Abstract
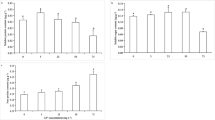
Lemna species are reported to accumulate a variety of metals from contaminated/polluted sites. Cadmium is a nonessential element for plant metabolism. In this work, we aimed to investigate physiological responses to low doses of cadmium (up to 100 μM). From exposure to the lowest Cd concentration (1 µM) to the highest (100 µM), photosynthetic pigments (Chl a, b, carotenoids) and the ratios of Chl a/b, Chl (a + b)/carotenoids decreased as a function of the Cd dose. The content of soluble proteins decreased in a dose-dependent manner, while total soluble thiols drastically increased. In Cd-treated fronds, the dose-dependent accumulation of a polypeptide with an apparent molecular weight of 24 kDa, as well as the appearance of two smaller polypeptides with molecular weights <6.5 kDa, was observed in sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Our results show that in Lemna trisulca, different adaptative mechanisms may be involved in counterbalancing low and high doses of a particular toxicant (cadmium). This feature makes this plant potentially useful material in biomonitoring and phytotoxicity testing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhilash PC, Pandey VC, Srivastava P, Rakesh PS, Chandran S, Singh N, Thomas AP (2009) Phytofiltration of cadmium from water by Limnocharis flava (L.) Buchenau grown in free-floating culture system. J Hazard Mater 170:791–797
Ahmad I, Naeem M, Khan NA, Samiullah (2009) Effects of cadmium stress upon activities of antioxidative enzymes, photosynthetic rate, and production of phytochelatins in leaves and chloroplasts of wheat cultivars differing in yield potential. Photosynthetica 47:146–151
Appenroth K, Teller S, Horn M (1996) Photophysiology of turion formation in Spirodela polyrhizza. Biol Plant 38:95–100
Ausubel F, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) (1995) Short protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York
Blum H, Beier H, Gross HJ (1987) Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 8:93–99
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Das SK, Routh J, Roychoudhury AN (2009) Biomarker evidence of macrophyte and plankton community changes in Zeekoevlei, a shallow lake in South Africa. J Paleolimnol 41:507–521
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Goering PL, Waalkes MP, Klassen CD (1994) Toxicology of cadmium. In: Goyer RA, Cherian MG (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology: toxicology of metals, biochemical effects, vol 115. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 189–214
He QB, Singh BR (1994) Crop uptake of cadmium from phosphorus fertilizers. I. Yield and cadmium content. Water Air Soil Pollut 74:251–265
Huebert DB, Shay JM (1991) The effect of cadmium and its interaction with external calcium in the submerged aquatic macrophyte Lemna trisulca L. Aquat Toxicol 20:57–72
Huebert DB, Shay JM (1993) The response of Lemna trisulca L. to cadmium. Environ Pollut 80:247–253
Khellaf N, Zerdaoui M (2009) Phytoaccumulation of zinc by the aquatic plant, Lemna gibba L. Bioresource Technol 100:6137–6140
Kumar GP, Prasad MNV (2004) Photosynthetic pigments and gaseous exchange in cadmium exposed Ceratophyllum demersum L. (a freshwater macrophyte)—a model for hormesis. J Plant Biol 31:1–8
Lichtenthaler H (1987) Chlorophylls and carotinoid: pigments of photosynthetic membranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382
Mazurek U, Naglik T, Wilczok A, Latocha M (1990) Effect of cadmium on photosynthetic pigments in synchronously growing Chlorella cells. Acta Biochim Pol 37:391–394
Myśliwa-Kurdziel B, Strzałka K (2002) Influence of metals on the biosynthesis of photosynthetic pigments. In: Prasad MNV, Strzalka K (eds) Physiology and biochemistry of metal toxicity and tolerance in plants. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 201–228
Myśliwa-Kurdziel B, Prasad MNV, Strzałka K (2004) Photosynthesis in metal plants. In: Prasad MNV (ed) Heavy metal stress in plants: from biomolecules to ecosystems, 2nd edn. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 146–181
Pham TPT, Cho C-W, Yun Y-S (2009) Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: a review. Water Res (in press)
Prasad MNV, Malec P, Waloszek A, Bojko M, Strzaka K (2001) Physiological responses of Lemna trisulca L. (duckweed) to cadmium and copper bioaccumulation. Plant Sci 161:881–889
Prasad MNV, Greger M, Aravind P (2006) Biogeochemical cycling of trace elements by aquatic and wetland plants: relevance to phytoremediation. In: Prasad MNV, Sajwan KS, Naidu R (eds) Trace elements in the environment: biogeochemistry, biotechnology and bioremediation. CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, Florida, pp 451–482
Rai UN, Gupta M, Tripathi RD, Chandra P (1998) Cadmium regulated nitrate reductase activity in Hydrilla verticillata. Water Air Soil Pollut 106:171–177
Rauser WE (1999) Structure and function of metal chelators produced by plants: the case for organic acids, amino acids, phytin, and metallothioneins. Cell Biochem Biophys 31:19–48
Ross SM (ed) (1994) Toxic metals in soil plant systems. Wiley, Chichester, p 469
Sanita di Toppi L, Vurro E, Rossi L, Marabottini R, Musetti R, Careri M, Maffini M, Mucchino C, Corradini C, Badiani M (2007) Different compensatory mechanisms in two metal-accumulating aquatic macrophytes exposed to acute cadmium stress in outdoor artificial lakes. Chemosphere 68:769–780
Vecchia FD, Rocca NL, Moro I, Faveri SD, Andreoli C, Rascio N (2005) Morphogenetic, ultrastructural and physiological damages suffered by submerged leaves of Elodea canadensis exposed to cadmium. Plant Sci 168:329–333
Wang W (1990) Literature review on duckweed toxicity testing. Environ Res 52:7–22
Zhang Y, Shen G, Yu Y, Zhu H (2009) The hormetic effect of cadmium on the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 157:3064–3068
Acknowledgments
KS and MNVP gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Department of Science and Technology (DST), the Government of India, New Delhi, and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (MNISW), Warsaw, Poland, within the framework of the Indo-Polish Programme of Cooperation in Science and Technology ref DST/INT/P-15/05 dt 7-11-2006. Cooperation with BIONAN net is thankfully acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malec, P., Maleva, M.G., Prasad, M.N.V. et al. Responses of Lemna trisulca L. (Duckweed) exposed to low doses of cadmium: thiols, metal binding complexes, and photosynthetic pigments as sensitive biomarkers of ecotoxicity. Protoplasma 240, 69–74 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-009-0091-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-009-0091-2