Abstract
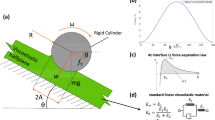
Nowadays, the dynamic behavior of rolling stocks is an essential problem. In dynamic simulation, the correct wheel-rail contact modeling is an important task. In this paper, the stiffness of the wheel-rail contact zone is found by a new, direct, and simplified formulation. This subject is developed by applying more details, such as surface roughness based on the surface topography and hardening effects of a real contact problem. These characteristics have not been considered altogether in other similar works. In this work, the contact stiffness and frequency results are obtained for different material properties and verified with analytical and experimental research. It is shown that the presented new direct method with an acceptable accuracy is easier to use than the complicated existing methods. This paper discusses the effects of contact parameter variations on contact stiffness and frequency. For example, it is shown that the contact stiffness decreases by increasing the surface roughness and increases by increasing the strain-hardening factor.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hertz, H.: On the contact of elastic solids. J. Reine Angew. Math. 92, 156–171 (1992)
Nayak, P.R.: Contact vibrations. J. Sound Vibrat. 22(3), 297–322 (1972)
Nayak, P.R.: Some aspects of surface roughness measurement. Wear 26, 165–174 (1973)
Greenwood, J.A., Williamson, J.B.P.: Contact of nominally flat surfaces. Proc. R. Soc. A (1966). https://doi.org/10.1098/1966.0242
Chang, W.R., Etsion, I., Bogy, D.B.: An elastic-plastic model for the contact of rough surfaces. J. Tribol. (1987). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3261348
Kogut, L., Etsion, I.: A finite element-based elastic-plastic model for the contact of rough surfaces. Model. Simul. Eng. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/561828
Abdo, J., Farhang, K.: Elastic-Plastic contact model for rough surfaces based on plastic asperity concept. Int. J. Near Mech. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2004.08.003
Zhao, Y., Maietta, D.M., Chang, L.: An asperity microcontact model incorporating the transition from elastic deformation to fully plastic flow. J. Tribol. (2000). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.555332
Brake, M.R.: An analytical elastic-perfectly plastic contact model. Int. J. Solids Struct. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2012.06.013
Ghaednia, H., Wang, X., Saha, S., Xu, Y., Sharma, A., Jackson, R.L.: A review of elastic-plastic contact mechanics. Appl. Mech. Rev. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4041537
Gao, Z., Fu, W., Wang, W., Kang, W.: The study of anisotropic rough surfaces contact considering lateral contact and interaction between asperities. Tribol. Int. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.01.056
Li, C., Wang, G.: A modified Greenwood-Williamson contact model with asperity interactions. J. Acta Mech. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-023-03538-x
Xiao, H., Sun, Y.: On the normal contact stiffness and contact resonance frequency of rough surface contact based on asperity micro-contact statistical models. Eur. J. Mech./A Solids (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2019.03.004
Xiao, H., Shao, Y., Brennan, M.J.: On the contact stiffness and nonlinear vibration of an elastic body with a rough surface in contact with a rigid flat surface. Eur. J. Mech./A Solids (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2014.08.005
Li, C., Ding, Y., Liang, X., Wang, G.: An improved elastic-plastic contact model with asperity interactions based on Greenwood-Williamson theory. J. Acta Mech. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-023-03662-8
Gao, Z., Fu, W., Wang, W.: Normal contact damping model of mechanical interface considering asperity shoulder to shoulder contact and interaction. J. Acta Mech. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-019-02392-0
Wei, C., Zhu, H., Lang, S.: A Modified complete normal contact stiffness model of a fractal surface considering contact friction. Int. J. App. Mech. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X20500814
Sun, J., Ji, Z., Zhang, Y., Yu, Q., Ma, C.: A contact mechanics model for rough surfaces based on a new fractal characterization method. Int. J. App. Mech. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1758825118500692
Pohrt, R., Popov, V.L.: Normal contact stiffness of elastic solids with fractal rough surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.104301
Pohrt, R., Popov, V.L., Filippov, A.E.: Normal contact stiffness of elastic solids with fractal rough surfaces for one-and three-dimensional systems. Phys. Rev. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.86.026710
Akarapu, S., Sharp, T., Robbins, M.O.: Stiffness of contacts between rough surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.204301
Campana, C., Muser, M.H.: Practical green’s function approach to the simulation of elastic semi-infinite solids. Phys. Rev. B (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.74.075420
Lorenz, B., Persson, B.N.J.: Interfacial separation between elastic solids with randomly rough surfaces. J. Phys. Condens. Matter (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/21/1/015003
Amini Sarabi, M., Hosseini Tehrani, P.: A new analytical-numerical model for contact problem counting asperities and strain-hardening effects. Proc. Inst. Mech. E Part C (2023). https://doi.org/10.1177/09544062231152710
Brake, M.R.: An analytical elastic-perfectly plastic contact model with strain-hardening and frictional effects for normal and oblique impacts. Int. J. Solids Struct. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2015.02.018
Meyer, E.: Untersuchen über hrteprüfung und hrte brinell methoden (Studies on hardness testing and the Brinell hardness method). Z. Ver. Dtsch. Ing. 52, 645–654 (1908)
Amini Sarabi, M., Hosseini Tehrani, P.: A new combined model for considering the plasticity effects in contacting asperities. Math. Probl. Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4640204
Gonzalez-Valadez, M., Baltazar, A., Dwyer-Joyce, R.S.: Study of the interfacial stiffness ratio of a rough surface in contact using a spring model. Wear (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.08.022
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Amini Sarabia, M., Hossein Tehrani, P. A new direct approach for evaluating the wheel-rail contact stiffness, including surface roughness and hardening effects. Acta Mech (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-024-03904-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-024-03904-3