson A-MB (1989) Toxicity of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb) to vascular plants. Water Air Soil Pollut 47:287–319
Pätsikkä E, Kairavuo M, Šeršen F, Aro E-M, Tyystjärvi E (2002) Excess copper predisposes photosystem II to photoinhibition in vivo by outcompeting iron and causing decrease in leaf chlorophyll. Plant Physiol 129:1359–1367
Quartacci MF, Irtelli B, Baker AJ, Navari-Izzo F (2007) The use of NTA and EDDS for enhanced phytoextraction of metals from a multiply contaminated soil by Brassica carinata. Chemosphere 68:1920–1928
Ristic Z, Ashworth E (1993) Changes in leaf ultrastructure and carbohydrates in Arabidopsis thaliana L. (Heyn) cv. Columbia during rapid cold acclimation. Protoplasma 172:111–123
Rolny N, Costa L, Carrión C, Guiamet JJ (2011) Is the electrolyte leakage assay an unequivocal test of membrane deterioration during leaf senescence? Plant Physiol Biochem 49:1220–1227
Salvi A, Carrupt P-A, Tillement J-P, Testa B (2001) Structural damage to proteins caused by free radicals: assessment, protection by antioxidants, and influence of protein binding. Biochem Pharmacol 61:1237–1242
Sudo E, Itouga M, Yoshida-Hatanaka K, Ono Y, Sakakibara H (2008) Gene expression and sensitivity in response to copper stress in rice leaves. J Exper Bot 59:3465–3474
Tandy S, Schulin R, Nowack B (2006) Uptake of metals during chelant-assisted phytoextraction with EDDS related to the solubilized metal concentration. Environ Sci Technol 40:2753–2758
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Choudhury S, Patra HK, Panda SK (2014) Zinc ameliorates copper-induced oxidative stress in developing rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Protoplasma 251:61–69
Tripathi B, Gaur J (2004) Relationship between copper- and zinc-induced oxidative stress and proline accumulation in Scenedesmus sp. Planta 219:397–404
Tsankova N, Renthal W, Kumar A, Nestler EJ (2007) Epigenetic regulation in psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:355–367
Uchida K, Kanematsu M, Sakai K, Matsuda T, Hattori N, Mizuno Y, Suzuki D, Miyata T, Noguchi N, Niki E (1998) Protein-bound acrolein: potential markers for oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:4882–4887
Vadas TM, Zhang X, Curran AM, Ahner BA (2007) Fate of DTPA, EDTA, and EDDS in hydroponic media and effects on plant mineral nutrition. J Plant Nutr 30:1229–1246
Vandevivere PC, Saveyn H, Verstraete W, Feijtel TC, Schowanek DR (2001) Biodegradation of metal-[S, S]-EDDS complexes. Environ Sci Technol 35:1765–1770
Vogelauer M, Wu J, Suka N, Grunstein M (2000) Global histone acetylation and deacetylation in yeast. Nature 408:495–498
Wei L, Luo C, Wang C, Li X, Shen Z (2007) Biodegradable chelating agent ethylenediaminedisuccinic acid reduces uptake of copper through alleviation of copper toxicity in hydroponically grown Chrysanthemum Coronarium L. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:749–754
Xu J, Yang L, Wang Z, Dong G, Huang J, Wang Y (2006) Toxicity of copper on rice growth and accumulation of copper in rice grain in copper contaminated soil. Chemosphere 62:602–607
Yan S, Zhao L, Li H, Zhang Q, Tan J, Huang M, He S, Li L (2013) Single-walled carbon nanotubes selectively influence maize root tissue development accompanied by the change in the related gene expression. J Hazard Mater 246–247:110–118
Yruela I (2009) Copper in plants: acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct Plant Biol 1445:409–430
Zhang L, Hu Y, Yan S, Li H, He S, Huang M, Li L (2012) ABA-mediated inhibition of seed germination is associated with ribosomal DNA chromatin condensation, decreased transcription, and ribosomal RNA gene hypoacetylation. Plant Mol Biol 79(3):285–293
Zhang L, Qiu Z, Hu Y, Yang F, Yan S, Zhao L, Li B, He S, Huang M, Li J (2011) ABA treatment of germinating maize seeds induces VP1 gene expression and selective promoter‐associated histone acetylation. Physiol Plant 143:287–296
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NSFC (no. 31171186) and Hubei Province Natural Science Fund.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled, “Exogenous EDDS modifies copper-induced various toxic responses in rice”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Liwen Jiang
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure 1
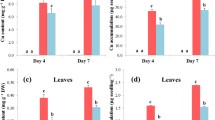
Copper concentrations in shoots and roots. Bars represent standard errors of the mean. * denotes significant differences (p < 0.05) from the unexposed control using the Student’s t test. Rice roots showed significantly high Cu uptake following treatment with 200 μM of CuSO4 and Cu-EDDS, compared with the control, but the Cu concentration is still lower in shoots although exposure to 200 μM of CuSO4 and Cu-EDDS also resulted in a slight increase in copper concentration. (JPEG 823 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, J., He, S., Yan, S. et al. Exogenous EDDS modifies copper-induced various toxic responses in rice. Protoplasma 251, 1213–1221 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0628-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0628-x