Summary.
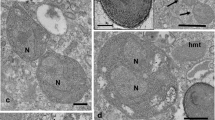
Among ciliate genera, only Paramecium and Euplotes species have been studied extensively as host organisms of bacterial endocytobionts. In this article, we show that members of the genus Spirostomum may also serve as a suitable system for endocytobiosis research. Two strains of Spirostomum minus (Heterotrichea, Ciliophora) collected in Germany and Italy, respectively, were found to harbor different types of bacterial infections. Bacteria of various sizes and shapes were observed in the cytoplasm or in the nuclei of the ciliates. The bacteria in the cytoplasm were either surrounded by a peribacterial membrane or lay naked. One of the bacterial species was found in the vicinity of the contractile fibrillar system (myonemes) of the ciliates. In rare cases, another type of bacteria was observed associated with mitochondria. The macronuclei of both the Italian and the German strains were crowded with endocytobionts. The endonuclear bacteria in the two S. minus strains differed with respect to their cytoplasmic structures but they were of similar size and both were rod shaped. According to the results of in situ hybridization, the endonuclear bacteria of the Italian strain belong to the subgroup of alphaproteobacteria, whereas the bacteria associated with the fibrillar system appeared to be gram-positive bacteria with high G+C content. While both the German and the Italian strains were found to permanently maintain their endocytobionts, they were at least partly colonized by different bacteria. This is taken as an indication that geographically separated populations of ciliates may be stably infected by different endocytobionts, possibly due to different ecological conditions. For S. minus and S. ambiguum a total of 7 different bacterial endocytobionts have now been recorded. We recommend the members of the genus Spirostomum as a suitable system for endocytobiosis research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Correspondence and reprints (present address): Laboratorio di Protistologia, Dipartimento di Etologia, Ecologia ed Evoluzione, Università di Pisa, Via A. Volta 4, 56126 Pisa, Italy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fokin, S., Schweikert, M., Brümmer, F. et al. Spirostomum spp. (Ciliophora, Protista), a suitable system for endocytobiosis research. Protoplasma 225, 93–102 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-004-0078-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-004-0078-y